The Triple-P Framework: AI & Search Brand Presence, Perception & Performance
As brands compete for market share across a whole range of AI platforms, each with its own way of presenting information, brands are on red alert.
The three pillars of presence, perception, and performance that I discuss in this article may help marketers navigate new times. This is especially true as search and AI undergo their biggest make-over ever.
What’s driving this change?
AI isn’t just retrieving information anymore – it’s actively evaluating, framing, and recommending brands before prospects even click a link.
It’s happening now, and it’s accelerating.
Think about it. Today, in many ways, ChatGPT has become just as synonymous with AI as Google was when it launched core search.
More and more users and marketers are experimenting with and utilizing Google AIO, ChatGPT, Perplexity, and more.
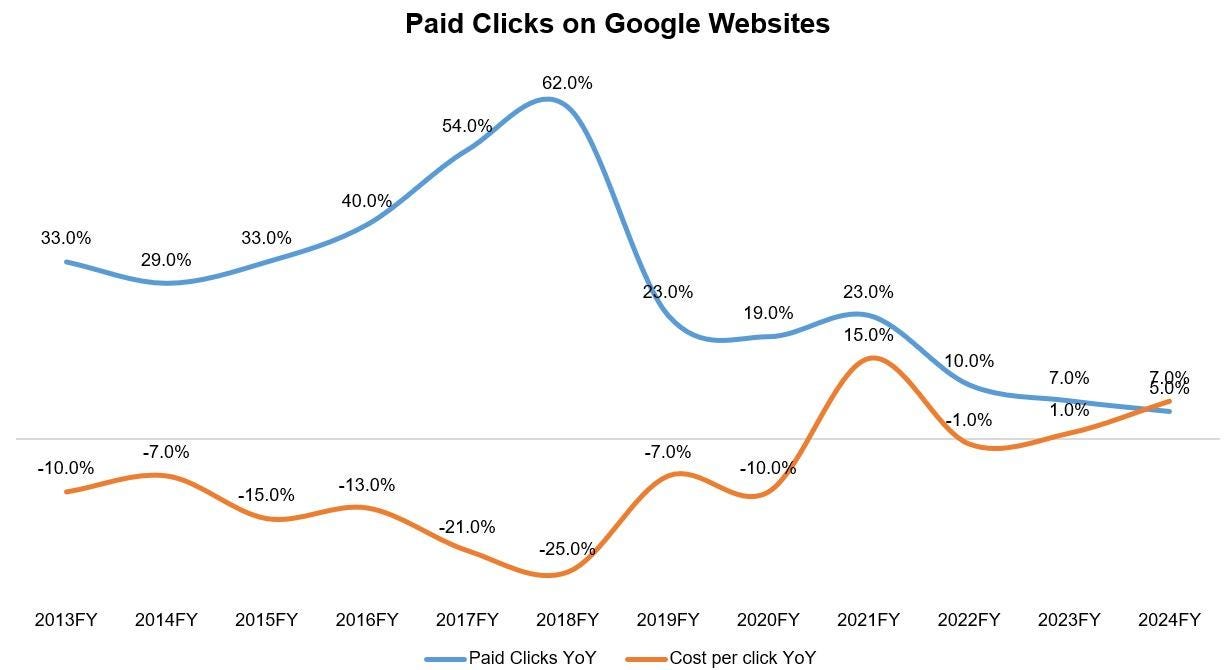
According to a recent BrightEdge survey, over 53% of marketers regularly use multiple (two or more) AI search platforms weekly.
AI Is Reshaping How Brands Are Presented And Perceived
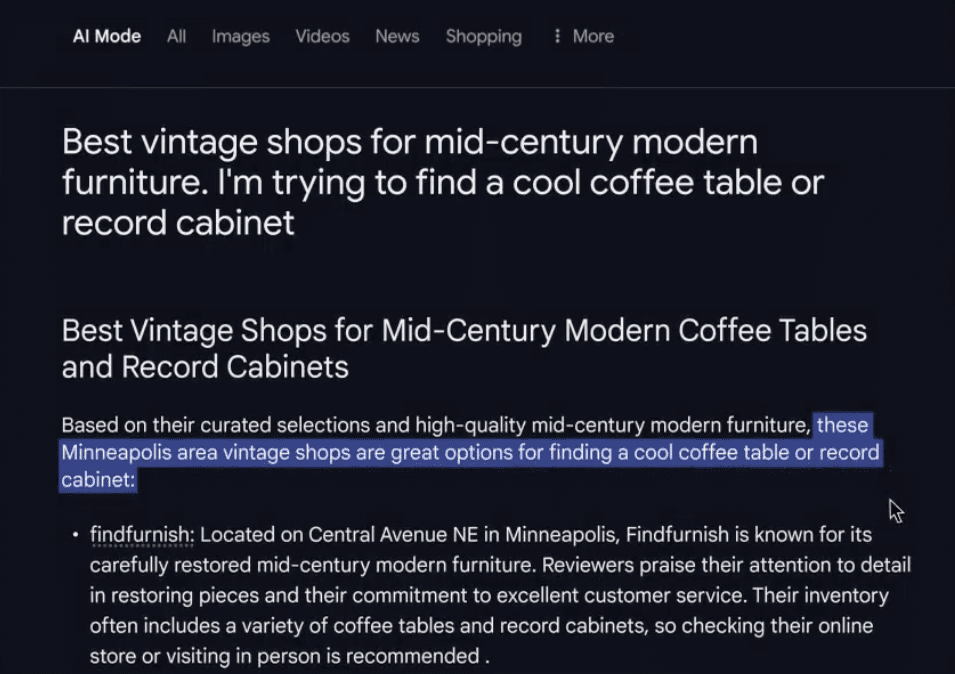
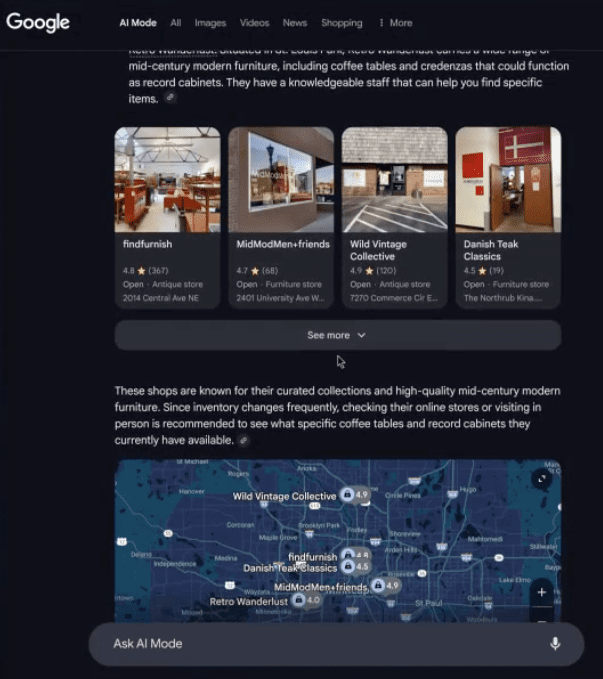
Consider how buyers research options today: In Google AIO, a traveler planning a Barcelona vacation once needed dozens of separate searches, each representing an opportunity for visibility.
