Stratospheric internet could finally start taking off this year
Today, an estimated 2.2 billion people still have either limited or no access to the internet, largely because they live in remote places. But that number could drop this year, thanks to tests of stratospheric airships, uncrewed aircraft, and other high-altitude platforms for internet delivery.
Even with nearly 10,000 active Starlink satellites in orbit and the OneWeb constellation of 650 satellites, solid internet coverage is not a given across vast swathes of the planet.
One of the most prominent efforts to plug the connectivity gap was Google X’s Loon project. Launched in 2011, it aimed to deliver access using high-altitude balloons stationed above predetermined spots on Earth. But the project faced literal headwinds—the Loons kept drifting away and new ones had to be released constantly, making the venture economically unfeasible.
Although Google shuttered the high-profile Loon in 2021, work on other kinds of high-altitude platform stations (HAPS) has continued behind the scenes. Now, several companies claim they have solved Loon’s problems with different designs—in particular, steerable airships and fixed-wing UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles)—and are getting ready to prove the tech’s internet beaming potential starting this year, in tests above Japan and Indonesia.
Regulators, too, seem to be thinking seriously about HAPS. In mid-December, for example, the US Federal Aviation Administration released a 50-page document outlining how large numbers of HAPS could be integrated into American airspace. According to the US Census Bureau’s 2024 American Community Survey (ACS) data, some 8 million US households (4.5% of the population) still live completely offline, and HAPS proponents think the technology might get them connected more cheaply than alternatives.
Despite the optimism of the companies involved, though, some analysts remain cautious.
“The HAPS market has been really slow and challenging to develop,” says Dallas Kasaboski, a space industry analyst at the consultancy Analysis Mason. After all, Kasaboski says, the approach has struggled before: “A few companies were very interested in it, very ambitious about it, and then it just didn’t happen.”
Beaming down connections
Hovering in the thin air at altitudes above 12 miles, HAPS have a unique vantage point to beam down low-latency, high-speed connectivity directly to smartphone users in places too remote and too sparsely populated to justify the cost of laying fiber-optic cables or building ground-based cellular base stations.
“Mobile network operators have some commitment to provide coverage, but they frequently prefer to pay a fine than cover these remote areas,” says Pierre-Antoine Aubourg, chief technology officer of Aalto HAPS, a spinoff from the European aerospace manufacturer Airbus. “With HAPS, we make this remote connectivity case profitable.”
