Scaling the agentic web with NLWeb
Imagine a web ecosystem where not just humans but AI agents communicate with websites, going beyond traditional browsing. Unlike conventional web experiences, where people click, scroll, and search, AI agents can navigate, interpret, and even perform tasks autonomously on your site. This is not a futuristic concept. It is already unfolding. This is the emergence of the agentic web.
Table of contents
Key takeaways
The agentic web enables AI agents to autonomously navigate and interact with websites, shifting user responsibilities from manual navigation to decision-making
Protocols are crucial for communication among AI agents; they must rely on structured, machine-readable data for effective coordination
SEO professionals must adapt to the agentic web by optimizing websites as endpoints for AI queries, ensuring structured data and clarity
NLWeb facilitates interaction between agents and websites by exposing structured data and allowing for natural language queries without traditional interface limitations
Yoast’s collaboration with NLWeb helps WordPress users prepare for the agentic web by organizing content and making it easier to integrate structured data
The big shift: From web for users to a web for users and agents
For years, the web followed a simple pattern. Humans searched, clicked, compared, and completed tasks manually. Even as search engines evolved, the interaction model stayed the same: search and click.
That model is changing.
The agentic web represents a shift from a web designed only for human users to one designed for both people and AI assistants. Instead of manually researching products, comparing services, filling out forms, and completing transactions, users will increasingly delegate those tasks to intelligent assistants that can search, interpret information, and act on their behalf. The user’s role shifts from active navigator to decision-maker.
From searching to delegating.
This is not about smarter chat interfaces. It is about autonomous agents that can interpret the search intent, compare options, and execute actions on behalf of users. Websites are no longer just pages to be visited. They are endpoints to be queried.
For that to work at scale, intelligence cannot reside in a single assistant or on a closed platform. It has to be distributed. Systems must be able to communicate with other systems without friction. That requires a web that is machine-readable, interoperable, and built for agent-to-agent interaction.
The agentic web is not a prediction. It is an architectural shift already underway!
Protocol thinking and the infrastructure of agentic web communication
If the agentic web is about intelligent systems interacting with websites, then the real question becomes simple: how do these systems understand each other?
The answer is not design. It is infrastructure.
The web has always depended on shared communication rules. HTTP allows browsers to request pages. RSS distributes updates. Structured data helps search engines interpret meaning. These are not features. They are protocols. They are agreements that enable large-scale coordination.
Now the same logic applies to AI agents.
In the agentic web, agents will not click buttons or visually scan pages. They will send requests, interpret structured responses, compare options, and complete tasks. For that to work across millions of websites, communication cannot be improvised. It must be standardized.
This is where protocol thinking becomes essential.
Protocol thinking means designing websites so they are predictable for machines. Instead of building custom integrations for every assistant or platform, websites expose a consistent interaction layer. Agents do not need to learn every interface. They rely on shared rules.
As emphasized in discussions of distributed intelligence, the goal is not to let a single chatbot control everything. The intelligence must be distributed. Systems need a simplified way to communicate without having to understand the technical details of every tool they connect to.
That only works when there is common ground.
In practical terms, this means:
Websites must expose structured, machine-readable data
Agents must know what they can ask
Responses must follow predictable formats
Communication must scale beyond one platform
Protocols create that shared language.
What does this mean for SEO professionals?
As the web evolves to support AI agents, SEO professionals are starting to ask a new question: how do you stay visible when answers are generated instead of ranked?
A clear example of this surfaced during Microsoft’s Ignite event. In a Q&A session, a consultant described a client who sells products like mayonnaise and wanted their brand to appear when someone asks an AI assistant about mayonnaise. The question was simple, but it revealed something deeper. If AI systems generate answers instead of listing search results, what does optimization look like?
This is where the shift becomes real.
The agentic web does not replace the open web. It adds another layer on top of it. Search engines still index pages. Rankings still matter. But intelligent systems can now query websites directly, compare information across sources, and generate synthesized responses.
For SEOs, this changes the website’s role.
It is no longer enough to think in terms of pages to be visited. Websites must be treated as endpoints to be queried.
This means structured data, clean information architecture, and machine-readable content are not just enhancements for rich results. They are the foundation that allows AI systems to interpret and select your content in the first place.
Watch the full event here!
Key takeaway for SEOs
The agentic web is an additional layer on the open web, not a replacement for it. To stay visible, SEO professionals must ensure their websites are structured, accessible, and ready to be queried by intelligent systems.
