Ask An SEO: How Do We Shift Google From Our Old Brand Name to Our New One? via @sejournal, @MordyOberstein
The question for this edition of Ask An SEO comes from a reader who’s trying to make their rebrand stick in search:
“Our company recently went through a rebrand with a new name. We’re seeing our old brand name still dominating search results, while our new brand barely registers.
What’s the best approach to transition brand equity in search from our old name to our new one?”
Having your old brand name appear on Google can be extremely frustrating. You just launched a new brand name, spent a lot of time working on it, and here you are stuck on the search engine results page with the old name.
It’s genuinely frustrating.
There are essentially three steps here:
- Handle your own ecosystem.
- Request changes to third-party sites.
- Build up your new brand name so you don’t have to rely on No. 2 happening.
Aligning The Assets You Control
The first, and obvious thing to do, is ensure your new brand name appears consistently across all the assets you own.
Some of these places are entirely obvious, like your homepage. Obviously, you’re going to change how you refer to yourself on your homepage.
However, there can be a lot of nooks and crannies across your ecosystem that may still mention your brand’s former name.
This can include:
- Title tags and meta descriptions.
- Alt text.
- Knowledge Base pages.
- Structured data markup.
- Unused social media accounts.
- Employee bios (both on and off your site).
It’s a matter of crossing your i’s and dotting your t’s. If you’re a big brand with a broad ecosystem, this can be more complicated than it might seem.
Let’s imagine for a moment that what changed is not the main brand name but a product name or the name of a sub-brand.
There could be thousands of pages that you would never even think of that might reference the old naming.
In such a case, you should conduct an extensive audit. I recommend this in general, even if you are not a huge website – it’s so easy to forget a page that references your naming and that such a page even existed.
This should help ensure your own brand SERP is aligned with the new naming as much as possible.
However, there are still elements even on these SERPs that will need some help, such as your Knowledge Panel. For this, we need to think beyond your owned assets.
Align Third-Party Assets
