America was winning the race to find Martian life. Then China jumped in.
To most people, rocks are just rocks. To geologists, they are much, much more: crystal-filled time capsules with the power to reveal the state of the planet at the very moment they were forged.
For decades, NASA had been on a time capsule hunt like none other—one across Mars.
Its rovers have journeyed around a nightmarish ocher desert that, billions of years ago, was home to rivers, lakes, perhaps even seas and oceans. They’ve been seeking to answer a momentous question: Once upon a time, did microbial life wriggle across its surface?
Then, in July 2024, after more than three years on the planet, the Perseverance rover came across a peculiar rocky outcrop. Instead of the usual crystals or layers of sediment, this one had spots. Two kinds, in fact: one that looked like poppy seeds, and another that resembled those on a leopard. It’s possible that run-of-the-mill chemical reactions could have cooked up these odd features. But on Earth, these marks are almost always produced by microbial life.
To put it plainly: Holy crap.
Sure, those specks are not definitive proof of alien life. But they are the best hint yet that life may not be a one-off event in the cosmos. And they meant the most existential question of all—Are we alone?—might soon be addressed. “If you do it, then human history is never the same,” says Casey Dreier, chief of space policy at the Planetary Society, a nonprofit that promotes planetary exploration and defense and the search for extraterrestrial life.
But the only way to confirm whether these seeds and spots are the fossilized imprint of alien biology is to bring a sample of that rock home to study.
Perseverance was the first stage of an ambitious scheme to do just that—in effect, to pull off a space heist. The mission—called Mars Sample Return and planned by the US, along with its European partners—would send a Rube Goldberg–like series of robotic missions to the planet to capture pristine rocks. The rover’s job was to find the most promising stones and extract samples; then it would pass them to another robot—the getaway driver—to take them off Mars and deliver them to Earth.
But now, just over a year and a half later, the project is on life support, with zero funding flowing in 2026 and little backing left in Congress. As a result, those oh-so-promising rocks may be stuck out there forever.
“We’ve spent 50 years preparing to get these samples back. We’re ready to do that,” says Philip Christensen, a planetary scientist at Arizona State University who works closely with NASA. “Now we’re two feet from the finish line—Oh, sorry, we’re not going to complete the job.”
This also means that, in the race to find evidence of alien life, America has effectively ceded its pole position to its greatest geopolitical rival: China. The superpower is moving full steam ahead with its own version of MSR. It’s leaner than America and Europe’s mission, and the rock samples it will snatch from Mars will likely not be as high quality. But that won’t be the headline people remember—the one in the scientific journals and the history books. “At the rate we’re going, there’s a very good chance they’ll do it before we do,” laments Christensen. “Being there first is what matters.”
Of course, any finding of extraterrestrial life advances human knowledge writ large, no matter the identity of the discoverers. But there is the not-so-small issue of pride in an already heated nationalistic competition, not to mention the fact that many scientists in America (to say nothing of US lawmakers) don’t necessarily want their future research and scientific progress subject to a foreign gatekeeper. And even for those not especially concerned about potentially unearthing alien microbes, MSR and the comparable Chinese mission are technological stepping stones toward a long-held dream shared by many beyond Elon Musk: getting astronauts onto the Red Planet and, eventually, setting up long-term bases for astronauts there. It’d be a huge blow to show up only after a competitor had already set up shop … or not to get there at all.
“If we can’t do this, how do we think we’re gonna send humans there and get back safely?” says Victoria Hamilton, a planetary geologist at the Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado, who is also the chair of the NASA-affiliated Mars Exploration Program Analysis Group.
Or as Paul Byrne, a planetary scientist from the Washington University in St. Louis, puts it: “If you’re going to bring humans back from Mars, you sure as shit have to figure out how to bring the samples back first.”
Nearly a dozen project insiders and scientists in both the US and China shared with me the story of how America blew its lead in the new space race. It’s full of wild dreams and promising discoveries—as well as mismanagement, eye-watering costs, and, ultimately, anger and disappointment.
“I spent most of my career studying Mars,” says Christensen. There are countless things about it that bewitch him. But by examining it, he suspects, we’ll get further than ever in the Homeric investigation of how life began.
Sure, the Mars of today is a postapocalyptic wasteland, an arid and cold desert bathed in lethal radiation. But billions of years ago, water lapped up against the slopes of fiery volcanoes that erupted under a clement sky. Then its geologic interior cooled down so quickly, changing everything. Its global magnetic field collapsed like a deflating balloon, and its protective atmosphere was stripped away by the sun.