Now? They ask one question to an AI assistant and receive a complete itinerary, compressing what 50 touchpoints once took into a single interaction.
AI is no longer a passive search engine. It’s an active evaluator, interpreting intent, forming opinions, and determining which brands deserve attention.
In enterprise SEO and B2B contexts, the shift is even more pronounced. AI is effectively writing the request for proposal (RFP), establishing evaluation criteria, and creating shortlists without brands having direct input.
Take enterprise software evaluation, for instance. When a CIO asks an AI about the “best enterprise resource planning solutions,” the AI’s response typically features:
- A curated shortlist of vendors.
- Evaluation criteria that the AI deems relevant.
- Strengths and limitations of each solution.
- Recommendations based on various scenarios.
These responses don’t just inform decisions. They frame the entire evaluation process before a vendor’s content is visited.
The question isn’t whether this transformation is happening. It’s whether your brand is prepared for it.
Read more: 5 Key Enterprise SEO And AI Trends For 2025
The Triple-P Framework For AI Search Success
After analyzing thousands of AI search responses using our BrightEdge Generative Parser™, I’ve developed the Triple-P framework (Presence, Perception, and Performance) as a strategic compass for navigating this new landscape.
Let’s break down each component.
Presence: Beyond Traditional Rankings
While Google still commands 89.71% of search market share, the ecosystem is diversifying rapidly:
- ChatGPT: 19% monthly traffic growth.
- Perplexity: 12% monthly traffic growth.
- Claude: 166% monthly traffic surge.
- Grok: 266% early-stage spike.
(Source: BrightEdge Generative Parser™ April 2025)
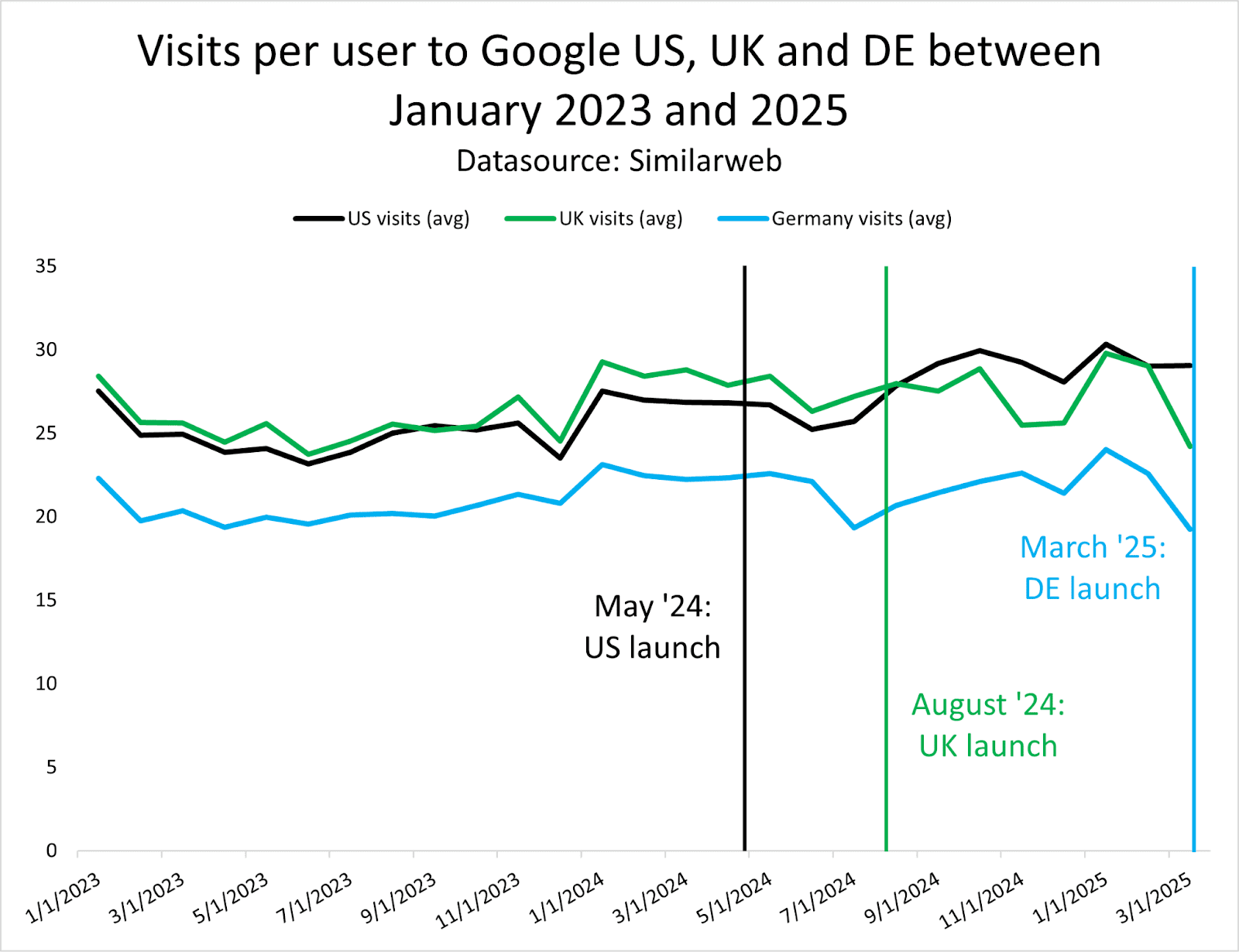
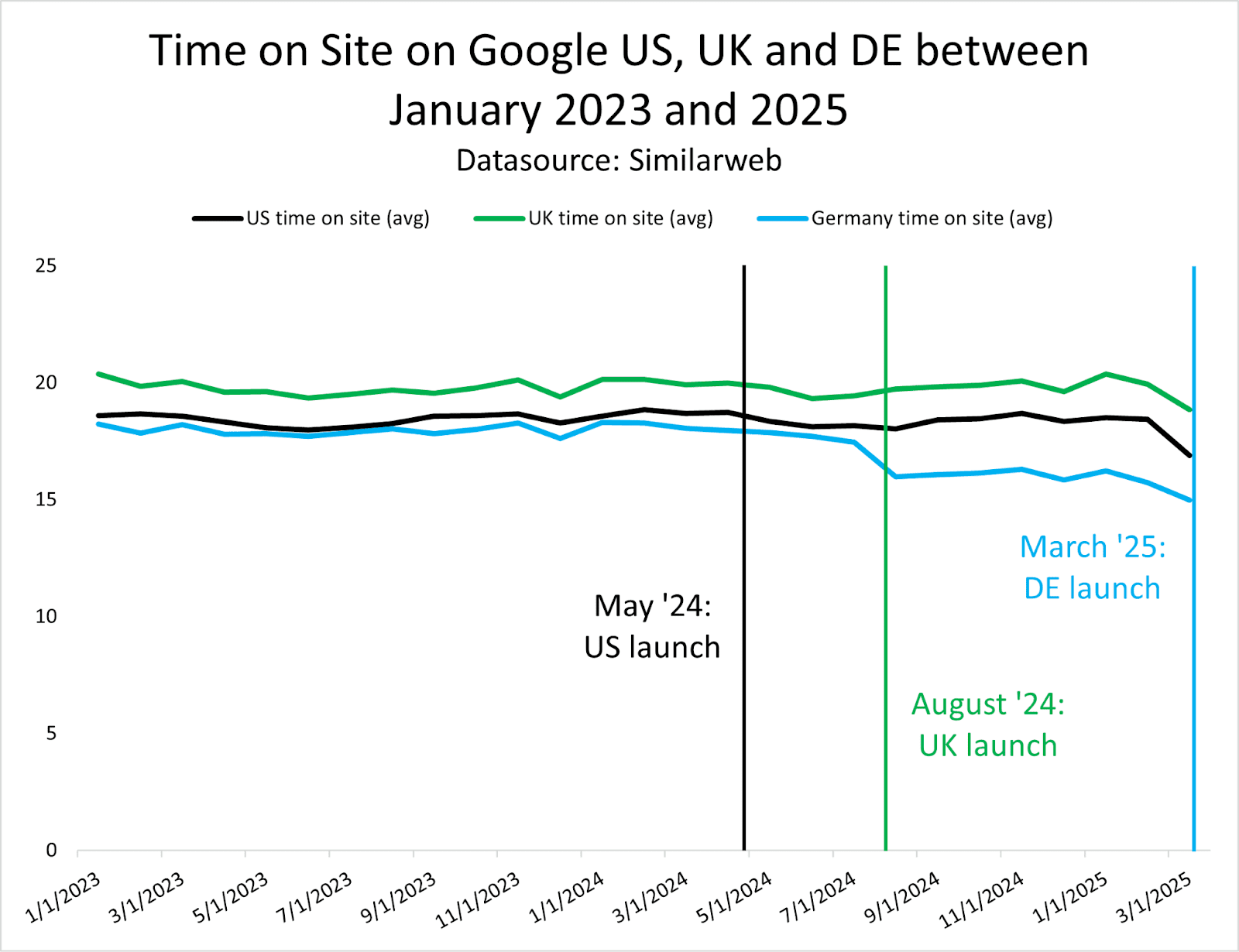
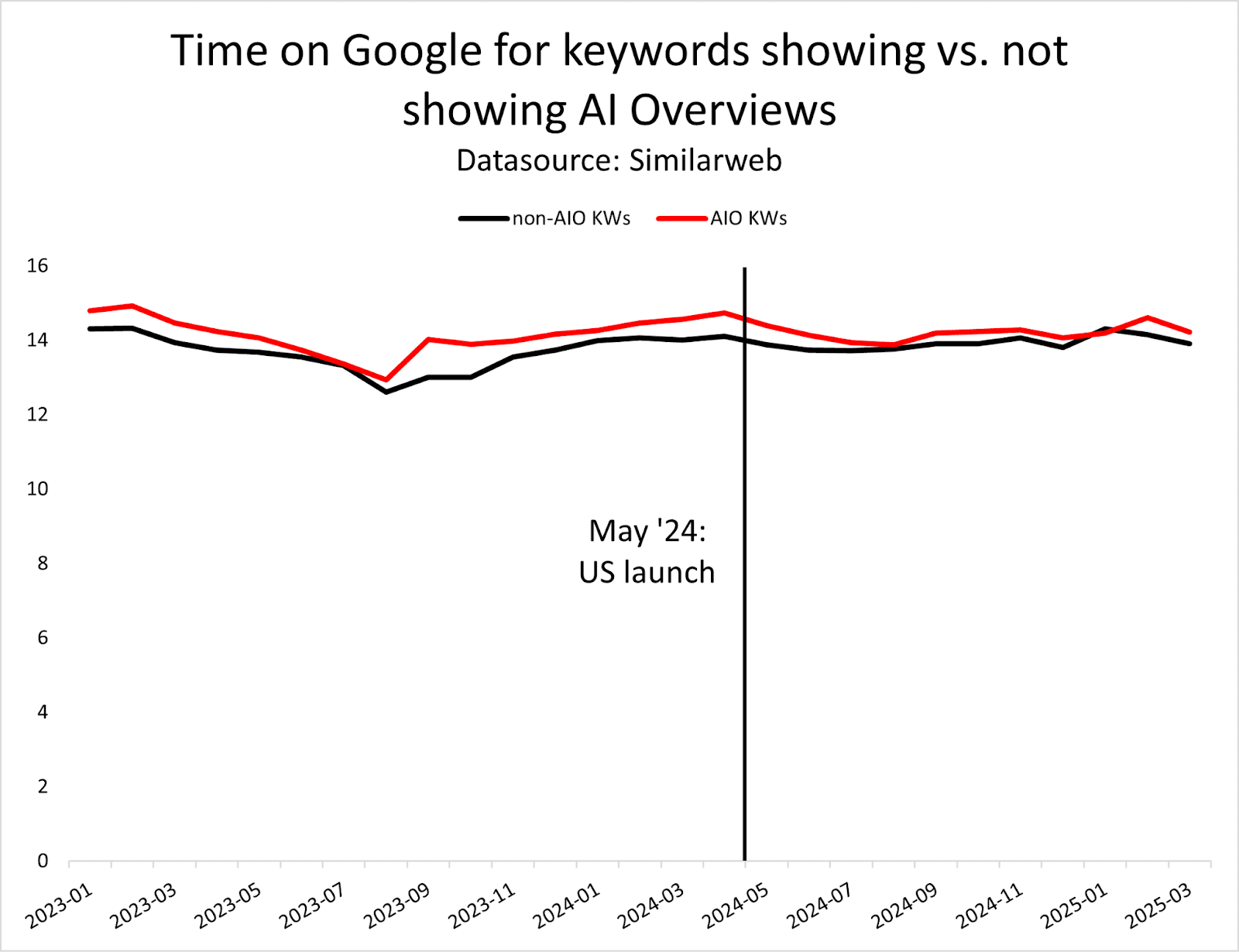
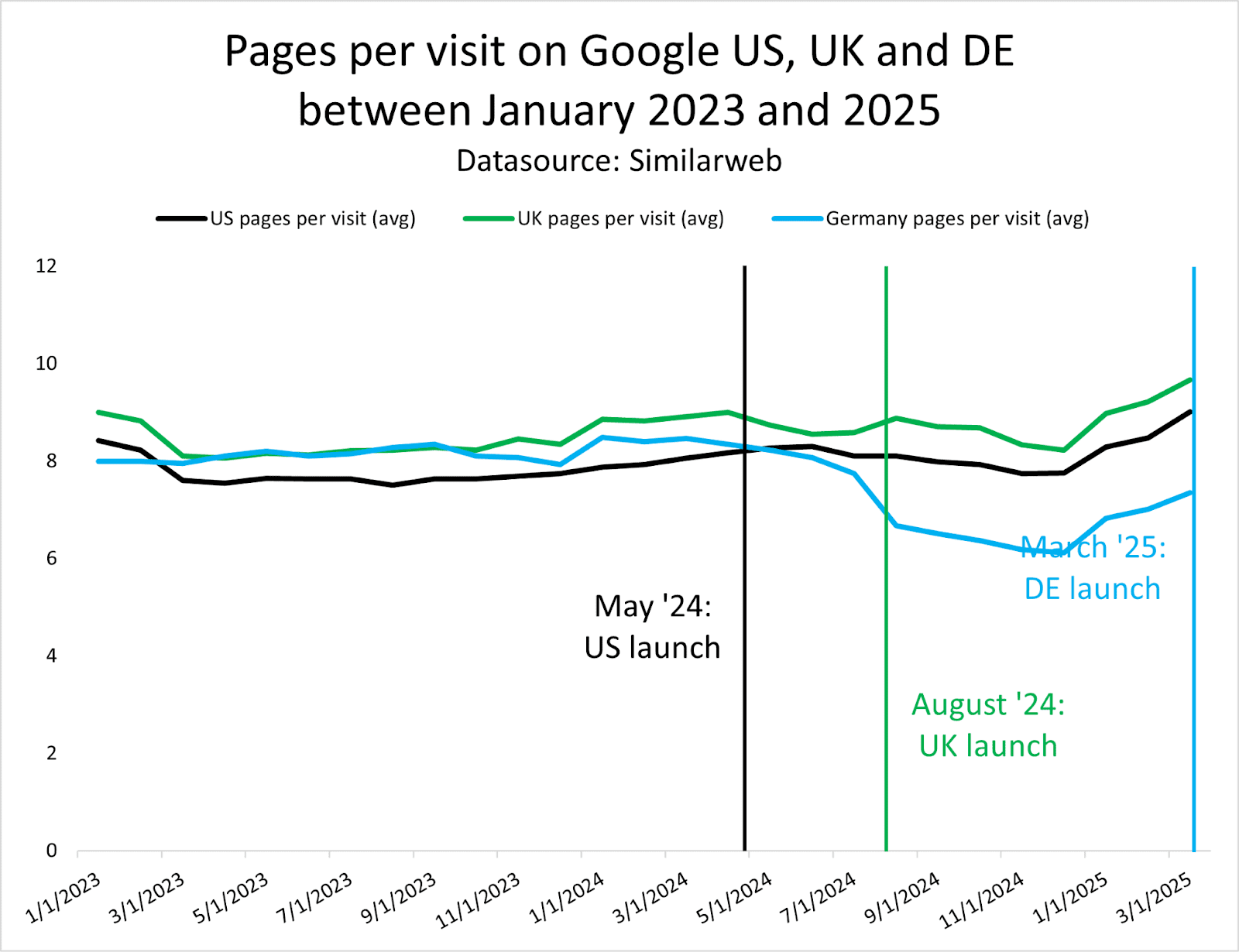
Our research shows that the presence of AI Overviews has nearly doubled since June 2024, with comparison features growing by 70-90% and product visualization features by 45-50% in B2B sectors.