Getting others to recognize your new brand name is a little tougher than just combing through your assets to ensure alignment (which, as I said earlier, might not be as straightforward as it may seem).
Getting third parties to pick up on your branding change is incredibly important.
The underlying goal or concept is: We want people to talk about you and to mention your new brand name when they do.
Within this task, there are things that are easier to accomplish and things that are much harder.
Start with the easier things. Getting these done will help you push areas that you have less influence over.
One easy place is author bios. If you, or anyone in your company, has contributed content to a third-party site (whether it be an article, webinar, podcast, etc.), there is often a bio that will mention, if not link to, your company.
Make sure these bios are up to date and reflect the current and only the current company name.
By the way, sometimes these bios have multiple places where the brand is mentioned; make sure all instances are up to date.
For example, in my Search Engine Journal bio, my company is mentioned twice:
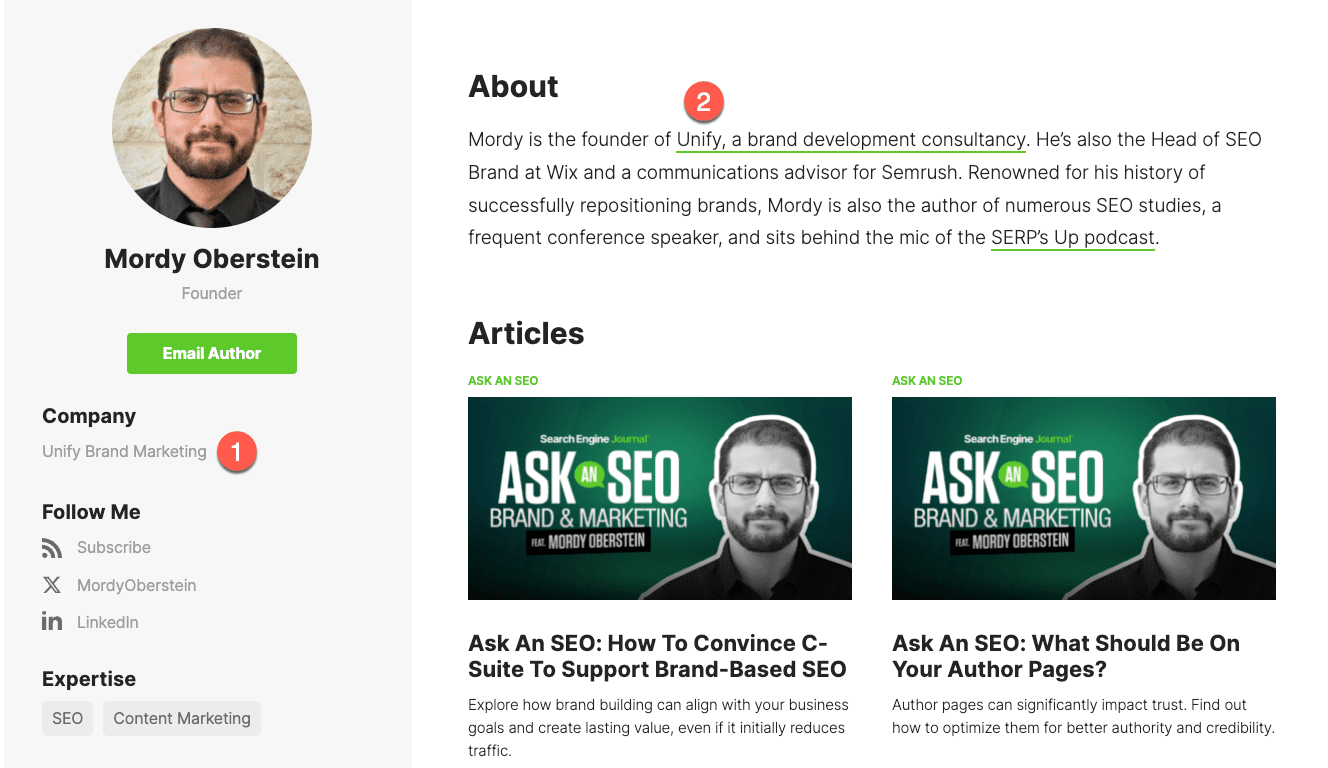 Screenshot from Search Engine Journal, May 2025
Screenshot from Search Engine Journal, May 2025Getting these updated should not be hard at all.
It’s easy to miss a few wins here.
But getting these citations right can help with the Google results.
When I went around and had my current company added to all of my bios across the internet, Google’s Knowledge Panel took notice.
While my old Wix bio still often appears as the main URL in the Knowledge Panel and as a top organic result, Google started to pull in the images from my site as well:
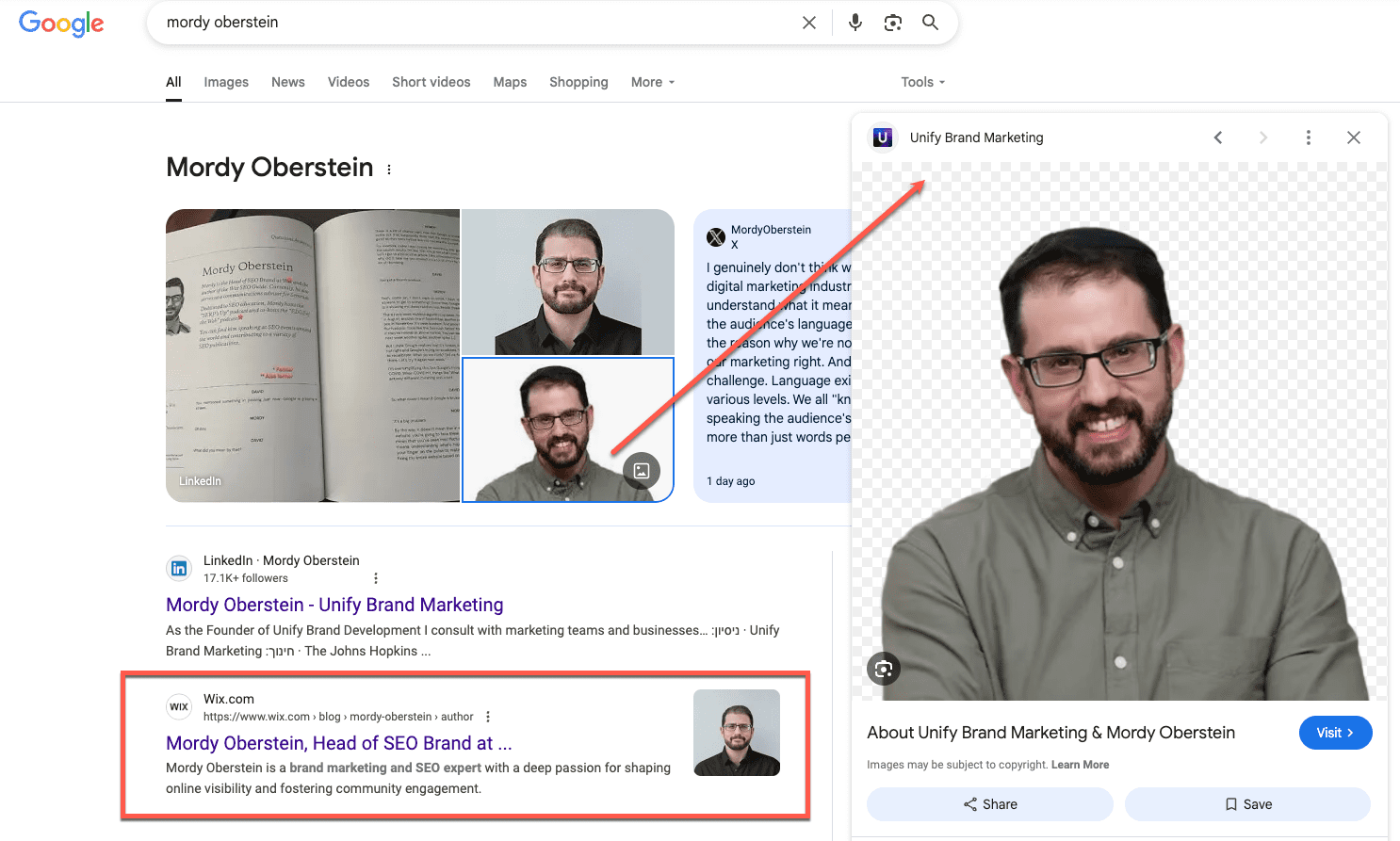


Notice, by the way, that because I took care of my social media. My current brand shows up as part of my LinkedIn profile, which is confusing considering what the Wix result says below it (i.e., that I work at Wix).
That’s exactly what I want. I want the person to ask, “Does he still really work at Wix?”
When Third-Parties Won’t Align
What happens when your brand is listed under its previous name on some random listicle that won’t respond to any of your requests to change the brand name?
What happens if on some forum (say Reddit), there are endless references to your previous brand name that you can’t remove?
For starters, it does show the logic behind running a campaign to announce your new branding.