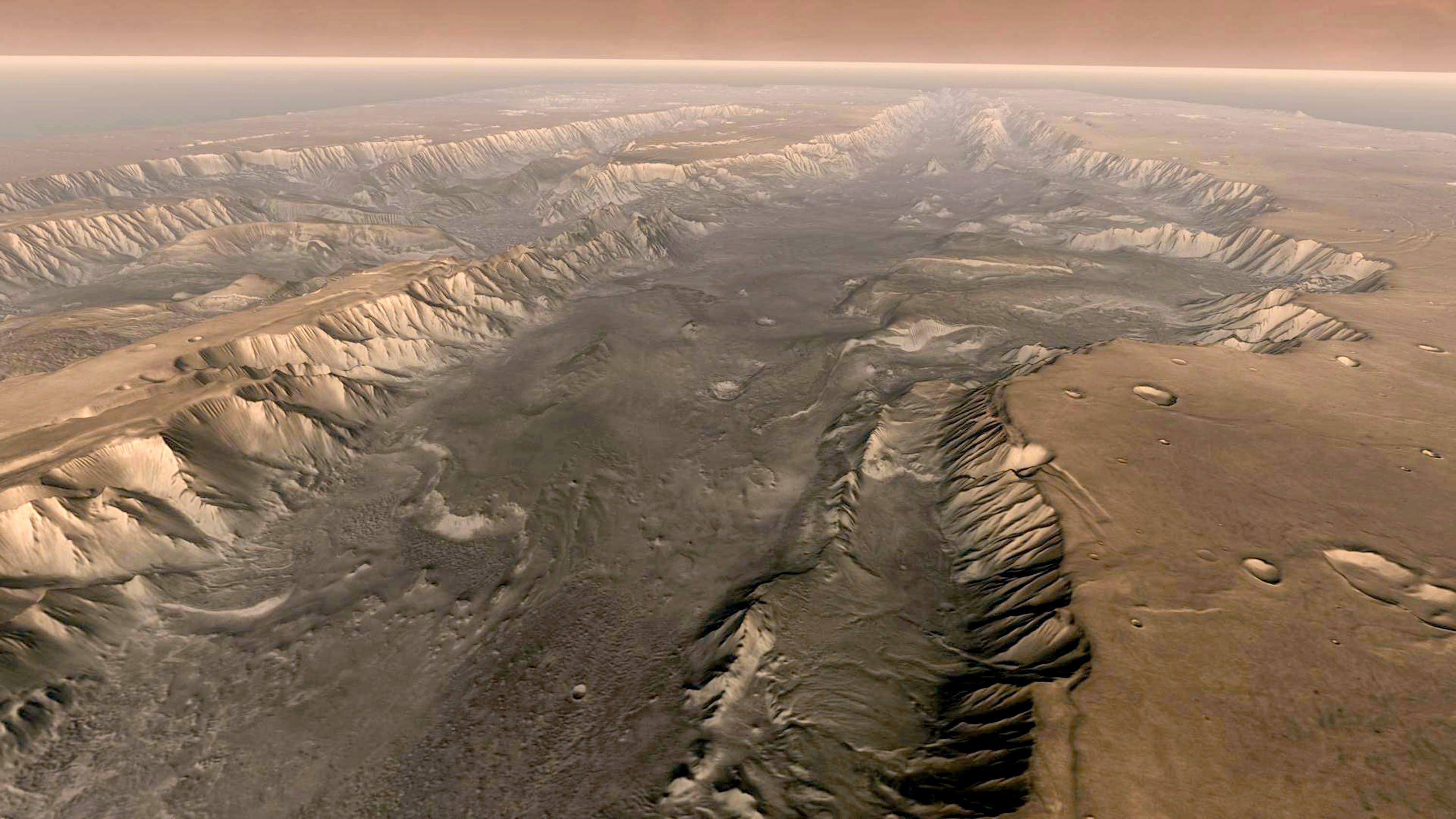

Its surface is now remarkably hostile to life as we know it. But deep below ground, where it’s shielded from space, and where it’s warmer and wetter, there could maybe be microbes inching about.
Scientists have long possessed several Martian meteorites that have been flung our way, but none of them are pristine; they were all damaged by cosmic radiation midflight, before getting scorched in Earth’s atmosphere. Plus, there’s another problem: “We currently have no rocks from Mars that are sedimentary, the rock type likely to contain fossils,” says Sara Russell, a planetary scientist at London’s Natural History Museum.
For those, humans (or robots) would need to get on the ground.
NASA first made the stuff of sci-fi films a reality 50 years ago, when two Viking landers touched down on the planet in 1976. One of their experiments dropped some radioactively tagged nutrients into soil samples, the idea being that if any microbes were present, they’d gobble up the nutrients and burp out some radioactive waste gas that the landers could detect. Tantalizingly, this experiment hinted that something microbe-like was interacting with those nutrients—but the result was inconclusive (and today most scientists don’t suspect biology was responsible).
Still, it was enough to elevate scientists’ curiosity about the genuine possibility of Martian life. Over the coming decades, America sent an ever-expanding fleet of robots to Mars—orbiting spacecraft, landers, and wheeled rovers. But no matter how hard they studied their adoptive planet’s rocks, they weren’t designed to definitively detect signs of life. For that, promising-looking rocks would need to be captured and, somehow, shuttled back to labs on Earth in carefully sealed containers.
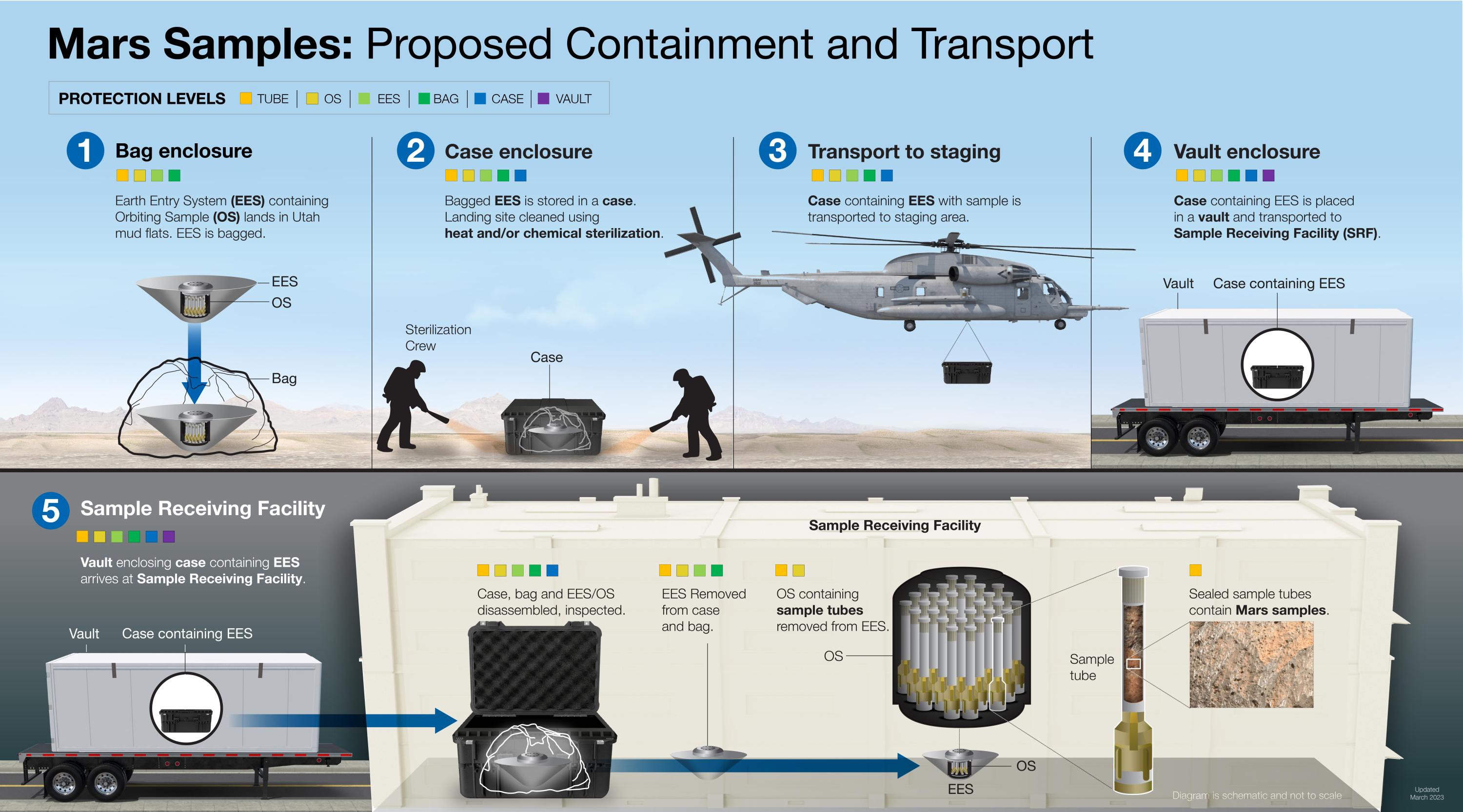


This became a top priority for the US planetary science community in 2003, following the publication of the first Planetary Decadal Survey, a census conducted at NASA’s request. The scientific case for the mission was clear—even to the people who didn’t think they’d find signs of life. “I bet there isn’t life on Mars. But if there is, or was, that would be an incredibly important discovery,” says Christensen. And if not, “Why not?”