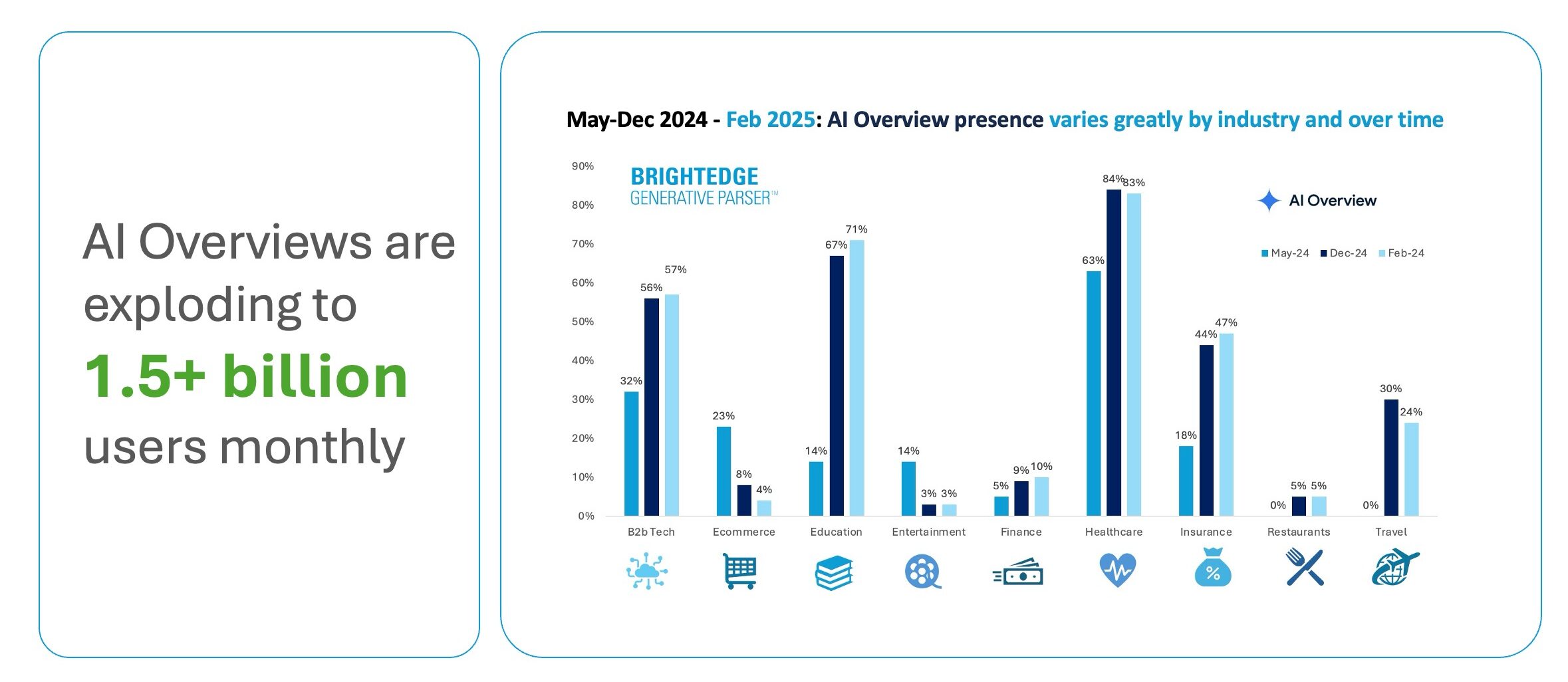 Image from author, May 2025
Image from author, May 2025For enterprise marketers, Google is always your starting point. However, it’s not just about ranking on Google anymore; it’s about showing up wherever AI models showcase your brand.
For example, consider these industry-specific implications:
- For CPG brands: When consumers ask about product sustainability, AI doesn’t just list eco-friendly options; it evaluates authenticity based on consistent messaging across digital touchpoints.
- For SaaS companies: Buyers researching integration capabilities receive AI-curated assessments that either position you as a compatibility leader or exclude you entirely.
- For healthcare providers: Patient questions about treatment options trigger AI responses that cite the most authoritative content, not necessarily the highest-ranking websites.
We are in an era of compressed decision-making. Invisibility equals elimination.