Often, companies will run a campaign announcing the new branding to generate buzz and interest or even to gain more conversions.
Nothing wrong with that, at all. However, even if none of that happens, it still makes sense to run a campaign when you change the name of your brand.
If only to signal that the brand name that once was, is no longer. This way, the next time someone talks about your brand on Reddit, they may stop themselves and use the new name.
If you’re lucky, when someone posts using your previous name, another user will comment that the brand name has actually been changed.
This is one less place to figure out how to go about changing how your brand is referenced and one less person who will continue to go around spreading the wrong name across the internet. That’s one less Reddit thread ranking on Google that mentions your old brand naming.
Now, let’s go back to that listicle. Your company is listed as a top 10 best whatever, and when you contact the website to update the name, they ghost you. What do you do?
Nothing.
You keep moving on. You keep doing more public appearances, writing more content, meeting more people, and generally building up your presence across the planet and the internet to the point where your new brand name is the default.
Until the point where Google’s Knowledge Graph is overwhelmed with Mordy Oberstein, founder of Unify Brand Marketing, and not Mordy Oberstein, head of SEO Brand at Wix.
Because then, that one website that hasn’t updated its content with your new naming is the one going against the grain. Now the pressure is on them to show they aren’t stale and out of date.
Set Expectations
I don’t expect this process to happen in a day nor should you. It takes time. Think of it more as a process.
Are more and more places across the digital landscape referencing your new brand name? If yes, you’re doing great. Are more people asking if you changed your name? Also, a good sign.
As you continue to spread your new brand name across the web, Google’s own Knowledge Graph will have more signals that the name that once was has been replaced.
Once your new brand name starts taking hold, anyone who cares about the accuracy of their content will start to either make the edit or reach out to you to make the edit.
Anyone else, at this point, is just running poor content that shouldn’t be there anyway (all things being equal).
More Resources:
Featured Image: PauloBobita/Search Engine Journal