Aalto HAPS has built a solar-powered UAV with a 25-meter wingspan that has conducted many long-duration test flights in recent years. In April 2025 the craft, called Zephyr, broke a HAPS record by staying afloat for 67 consecutive days. The first months of 2026 will be busy for the company, according to Aubourg; Zephyr will do a test run over southern Japan to trial connectivity delivery to residents of some of the country’s smallest and most poorly connected inhabited islands.
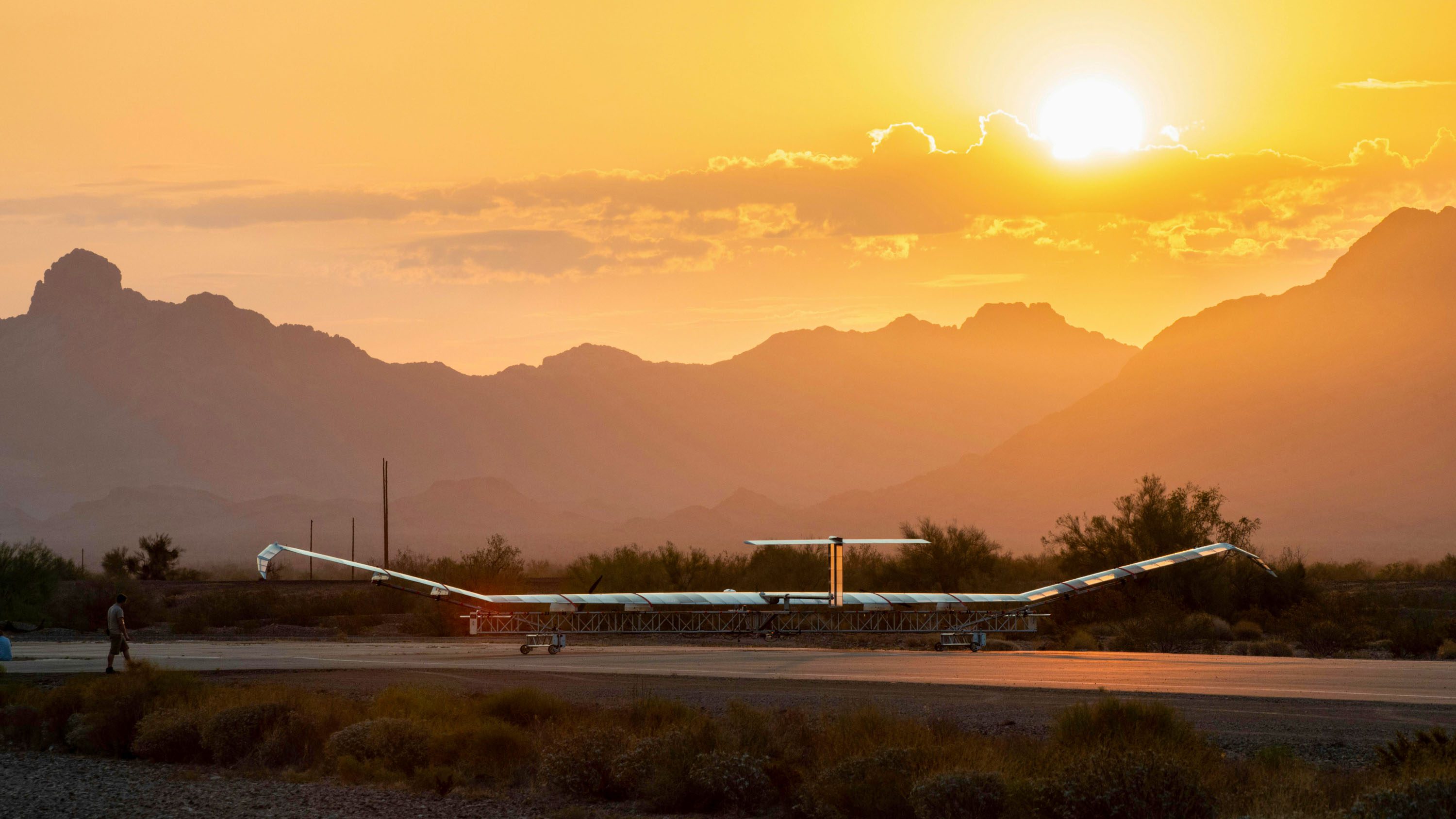

Because of its unique geography, Japan is a perfect test bed for HAPS. Many of the country’s roughly 430 inhabited islands are remote, mountainous, and sparsely populated, making them too costly to connect with terrestrial cell towers. Aalto HAPS is partnering with Japan’s largest mobile network operators, NTT DOCOMO and the telecom satellite operator Space Compass, which want to use Zephyr as part of next-generation telecommunication infrastructure.
“Non-terrestrial networks have the potential to transform Japan’s communications ecosystem, addressing access to connectivity in hard-to-reach areas while supporting our country’s response to emergencies,” Shigehiro Hori, co-CEO of Space Compass, said in a statement.
Zephyr, Aubourg explains, will function like another cell tower in the NTT DOCOMO network, only it will be located well above the planet instead of on its surface. It will beam high-speed 5G connectivity to smartphone users without the need for the specialized terminals that are usually required to receive satellite internet. “For the user on the ground, there is no difference when they switch from the terrestrial network to the HAPS network,” Aubourg says. “It’s exactly the same frequency and the same network.”
New Mexico–based Sceye, which has developed a solar-powered helium-filled airship, is also eyeing Japan for pre-commercial trials of its stratospheric connectivity service this year. The firm, which extensively tested its slick 65-meter-long vehicle in 2025, is working with the Japanese telecommunications giant SoftBank. Just like NTT DOCOMO, Softbank is betting on HAPS to take its networks to another level.
Mikkel Frandsen, Sceye’s founder and CEO, says that his firm succeeded where Loon failed by betting on the advantages offered by the more controllable airship shape, intelligent avionics, and innovative batteries that can power an electric fan to keep the aircraft in place.
“Google’s Loon was groundbreaking, but they used a balloon form factor, and despite advanced algorithms—and the ability to change altitude to find desired wind directions and wind speeds—Loon’s system relied on favorable winds to stay over a target area, resulting in unpredictable station-seeking performance,” Frandsen says. “This required a large amount of balloons in the air to have relative certainty that one would stay over the area of operation, which was financially unviable.”
He adds that Sceye’s airship can “point into the wind” and more effectively maintain its position.
“We have significant surface area, providing enough physical space to lift 250-plus kilograms and host solar panels and batteries,” he says, “allowing Sceye to maintain power through day-night cycles, and therefore staying over an area of operation while maintaining altitude.”