He adds: “We may understand more about why life started on Earth by understanding why it may not have started on Mars. What was that key difference between those two planets?”
And so, MSR was born. America went all in, and the European Space Agency joined the team. Over the next decade or so, a complex plan was drawn up.
First, a NASA rover would land on Mars in a spot that once was potentially habitable—later determined to be Jezero Crater. It would zip about, look for layered rocks of the sort that you’d find in lakes and riverbeds, extract cores of them, and cache them in sealed containers. Then a second NASA spacecraft would land on Mars, receive the rover’s sample tubes (in one of several different ways), and transfer the samples to a rocket that would launch them into Martian orbit. A European-provided orbiter would catch that rocket like a baseball glove before returning home and dropping the rocks into Earth’s atmosphere, where they would be guided, via parachute, to eagerly awaiting scientists no later than the mid-2030s.
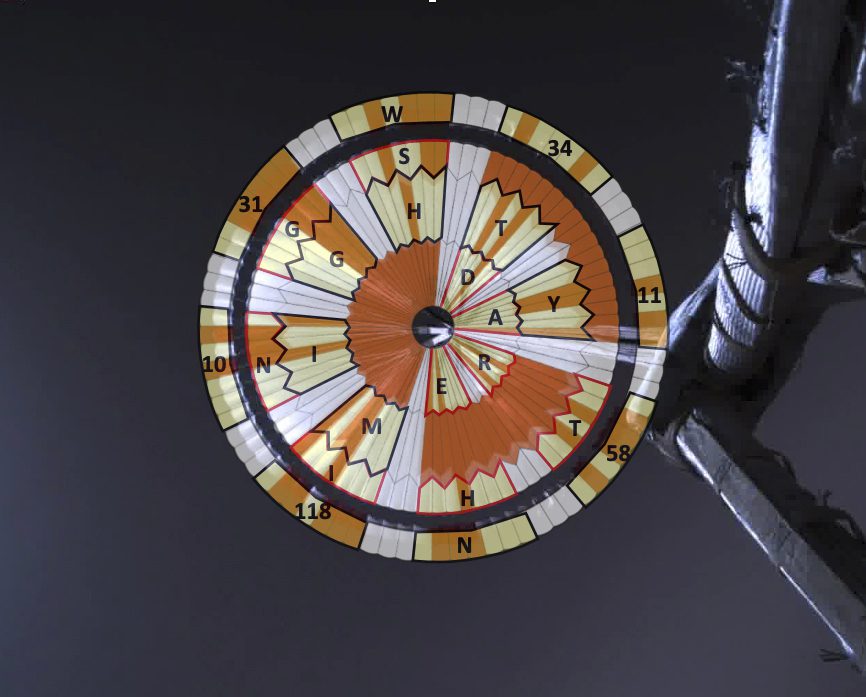



“Put simply, this is the most scientifically careful sample collection mission possible, conducted in one of the most promising places on Mars to look for signs of past life,” says Jonathan Lunine, the chief scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. “And, of course, should evidence of life be found in the sediments, that would be an historic discovery.”
It got off to an auspicious start. On July 30, 2020, in the throes of the covid-19 pandemic, NASA’s Perseverance rover launched atop a rocket from Florida’s Cape Canaveral. The NASA administrator at the time, Jim Bridenstine, didn’t mince words: “We are in extraordinary times right now,” he told reporters, “yet we have in fact persevered, and we have protected this mission because it is so important.”
But just earlier that same month, the mission to Mars had turned into a race. China was now prepping its own sample return spacecraft.
And that’s when things for MSR started to unravel.



China was comparatively late to develop a competitive space program, but once it began doing so, it wasted no time. In 2003, it first sent one of its astronauts into space, via its own bespoke rocket; in the two decades since, it has launched its own space station and sent multiple uncrewed spacecraft to the moon—first orbiters, then landers—as part of its Chang’e Project, named after a lunar goddess.
But a real turning point for China’s interplanetary ambitions came in 2020, the same year as Perseverance’s launch to Mars.
That December, Chang’e-5 touched down in the moon’s Ocean of Storms, a realm of frozen lava 1,600 miles long. It grabbed some 2-billion-year-old rocks, put them in a rocket, and blasted them into the firmament. The samples were captured by a small orbiting spacecraft; crucially, the idea was not all that dissimilar from how MSR imagined catching its own samples, baseball-glove style. China’s lunar haul was then dropped off back on Earth just before Christmas. It marked the first time since 1976 that samples had been returned from the moon, and the mission was seamless.