Perception: When AI Forms Opinions
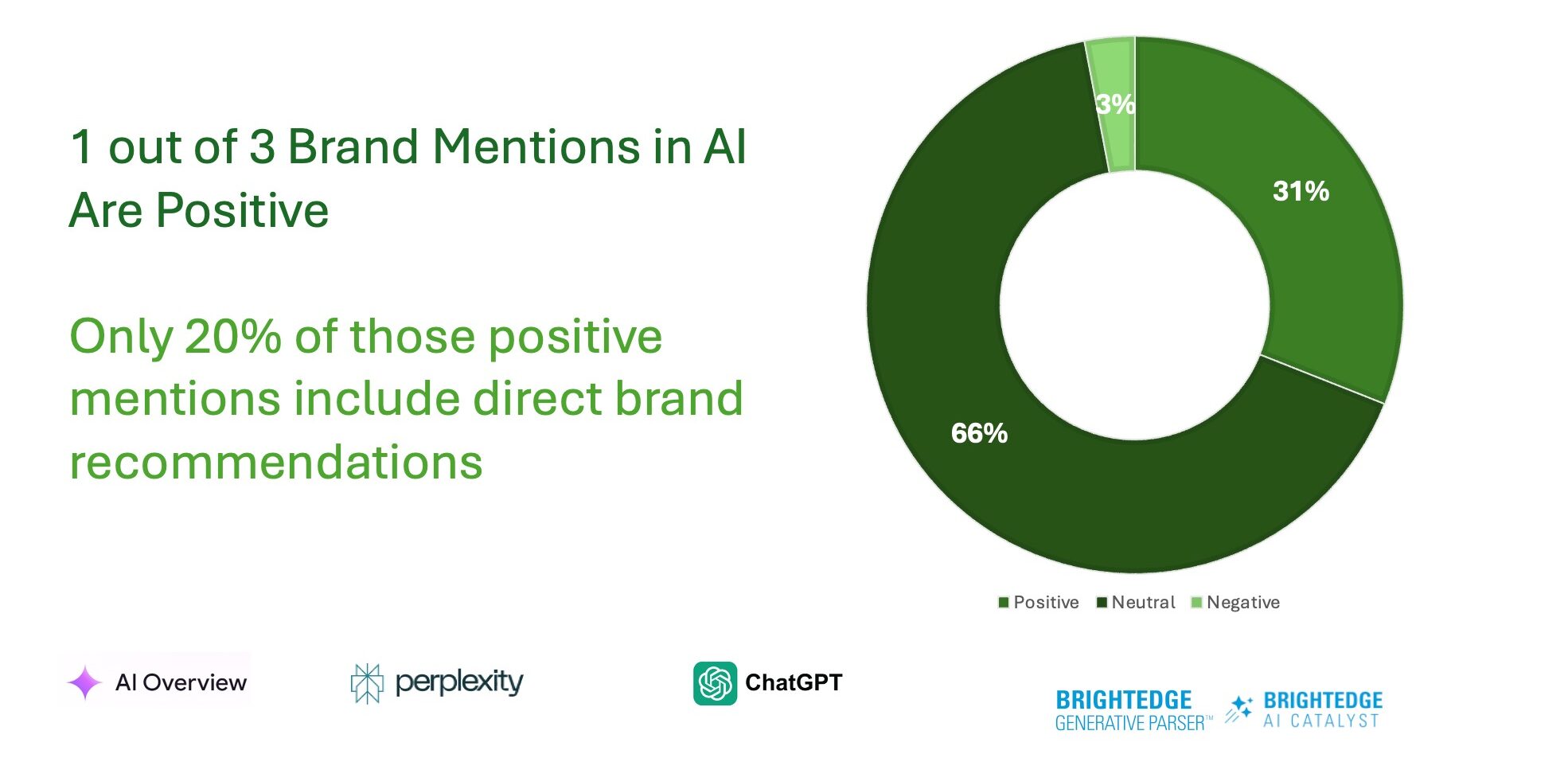
The most revealing insight from our research is that only 31% of AI-generated brand mentions are positive; of those, just 20% include direct recommendations.
This is a wake-up call for all marketers, especially those managing a brand.
Even when your brand appears in AI results, how it’s framed varies dramatically depending on the AI model, training data, and interpretive logic.
In some AI engines, your brand may appear as the industry leader. In others, you may be completely absent.
What The Data Shows:
- Brands with strong pre-existing recognition receive more positive mentions in AI responses.
- Consistent messaging across digital touchpoints makes brands more likely to be cited positively.
- AI systems appear to “average” brand signals across the web when forming perceptions.
When we analyzed sentiment distribution (April 2025) in AI responses by industry, we saw significant variation, which you could group-match to verticals. For example:
- Finance: Positive mentions aligned around good content on regulatory compliance and security.
- Healthcare: Positive mentions aligned around good content with accuracy and credibility as key factors.
- Retail: Positive mentions aligned around good customer experience and shopping.
- Technology: Positive mentions aligned around content on innovation and reliability as primary criteria.
The implications are clear: Perception management is now as crucial as presence.
How does this play out in practice?
When brands implement coordinated perception management strategies across multiple channels, they see improvements in AI sentiment within 60-90 days.
Performance: New Metrics That Matter
The final P (Performance) requires entirely new measurement approaches.
When AI overviews appear in search results, click-through rates often drop by up to 50% according to internal BrightEdge data. Yet, conversion rates typically remain strong, suggesting AI qualifies leads before they reach your site.
We’re entering an era where impressions will be high, click-through rates may drop, but conversions will increase.
I explained at our recent quarterly briefing. AI filters options and delivers buyers who are closer to decisions.
The impact varies dramatically by query type:
- Informational queries: Reduction in clicks, minimal conversion impact.
- Navigational queries: Reduction in clicks, negligible conversion impact.
- Commercial queries: Reduction in clicks, higher conversion rates.
- Transactional queries: Reduction in clicks, higher conversion rates.
This pattern suggests AI is most effective at qualifying commercial intent, delivering more purchase-ready traffic.
And impressions matter now – they are a new brand metric.
Five Essential AI Search Metrics:
- AI Presence Rate: Percentage of target queries where your brand appears in AI responses.
- Citation Authority: How consistently you are cited as the primary source.
