WP Engine Escalates Legal Battle With Automattic and Mullenweg via @sejournal, @martinibuster
WP Engine escalated its Federal complaint by citing Automattic’s publication of the WP Engine Tracker website as evidence of intent to harm WP Engine and exposing customers to potential cybercrimes. The updated complaint incorporates recent actions by Mullenweg to further strengthen their case.
A spokesperson for WP Engine issued a statement to Search Engine Journal about the WP Engine Tracker website:
“Automattic’s wrongful and reckless publication of customer’s information without their consent underscores why we have moved for a preliminary injunction. WP Engine has requested the immediate takedown of this information and looks forward to the November 26th hearing on the injunction.”
Legal Complaint Amended With More Evidence
WP Engine (WPE) filed a complaint in Federal court seeking a preliminary injunction to prevent Matt Mullenweg and Automattic from continuing actions that harm WPE’s business and their relationships with their customers. That complaint was amended with further details to support their allegations against Mullenweg and Automattic.
The legal complaint begins by stating in general terms what gives rise to their claim:
“This is a case about abuse of power, extortion, and greed.”
It then grows progressively specific by introducing evidence of how Automattic and Mullenweg continue their “bad acts unabated” for the purpose of harming WP Engine (WPE).
The amended claim adds the following, quoting Mullenweg himself:
“Since then, Defendants have continued to escalate their war, unleashing a campaign to steal WPE’s software, customers and employees. Indeed, just days ago, Defendants were unambiguous about their future plans:”
This is the statement Mullenweg made that is quoted in the amended complaint:
“[S]ince this started [with WPE] they’ve had uh, we estimate tens of thousands of customers leave. . . . So, um you know, I think over the next few weeks, they’re actually gonna lose far more than 8% of their business . . . we’re at war with them. We’re . . . going to go brick by brick and take . . . take every single one of their customers . . . if they weren’t around guess what? . . . We’d happily have those customers, and in fact we’re getting a lot of them.”
WP Engine Tracker Site Used As Evidence
Automattic recently created a website on the WordPressEngineTracker.com domain called WP Engine Tracker that encourages WordPress Engine customers to leave, offering links to promotions that offer discounts and promise a smooth transition to other web hosts.
WPE states that the WP Engine Tracker website is part of a campaign to encourage WPE customers to abandon it, writing:
“Defendants also created a webpage at wordpress.org offering “Promotions and Coupons” to convince WPE customers to stop doing business with WPE and switch over to Automattic’s competitor hosting companies like wordpress.com and Pressable; they later added links to other competitors as well.”
The WordPress Engine Tracker website calls attention to the number of sites that have abandoned WP Engine (WPE) since Matt Mullenweg’s September 21st public denunciation of WP Engine and the start of his “nuclear” war against the web host. The amended Federal lawsuit points to the September 21st date listed on that site as additional evidence tying Automattic to a campaign to harm WP Engine’s business.
The legal document explains:
“Just last week, in an apparent effort to brag about how successful they have been in harming WPE, Defendants created a website—www.wordpressenginetracker.com—that “list[s] . . . every domain hosted by @wpengine, which you can see decline every day. 15,080 sites have left already since September 21st.
September 21 was not selected randomly. It is the day after Defendants’ self-proclaimed nuclear war began – an admission that these customer losses were caused by Defendants’ wrongful actions. In this extraordinary attack on WPE and its customers, Defendants included on their disparaging website a downloadable file of ‘all [WPE] sites ready for a new home’—that is, WPE’s customer list, literally inviting others to target and poach WPE’s clients while Defendants’ attacks on WPE continued..”
The purpose of the above allegations are to build as much evidence that lend credence to WP Engine’s claim that Automattic is actively trying to cause harm WP Engine’s business.
WPE Accuses Automattic Of Additional Harms
Another new allegation against Automattic is that the spreadsheet offered for download on the WP Engine Tracker website includes sensitive information that is not publicly available and could cause direct harm to WPE customers.
The amended Federal lawsuit explains:
“Worse, this downloadable file contains private information regarding WPE’s customers’ domain names, including development, test, and pre-production servers—many of which are not intended to be accessed publicly and contain sensitive or private information. Many of these servers are intentionally not indexed or otherwise included in public search results because the servers are not safe, secure or production-ready and not intended to be accessed by the general public.
By disclosing this information to the general public, Defendants put these development, test, and pre-production domains at risk for hacking and unauthorized access.”
WP Engine Tracker Site Part Of A Larger Strategy
WPE’s amended complaint alleges that the WP Engine Tracker site is one part of a larger strategy to cause harm to WP Engine’s business that includes encouraging WPE employees to resign. The legal document adds new information of how the WP Engine Tracker website is just one part of a larger strategy to harm WPE’s business.
The updated document adds the following new allegations as evidence of WPE’s claims:
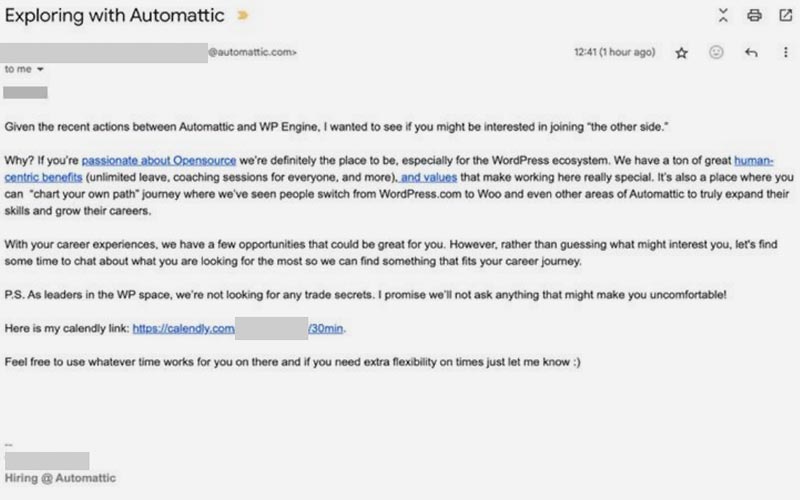
“Not content with interfering with WPE’s customer relations, Automattic has recently escalated its tactics by actively recruiting hundreds of WPE employees, in an apparent effort to weaken WPE by sowing doubts about the company’s future and enticing WPE’s employees to join Automattic:”
The document includes a screenshot of an email solicitation apparently sent to an employee that encourages them to join Automattic.
Screenshot Of Evidence Presented In Amended Complaint
Escalation Of Federal Complaint
WP Engine’s amended complaint against Mullenweg and Automattic invokes the Sherman Act (prohibiting monopolization to maintain a competitive marketplace), the Lanham Act (governing trademarks, false advertising, and unfair competition), and the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (addressing unauthorized computer access and cybercrimes). The amendments tie recent actions by Mullenweg and Automattic—such as the creation of the WP Engine Tracker website—directly to their claims, turning Mullenweg’s attacks on WP Engine into evidence.
Read the amended Federal complaint here: (PDF).
Featured Image by Shutterstock/chaiyapruek youprasert