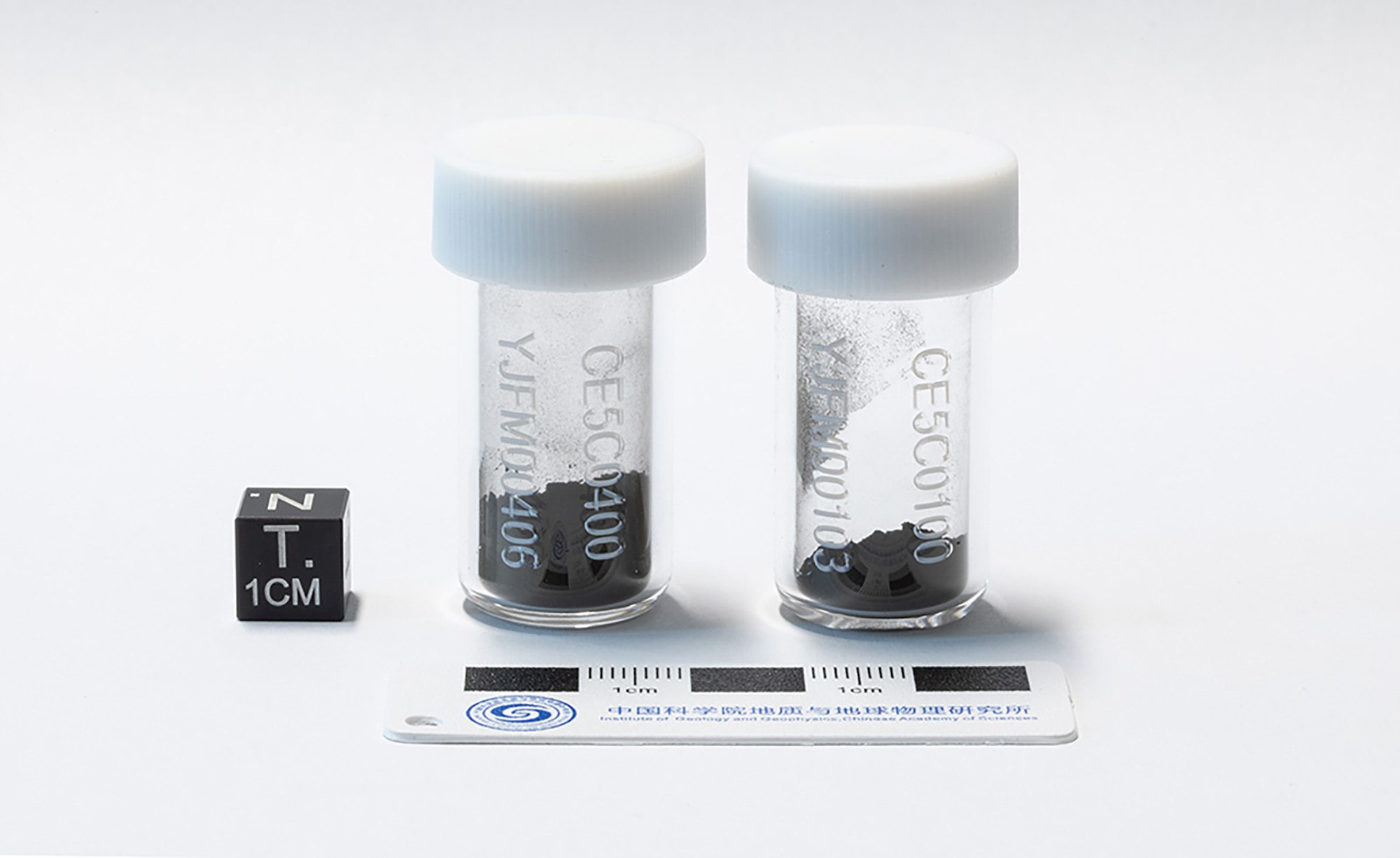


That same year, China made its first foray toward Mars. The project was called Tianwen-1, meaning “Questions to Heaven”—the first in a new series of audacious space missions to the Red Planet and orbiting asteroids. While its success was far from guaranteed, China was willing to kick into high gear immediately, sending both an orbiting spacecraft and a rover to Mars at the same time. No other country had ever managed to perform this act of spaceflight acrobatics on its first try.
Just as China ramped up its space schemes, some people in the scientific community began to wonder if NASA was (inadvertently) promising too much with MSR—and whether the heist would be worth the cost.
In 2020, the price tag for the program had jumped from an already expensive $5.3 billion to an estimated $7 billion. (For context, NASA’s Near-Earth Object Surveyor mission, which is currently being pieced together, has a price tag of around $1.2 billion. This space observatory is designed to find Earthbound asteroids and is tasked with defending all 8 billion of us from a catastrophic impact.)
But Perseverance was already on its way to Mars. It wasn’t as if this expensive train could go back to the station. The project’s advocates just hoped it’d actually make it there in one piece.
While the US had previously entered Martian orbit successfully, several other entry, descent, and landing attempts on the planet had ended in explosive disaster; the primary antagonist is the Martian atmosphere, which can cause spacecraft to tumble wildly out of control or heat up and ignite. Perseverance would be traveling at nearly 12,500 miles per hour as it entered Mars’s airspace, and to land it’d need to decelerate, deploy a parachute, fire several rockets, and pilot itself to the skies above Jezero Crater—before a levitating crane would drop off the actual rover.