- Share Of AI Conversation: Your semantic real estate in AI answers versus competitors.
- Prompt Effectiveness: How well your content answers natural language prompts.
- Response-To-Conversion Velocity: How quickly AI-influenced prospects convert. Brands with strong pre-existing recognition will receive more positive mentions in AI responses.
Position within AI responses matters as much as position in traditional SERPs once did.
Monthly reporting cycles are becoming obsolete. AI-generated results can shift within hours, demanding real-time monitoring capabilities.
The DNA Of AI-Optimized Content
In my experience, content is more likely to be cited by AI with:
- Comprehensive coverage: Content addressing multiple related questions outperforms narrow content.
- Structured data implementation: Pages with robust schema markup see higher citation rates.
- Expert validation: Content with clear expert authorship signals receives more citations.
- Multi-format delivery: Topics presented in multiple formats (text, video, data visualizations) earn more citations.
- First-party data inclusion: Original research and proprietary data increase citation likelihood.
These patterns suggest AI systems are increasingly sophisticated in their ability to identify genuinely authoritative content versus content merely optimized for traditional ranking factors.
In my last article, I discussed how Google AIO, ChatGPT, and Perplexity differ and where they share some common optimization traits.
Five Actionable Strategies For Triple-P Success
Based on our extensive research, here are five implementation strategies aligned with this framework:
1. Adopt Entity-Based SEO
AI prioritizes content from known, trusted entities. Stop optimizing for fragmented keywords and start building comprehensive topic authority.
Our data shows that authoritative content is three times more likely to be cited in AI responses than narrowly focused pages.
Implementation Steps:
- Perform an entity audit: Identify how search engines currently understand your brand as an entity.
- Develop topical maps: Create comprehensive coverage of core topics rather than isolated keywords
- Implement entity-based schema: Use structured data to explicitly define your brand’s relationship to key topics.
- Build consistent entity references: Ensure name, address, and phone (NAP) consistency across all digital properties.
- Cultivate authoritative connections: Earn mentions and links from recognized authorities in your space.
Enterprise brands implementing entity-based SEO will see an uplift in AI citations.
2. Implement Perception Management
With 69% of AI brand mentions not explicitly positive, you must actively shape sentiment.
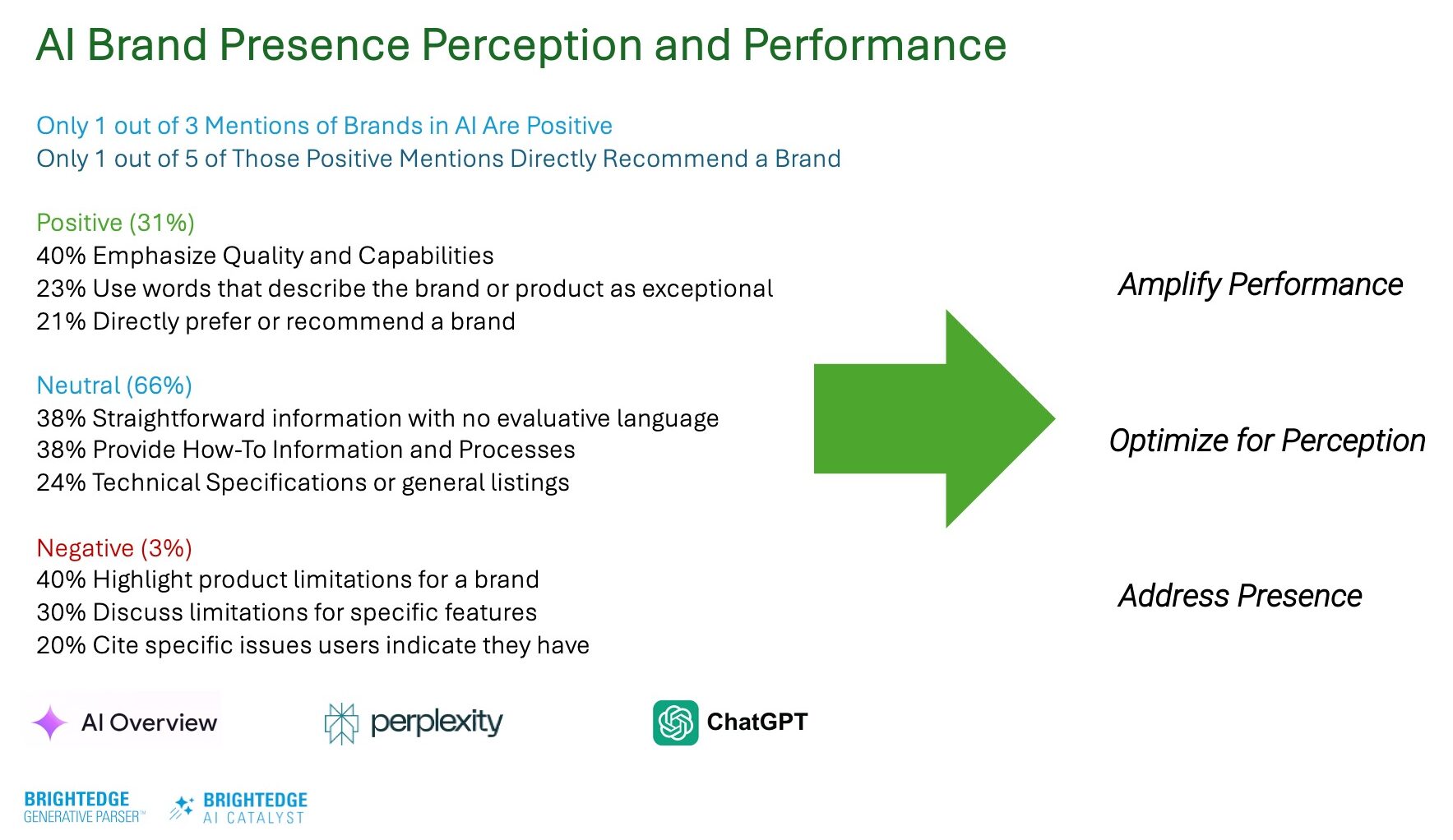


Brands that implement proactive sentiment management strategies will see success.