Visibility in this new layer depends on clarity, interoperability, and infrastructure.
Must read: Why does having insights across multiple LLMs matter for brand visibility?
Introducing NLWeb
NLWeb was first introduced by Microsoft in May 2025 as an open project designed to make it simple for websites to offer rich natural language interfaces using their own data and model of choice. Later, in November at Microsoft Ignite, Microsoft presented NLWeb again alongside its first enterprise offering through Microsoft Foundry.
At its core, NLWeb aims to make it easy for a website to function like an AI app. Instead of navigating pages manually, users and agents can query a site’s content directly using natural language.
But NLWeb is more than just a conversational layer.
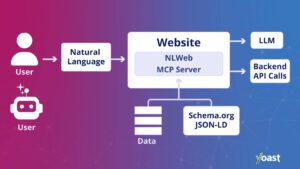
Every NLWeb instance is also a Model Context Protocol, or MCP, server. This means that when a website enables NLWeb, it becomes inherently discoverable and accessible to agents operating within the MCP ecosystem. In simple terms, agents do not need custom integrations for every site. If a website supports NLWeb, agents can recognize it and interact with it in a standardized way.
NLWeb is a conversational layer that interacts with a website and retrieves information
NLWeb builds on formats that websites already use, such as Schema.org and RSS. It combines that structured data with large language models to generate natural language responses. This allows websites to expose their content in a way that both humans and AI agents can understand.
Importantly, NLWeb is technology agnostic. Site owners can choose their preferred infrastructure, models, and databases. The goal is interoperability, not platform lock-in.
In many ways, NLWeb is positioned to play a role in the agentic web similar to what HTML did for the early web. It provides a shared communication layer that allows agents to query websites directly, without relying only on traditional crawling or visual interfaces.
How is NLWeb different from standard LLM citations?
With standard LLM citations, the model generates an answer first, then adds sources. The response is still probabilistic, which can introduce inaccuracies or hallucinations.
NLWeb works differently.
It treats the language model as a smart retrieval layer. Instead of inventing answers, it pulls verified objects directly from the website’s structured data and presents them in natural language.
That distinction matters. It means responses are grounded in the publisher’s own data from the start, reducing the risk of hallucination and giving site owners greater control over how their content is represented.
What NLWeb means for the agentic web
The agentic web depends on systems being able to communicate at scale. Agents cannot manually interpret every interface or navigate every page visually. They need structured, machine-readable access.
NLWeb helps enable that.
Instead of requiring custom integrations for every assistant or platform, a website can expose an NLWeb-enabled endpoint. Agents only need to know that a site supports NLWeb. The protocol handles how requests are made and how responses are structured.
This supports a more distributed ecosystem. The goal is not to let one chatbot control everything. Intelligence must be distributed across the web.
Generative interfaces do not replace content. They depend on well-structured, accessible content. When an AI system summarizes results or compares options, it is still drawing from the information that websites provide. NLWeb simply creates a clearer path for that interaction.
Yoast’s collaboration with NLweb and what it means for WordPress users
As part of the NLWeb announcement, Microsoft highlighted Yoast as a partner helping bring agentic search capabilities to WordPress. You can read more about this collaboration in our official press announcement on Yoast and Microsoft’s NLWeb integration.
For many WordPress site owners, concepts like infrastructure, endpoints, and protocols can feel abstract. That is exactly where preparation matters.
While Yoast does not automatically deploy NLWeb for users, the schema aggregation feature in Yoast SEO, Yoast SEO Premium, Yoast WooCommerce SEO, and Yoast SEO AI+ organizes and structures content, making it significantly easier to build NLWeb. When site owners enable the relevant Yoast feature, nothing changes visually on the front end. What changes is the underlying structure.
In short, we map and organize structured data to reduce the technical effort required to build NLWeb on top of it. In other words, we help publishers complete much of the groundwork.
The agentic web is not about chasing a trend. It is about ensuring your content remains discoverable, understandable, and usable in a world where intelligent systems increasingly act on behalf of users.
Ahad Qureshi
I’m a Computer Science grad who accidentally stumbled into writing—and stayed because I fell in love with it. Over the past six years, I’ve been deep in the world of SEO and tech content, turning jargon into stories that actually make sense. When I’m not writing, you’ll probably find me lifting weights to balance my love for food (because yes, gym and biryani can coexist) or catching up with friends over a good cup of chai.