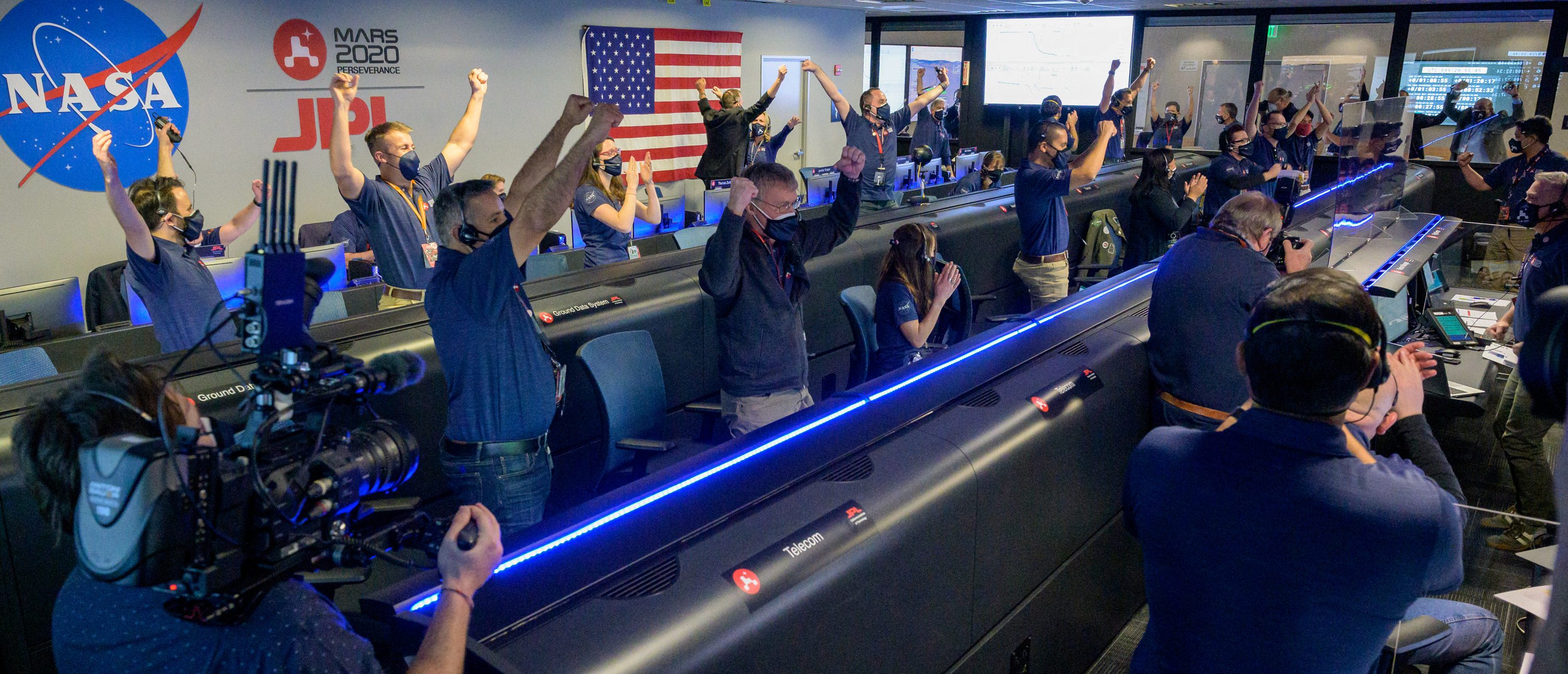
Thankfully, Perseverance’s deployment went off without a hitch. On February 18, 2021, Mars became its new home—and the rover’s makers hugged, high-fived, and whooped for joy in NASA’s flight control room.
As Lori Glaze, then director of NASA’s planetary science division, said at the time, “Now the fun really starts.”



That very same month, China arrived at Mars’s doorstep for the first time.
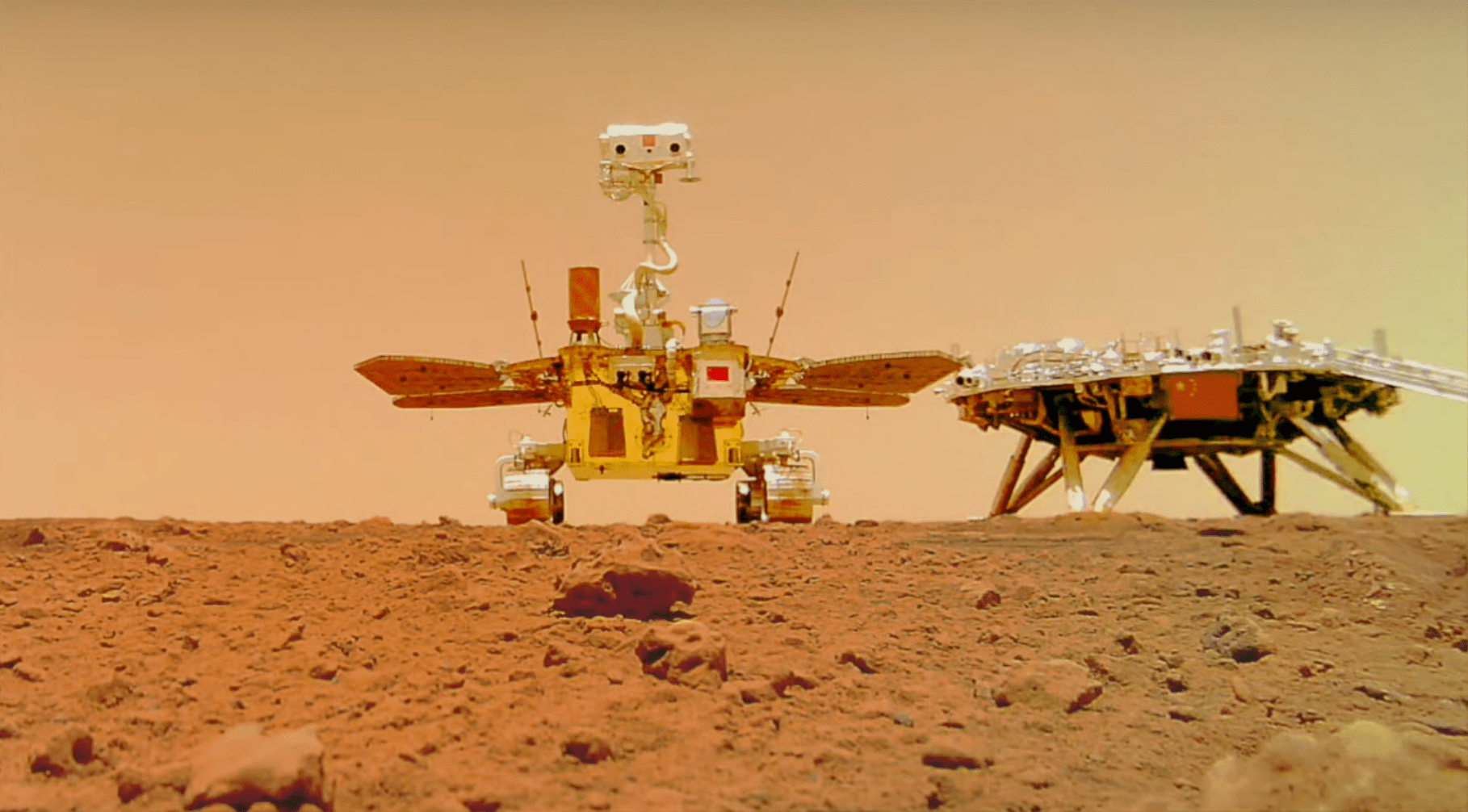
On February 10, 2021, Tianwen-1 began to orbit the planet. Then, on May 14, it slipped a drop shipment through the spacecraft-frying atmosphere to deliver a rover onto an expansive landscape called Utopia Planitia—giving Perseverance a neighbor, albeit one 1,200 miles away.