Implementation Steps:
- Monitor AI sentiment tracking: Establish baseline sentiment across AI platforms.
- Identify perception gaps: Compare AI perceptions against desired brand positioning.
- Address criticism proactively: Create content that honestly addresses common concerns.
- Amplify authentic strengths: Develop evidence-based content highlighting genuine advantages.
- Build consistent messaging: Align key messages across all digital touchpoints.
3. Integrate Real-Time Citation Monitoring
Tracking AI citations regularly is now vital to improve mention rates.
This requires capability beyond traditional rank tracking or Google Search Console analysis.
Implementation Steps:
- Deploy continuous monitoring: Track AI responses for priority queries across platforms.
- Implement competitor citation alerts: Get notified when competitors gain or lose citations.
- Conduct prompt variation testing: Analyze how different user phrasings affect your brand’s inclusion.
- Track citation position: Monitor where within AI responses your brand appears.
- Measure citation authority: Assess whether you’re positioned as a primary or secondary source.
4. Deploy Cross-Core Search And AI Platforms
Companies that take an integrated approach across traditional search and multiple AI platforms will see higher return on investment (ROI) on search investments.
The future belongs to unified measurement frameworks that connect traditional SEO metrics with emerging AI citation patterns.
Implementation Steps:
- Build unified dashboards: Integrate traditional search metrics with AI citation data.
- Map keyword-to-prompt relationships: Connect traditional keywords to conversational AI prompts.
- Analyze traffic source shifts: Track changing patterns between direct search and AI-referred traffic.
- Segment by AI platform: Monitor performance variations across different AI search environments.
- Connect to business outcomes: Tie AI presence metrics directly to conversion and revenue data.
5. Use AI To Win At AI
This isn’t theoretical. It’s delivering measurable results:
- BrightEdge Autopilot users averaged a 65% performance improvement.
- BrightEdge Copilot users saved 1.2 million content research hours.
The brands succeeding most in AI search leverage AI in their workflows.
Implementation Steps:
- Automate content research: Use AI to identify comprehensive topic coverage opportunities.
- Implement AI-driven schema markup: Systematically structure data for machine interpretation.
- Deploy prompt effectiveness testing: Continuously test how well content answers real user prompts.
- Create AI-optimized content briefs: Define exactly what comprehensive coverage means for each topic.
- Analyze AI citation patterns: Identify what characteristics make competitor content citation-worthy.
Teams using AI for AI optimization will benefit from higher productivity and improved performance to gain that must-have competitive edge in search and AI today.
What’s Coming Next: AI-To-AI Marketing
Looking ahead to two to three years, expect AI to evolve from an information assistant to a trusted advisor that buyers rely on for evaluation, comparison, and vendor selection.
We’re already seeing early indicators of AI-to-AI marketing, where procurement teams use AI agents to automate research and vendor vetting.
Emerging Trends:
- Digital twin marketplaces: Buyers will interact with simulated versions of B2B solutions before speaking with vendors
- Vertical-specific AI companions: Industry-specialized models for cybersecurity, manufacturing, and healthcare.
- AI agent purchasing: Autonomous systems are not just researching but also completing transactions on users’ behalf.
- Continuous entity validation: AI systems continuously monitor brand claims against real-world evidence.
- Multi-modal search experiences: Voice, image, and text-based AI interactions requiring omnichannel optimization.
Read more: As Chatbots And AI Search Engines Converge: Key Strategies For SEO
The Trust Premium In AI Search
Consumers are always more likely to trust brands they already recognize.
- AI functions as a trust bridge.
- When consumers delegate decision-making to AI, pre-existing brand familiarity becomes disproportionately influential.
- The impact is most pronounced in high-consideration purchases.
This creates both a challenge and an opportunity. Established brands must protect their advantage, while emerging brands must strategically build recognition signals detectable by AI.
Organizational Structure For AI Search Success
Leading organizations are already creating “collaborative intelligence” roles – specialists managing the interplay between human creativity and AI amplification.
Successful teams typically include:
- AI Search Strategists: Focus on overall presence, perception, and performance.
- Prompt Engineers: Specialize in understanding how users phrase requests to AI.
- Content Scientists: Develop evidence-based approaches to comprehensive coverage.
- AI Citation Analysts: Monitor and optimize for inclusion in AI responses.
- Schema Specialists: Ensure that the machine-readable structure enhances entity understanding.
These cross-functional teams integrate with traditional SEO, content marketing, analytics, and business intelligence functions.
The Bottom Line
In this new landscape, the question isn’t whether your website ranks. It’s whether AI recommends your brand when it matters most.
The Triple-P framework gives you the structure to navigate this future with confidence.
Here’s what I recommend getting started:
- Conduct an AI presence audit: Understand where your brand appears in AI responses across key platforms.
- Analyze sentiment distribution: Assess not just if you’re mentioned, but how you’re portrayed in AI-generated content.
- Connect AI metrics to business results: Start tracking the relationship between AI presence and conversion patterns.
- Identify entity perception gaps: Compare how AI systems understand your brand versus your desired positioning.
- Deploy real-time monitoring: Implement systems to track citation changes as they happen.
The branded AI search revolution isn’t coming – it’s already here.
The brands that embrace the Triple-P framework today will be the ones AI recommends tomorrow.
Note: In March 2025, BrightEdge surveyed over 1,000 of its customers who are marketers. Findings from this survey are referenced above.
More Resources:
Featured Image: Moon Safari/Shutterstock