The persistent digital divide
Satellite internet currently comes at a price tag that can be too high for people in developing countries, says Kasaboski. For example, Starlink subscriptions start at $10 per month in Africa, but millions of people in these regions are surviving on a mere $2 a day.
Frandsen and Aubourg both claim that HAPS can connect the world’s unconnected more cheaply. Because satellites in low Earth orbit circle the planet at very high speeds, they quickly disappear from a ground terminal’s view, meaning large quantities of those satellites are needed to provide continuous coverage. HAPS can hover, affording a constant view of a region, and more HAPS can be launched to meet higher demand.
“If you want to deliver connectivity with a low-Earth-orbit constellation into one place, you still need a complete constellation,” says Aubourg. “We can deliver connectivity with one aircraft to one location. And then we can tailor much more the size of the fleet according to the market coverage that we need.”
Starlink gets a lot of attention, but satellite internet has some major drawbacks, says Frandsen. A big one is that its bandwidth gets diluted once the number of users in an area grows.
In a recent interview, Starlink cofounder Elon Musk compared the Starlink beams to a flashlight. Given the distance at which those satellites orbit the planet, the cone is wide, covering a large area. That’s okay when users are few and far between, but it can become a problem with higher densities of users.
For example, Ukrainian defense technologists have said that Starlink bandwidth can drop on the front line to a mere 10 megabits per second, compared with the peak offering of 220 Mbps when drones and ground robots are in heavy use. Users in Indonesia, which like Japan is an island nation, also began reporting problems with Starlink shortly after the service was introduced in the country in 2024. Again, bandwidth declined as the number of subscribers grew.
In fact, Frandsen says, Starlink’s performance is less than optimal once the number of users exceeds one person per square kilometer. And that can happen almost anywhere—even relatively isolated island communities can have hundreds or thousands of residents in a small area. “There is a relationship between the altitude and the population you can serve,” Frandsen says. “You can’t bring space closer to the surface of the planet. So the telco companies want to use the stratosphere so that they can get out to more rural populations than they could otherwise serve.” Starlink did not respond to our queries about these challenges.
Cheaper and faster
Sceye and Aalto HAPS see their stratospheric vehicles as part of integrated telecom networks that include both terrestrial cell towers and satellites. But they’re far from the only game in town.
World Mobile, a telecommunications company headquartered in London, thinks its hydrogen-powered high-altitude UAV can compete directly with satellite mega-constellations. The company acquired the HAPS developer Stratospheric Platforms last year. This year, it plans to flight-test an innovative phased array antenna, which it claims will be able to deliver bandwidth of 200 megabits per second (enough to enable ultra-HD video streaming to 500,000 users at the same time over an area of 15,000 square kilometers—equivalent to the coverage of more than 500 terrestrial cell towers, the company says).
Last year, World Mobile also signed a partnership with the Indonesian telecom operator Protelindo to build a prototype Stratomast aircraft, with tests scheduled to begin in late 2027.
Richard Deakin, CEO of World Mobile’s HAPS division World Mobile Stratospheric, says that just nine Stratomasts could supply Scotland’s 5.5 million residents with high-speed internet connectivity at a cost of £40 million ($54 million) per year. That’s equivalent to about 60 pence (80 cents) per person per month, he says. Starlink subscriptions in the UK, of which Scotland is a part, come at £75 ($100) per month.
A troubled past
Companies working on HAPS also extol the convenience of prompt deployments in areas struck by war or natural disasters like Hurricane Maria in Puerto Rico, after which Loon played an important role. And they say that HAPS could make it possible for smaller nations to obtain complete control over their celestial internet-beaming infrastructure rather than relying on mega-constellations controlled by larger nations, a major boon at a time of rising geopolitical tensions and crumbling political alliances.
Analysts, however, remain cautious, projecting a HAPS market totaling a modest $1.9 billion by 2033. The satellite internet industry, on the other hand, is expected to be worth $33.44 billion by 2030, according to some estimates.
The use of HAPS for internet delivery to remote locations has been explored since the 1990s, about as long as the concept of low-Earth-orbit mega-constellations. The seemingly more cost-effective stratospheric technology, however, lost to the space fleets thanks to the falling cost of space launches and ambitious investment by Musk’s SpaceX.
Google wasn’t the only tech giant to explore the HAPS idea. Facebook also had a project, called Aquila, that was discontinued after it too faced technical difficulties. Although the current cohort of HAPS makers claim they have solved the challenges that killed their predecessors, Kasaboski warns that they’re playing a different game: catching up with now-established internet-beaming mega constellations. By the end of this year, it’ll be much clearer whether they stand a good chance of doing so.