This explorer was nowhere near as sophisticated as Perseverance, and its assignment was a far cry from a sample return mission. It had some cameras and scientific instruments for studying its environment, making it comparable to one of NASA’s older rovers. It was also supposed to operate for just three months (though it ended up persisting for an entire year before being fatally smothered by pernicious Martian dust).
Nevertheless, Tianwen-1 was a remarkable achievement for China, one that the US couldn’t help but applaud. “This is a really big deal,” said Roger Launius, then NASA’s chief historian.
And even if grabbing pieces of Mars was increasingly likely in China’s future, it was already happening in the present for the US. The race, the Americans thought, was over before it had even begun … right?
Over the next few years, Perseverance went on an extraterrestrial joyride. It meandered through frozen flows of lava and journeyed over fans of sediment once washed about by copious liquid water. It pulled out rocks that preserved salty, muddy layers—exactly the environment that, on Earth, would be teeming with microorganisms and organic matter.
“Jezero Crater clearly meets the astrobiological criterion for a sampling site where life may once have existed,” says Lunine from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab. “Rocks of broadly similar age and setting on Earth contain some of the earliest evidence for life on our own planet.”
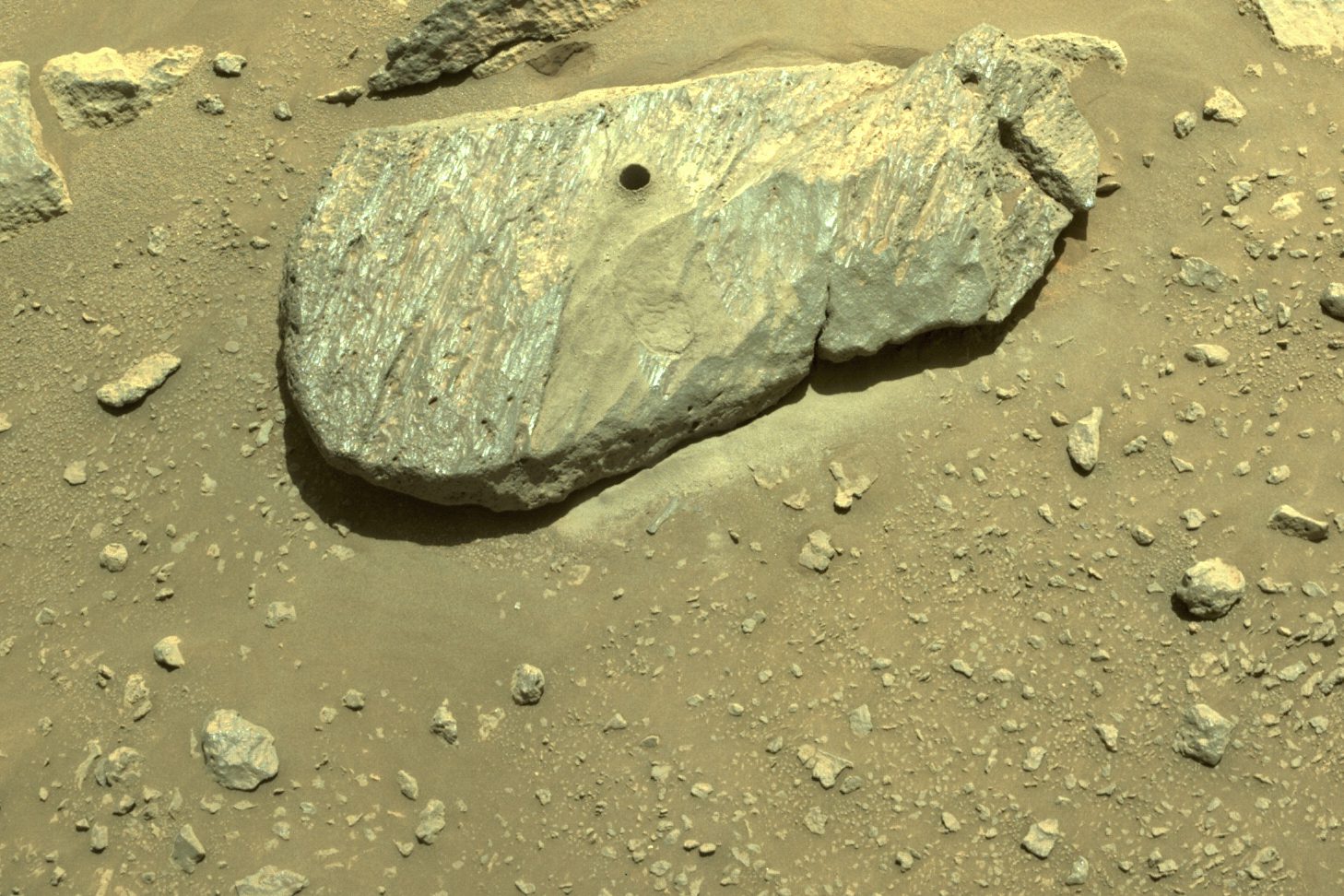



Then, in September 2023, as Perseverance was trundling across the ruins of what may once have been a microbial metropolis, an independent panel of researchers published a report that made it clear, in no uncertain terms, that MSR was the opposite of okay.
They found that the project was too decentralized among the nation’s plethora of NASA centers, leaving confusion as to who was actually in charge. And at its current pace, MSR wouldn’t get its Mars rocks back home until the 2040s at the earliest—as much as a whole decade later than initial estimates. And it would cost as much as $11 billion, more than doubling the initial tab.
“MSR was established with unrealistic budget and schedule expectations from the beginning,” the report reads. “MSR was also organized under an unwieldy structure. As a result, there is currently no credible, congruent technical, nor properly margined schedule, cost, and technical baseline that can be accomplished with the likely available funding.”
Members of Congress started to wonder aloud whether MSR should be canceled outright, and the scientific community that had once so enthusiastically supported the mission faced a moment of reckoning.
Byrne, the planetary scientist from the Washington University in St. Louis, had always been something of a rebel, never really a fan of NASA’s multi-decadal, over-the-top fascination with Mars. The solar system, he argued, is filled with curious worlds to explore—especially Venus, another nearby rocky world that was once rather Earth-like. Couldn’t we spare some of NASA’s budget to make sure we explore Venus, too?
Still, like many other critical colleagues, Byrne did not want to see MSR put down. The report’s findings didn’t change the fact that Perseverance was dutifully working around the clock to accomplish the mission’s opening stages. What would be the point of gathering all those samples if they were going to be left to stay on Mars? The community, Byrne explains, just needed to answer one question: “How do you do this in a way that’s faster and cheaper?”
In April 2024, NASA publicly sought help from its industry partners in the space sector: Could anyone come up with a way to save MSR? Various players with spaceflight experience, like Lockheed Martin, sent in proposals for consideration.
Then, just a few months later in July 2024, Perseverance came in clutch, finding those special leopard-spotted and speckled rocks in an old river valley—a sign of hope that NASA had been desperately seeking. Now the agency’s request for help was all the more urgent—these rocks had to get home. After various panels assessed plans that could effectively save MSR, two potential options for a faster, leaner, less expensive version were previewed at a January 2025 press briefing.
One option brought in tried-and-tested tech: Since Perseverance had been safely deployed onto the surface of Mars using a hovering platform known as a sky crane, it was proposed that the sample-gathering lander for MSR could also be dropped off using a sky crane, which would simplify this step and reduce the overall cost of the program. The other suggestion was that the lander could be delivered to Mars via a spaceship from a commercial spaceflight company. The lander design itself could also be streamlined, and tweaks could be made to the rocket that would launch the samples back into space.
The proposals needed greater study, but everyone’s spirits were lifted by the fact these plans could, at least theoretically, get samples back in the 2030s, not the 2040s. And, crucially, “it was possible to get the cost down,” says Jack Mustard, an Earth and planetary scientist at Brown University and a member of one of the two proposal-reviewing panels. Still, it didn’t save a lot: They could do MSR for $8 billion.
“What we came up with was very reasonable, rational, much simpler,” says Christensen, who was part of the same review panel. “And $8 billion is about the right amount it would take to guarantee that it’s going to work.”


While the US became increasingly consumed with its own interplanetary woes, China was riding high.
In June 2024, the sixth installment in the Chang’e project made history. It was another lunar sample return mission, but this one did something nobody had ever done in the history of spaceflight: It landed on the difficult-to-reach, out-of-view far side of the moon and snagged samples from it.
China made it look effortless when a capsule containing matter from this previously untouched region safely landed in Inner Mongolia. Long Xiao, a planetary geoscientist at the China University of Geosciences, told reporters at the time that the mission’s success was “a cause for celebration for all humanity.”
But it was also effectively a bombshell for NASA. Yes, the moon is much closer to Earth, and it doesn’t have a spaceship-destroying atmosphere like Mars. But China was speedrunning through the race while America was largely looking the other way.
Then, in May 2025, China launched Tianwen-2. Its destination was not Mars but a near-Earth asteroid. The plan is that it will scoop up some of the space rock’s primordial pebbles later this year and deliver them back to Earth in late 2027. In light of China’s past successes, many suspect it’ll nail this project, too.



But perhaps the biggest blow to the US came in June 2025: China revealed its formal designs on returning samples from Mars—and potentially addressing the existence of life elsewhere in the cosmos. Chinese researchers outlined a bold plan for Tianwen-3 in the journal Nature Astronomy. “Searching for signs of life, or astrobiology studies, are the first priority,” says Yuqi Qian, a lunar geologist at the University of Hong Kong. And while many observers had long been cognizant of this ambition, seeing it so clearly spelled out in academic writing made it real.
“The selection of the landing site is still ongoing,” says Li Yiliang, an astrobiologist at the University of Hong Kong, an author of the Tianwen-3 study, and a member of the spacecraft’s landing site selection team. But the paper notes, in no uncertain terms, that the mission will move at a breakneck pace. “The aim of China’s Mars sample return mission, known as Tianwen-3, is to collect at least 500g of samples from Mars and return them to Earth around 2031.”
2031. Even on its original, speedier timeline, America’s MSR plan wouldn’t get samples back by that date. So how is China planning to pull it off?
Qian explains that Tianwen-3 is building on the success of the lunar sample return program. Doing something similar for Mars is a rather giant technological leap (requiring two rockets, not one)—but, he argues, “the technologies here are similar.”
The plan is for a duet of rockets to blast off from Earth in 2028. The first will contain the lander-ascender combination, or LAC. The second is the orbiter-returner combination, or ORC. The LAC will get to Mars and deploy a lander as well as a small helicopter, which will scout promising locations around the landing site while using a claw to bring several small samples back to the lander.


The LAC will then travel to the most promising site. The lander’s drill, which can get down to around seven feet below the surface, is the most important part of the mission. At that depth, there are greater odds of capturing signs of past life. When at least 500 grams of pristine rocks have been loaded aboard the lander, the samples will be launched into space, where the orbiter will be waiting to capture them and send them back home sometime in 2031.
“The returned samples will be quarantined strictly in an under-planning facility near Hefei city,” says Yiliang. And there, in those bio-secure labs, scientists might very well find the first clear signs of alien life, past or present.
The very same month that Chinese researchers published their daring plans for returning Mars samples, the new Trump administration released a draconian NASA budget for Congress to consider—one that sparked panic across the planetary science community.
If enacted, it would have been a historic catastrophe for the venerable space agency, giving NASA its smallest budget since 1961. This would have forced it to let go of a huge number of staffers, slash its science program budget in half, and terminate 19 missions currently in operation. MSR was in the crosshairs, too.
“Grim is the word,” says Dreier of the Planetary Society.
Over the next few months, Congress pushed back on the potential gutting of NASA, but largely to save ongoing solar system exploration missions. MSR was not considered an active effort; Perseverance was effectively a scientific scout acting independently by this point. A counterproposal by the House offered up $300 million for MSR, but no policymaker was cheerleading for it. (The US Office of Management and Budget, the House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology, and the office of Sen. Ted Cruz of Texas, who chairs the Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation did not respond to requests for comment.)
“Mars Sample Return doesn’t seem to have very many advocates right now,” says Byrne. The project “isn’t featuring in anyone’s conversation at the moment, with all of the existential shit that’s happening to NASA.” Everyone working on a NASA mission hoped that they, and their spacecraft, would survive the onslaught. As Byrne adds: “[People are] just trying to keep their heads down.”
Researchers in America suddenly found themselves at an inflection point. “The attack on science, and the attack on NASA science, has been very successful, in that it has completely demoralized the science community,” says Christensen. “Everyone’s in a state of shock.”
When I contacted NASA in July about the state of MSR, which was then in the middle of a months-long limbo, I was told that experts weren’t available to comment. Roxana Bardan, a spokesperson, instead sent a statement: “Under President Trump’s America First agenda, NASA is committed to sustained U.S. space leadership. We will continue to innovate, explore, and excel to ensure American preeminence in space.” (The agency did not respond to a follow-up request for comment.)
That notion stood in direct contrast to what Christensen told me around the same time. “The US … has led the exploration of Mars for 50 years,” he said. “And as we approach one of the key discovery points, we’re about to concede that leadership to someone else.”
From China’s perspective, the fumbling of MSR is more confusing than anything else. “NASA has so well prepared for her MSR mission in both technology and science, and I and my colleagues have learned so much from NASA’s scientific communities,” says Yiliang.
And if China wins the race because America decided to shoot itself in the foot? “This is sad,” he says. “If this comes true, I believe the Chinese will not be that happy to win the race in this way.”
Tianwen-3 will still have to overcome many of the same hurdles as MSR. Nobody, for example, has autonomously launched a rocket of any kind off the surface of Mars. But many believe the Chinese can succeed, even at their program’s superspeed. Christensen, for one, fully expected several of their past robotic missions to the moon and Mars to fail—but “the fact that they pulled it off the first time really says a lot about their engineering capability,” he says.
Mustard agrees: “They know how to land; they know how to leave. I have a lot of confidence that they’ve learned enough from the lunar work that they’ll be able to do it.”
Plus, Tianwen-3’s architecture is simpler than the US-European mission. It has fewer components, and fewer points of potential failure. This also means, though, that the quality of the loot will be somewhat lacking. Tianwen-3 will sample from only one small patch of Mars. Conversely, Perseverance is roving around a vast and geologically diverse landscape, sampling as it goes, which would translate to “literally orders of magnitude more science than what will come from the Chinese samples,” says Christensen.
But China could serendipitously land on a biologically rich patch of the planet. As the Southwest Research Institute’s Hamilton says, the mission could “pick up something entirely unexpected and, you know, miraculous.”
The likeliest outcome is still that neither nation finds fossilized microbes, but that China brings back rocks from Mars first. At the end of the day, that’s what Americans (and Europeans) will hear: “You’re second. You lost,” says Mustard.
Like many of his colleagues, Christensen is irked by the thought of losing the race to Mars, because it would be such an own goal. The US has been sending robots over there for decades and investing billions in forging the technology that would be required to make MSR a success. And suddenly “the Chinese come along and say, Thank you very much, we’ll take all of that information—we’ll build one mission and go and do what you guys did the groundwork for,” Christensen says. “As a taxpayer, I’m like: It just seems foolish to me.”
Even the MSR skeptics concede that this kind of loss would have sweeping ramifications. Byrne worries that if something like MSR can be snuffed out so easily, what’s to say the next big mission—to Jupiter, Saturn, and beyond—won’t suffer the same ignoble fate? In other words, the death of MSR would severely damage “the ability of the planetary community to dream big,” he says. “If we don’t pull this off, what does that mean? Are we not going to do big, expensive, difficult things?”
Another big, expensive, difficult thing? Putting humans on Mars. Both critics and advocates of MSR largely agree it is an invaluable dress rehearsal. Making sure you can safely launch a rocket off Mars is a necessary prerequisite to ensuring that an array of equipment can survive for a long time on the planet’s lethal surface.
China, too, has explicitly acknowledged this. As one of the first lines of the Tianwen-3 study states, “Mars is the most promising planet for humanity’s expansion beyond Earth, with its potential for future habitability and accessible resources.”
Though such expansion is still of course a far-future dream, it’s not hard to see how losing the race here would put the US at a huge disadvantage. Members of America’s planetary science community say that to try to sway politicians in their favor, they have framed MSR as a national security issue. But they haven’t had much luck. “We’ve been in discussions with decision-makers who have never heard that perspective before,” says the Planetary Society’s Dreier.
“It is surprising that doesn’t have more weight,” adds Mustard.
Despite months of purgatory, it still stung when the coup de grâce arrived in January. In the draft for a must-pass spending bill, House and Senate appropriators spared NASA from the harshest proposed cuts, thereby saving dozens of spaceflight missions and preserving much of the agency’s planetary science output. But the bill provided absolutely zero political or financial support for MSR. There it was, in black and white: America’s plans to perform a history-making heist on Mars were dead. The bill became law in January and Perseverance, it seems, is now destined to rove alone on the Red Planet until its nuclear battery burns out.
This austere reality clashes with the soaring aspirations outlined in the first Planetary Decadal Survey, written just over two decades ago. It stated that the US exploration of the solar system “has a proud past, a productive present, and an auspicious future.” It also noted that “answers to profound questions about our origins and our future may be within our grasp.”
Now the answers have all but slipped away. Even though Perseverance continues to roam, it’s increasingly likely we’ll never see those promising bespeckled rocks with human eyes, let alone any other rocks the rover finds intriguing. It is far easier to imagine that in the near future, perhaps in the early 2030s, Perseverance will point its camera up at the night sky above Jezero Crater. It will catch a small glimmer: Tianwen-3’s orbiter, preparing to send ancient rocks back to Earth. Meanwhile, Perseverance’s own sample tubes—perhaps some containing signs of life—will be trapped on the Martian surface, gathering dust.


It is a sobering thought for Christensen. “We’ll wake up one day and go: What the hell?” he says. “How did we let this happen?”
Robin George Andrews is an award-winning science journalist and doctor of volcanoes based in London. He regularly writes about the Earth, space, and planetary sciences, and is the author of two critically acclaimed books: Super Volcanoes (2021) and How to Kill An Asteroid (2024).