OpenAI Launches SearchGPT: AI-Powered Search Prototype via @sejournal, @MattGSouthern
OpenAI has announced the launch of SearchGPT, a prototype AI-powered search engine.
This move marks the company’s entry into the competitive search market, potentially challenging established players.
Key Features & Functionality
SearchGPT aims to directly answer user queries by combining AI language models with real-time web information.
Rather than offering a list of links, SearchGPT attempts to deliver concise responses with citations to source material.
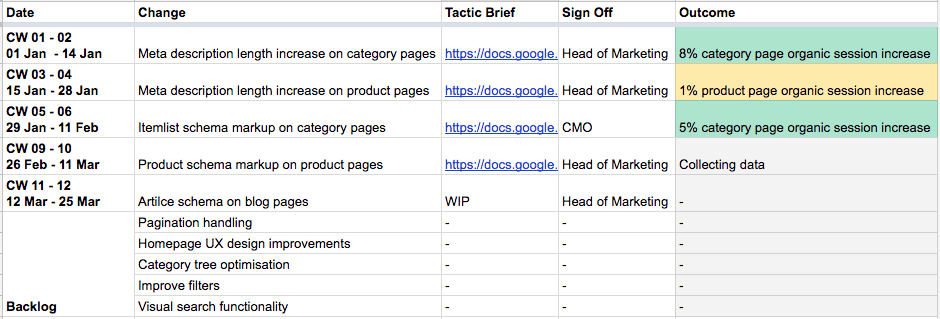
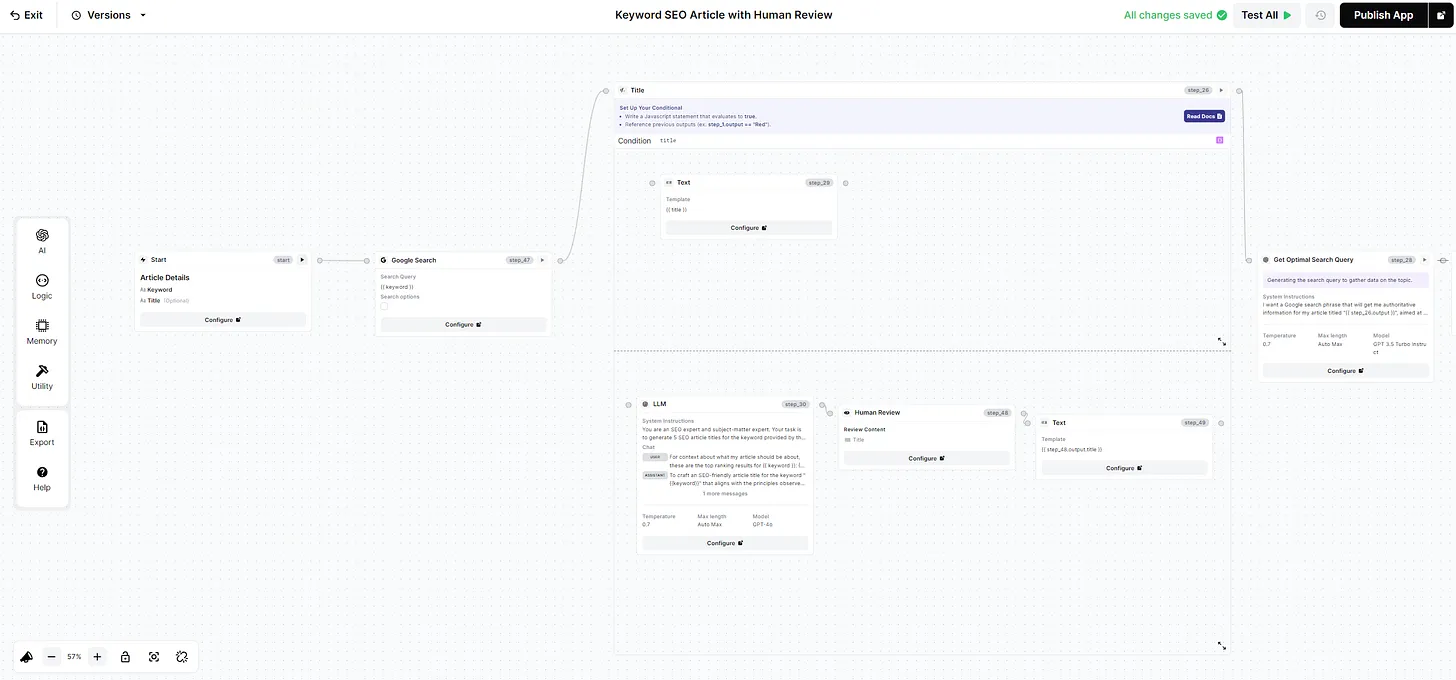
Here’s an example of a search results page for the query: “music festivals in boone north carolina in august.”
 Screenshot from openai.com/index/searchgpt-prototype/, July 2024.
Screenshot from openai.com/index/searchgpt-prototype/, July 2024.The SearchGPT prototype includes:
- A conversational interface allowing follow-up questions
- Real-time information retrieval from web sources
- In-line attributions and links to original content
Publisher Controls & Content Management
OpenAI is also introducing tools for publishers to manage how their content appears in SearchGPT, giving them more control over their presence in AI-powered search results.
Key points about the publisher controls include:
- Separate from AI training: OpenAI emphasizes that SearchGPT is distinct from the training of their generative AI models. Sites can appear in search results even if they opt out of AI training data.
- Content management options: Publishers can influence how their content is displayed and used within SearchGPT.
- Feedback mechanism: OpenAI has provided an email (publishers-feedback@openai.com) for publishers to share their thoughts and concerns.
- Performance insights: The company plans to share information with publishers about their content’s performance within the AI search ecosystem.
These tools are OpenAI’s response to ongoing debates about AI’s use of web content and concerns over intellectual property rights.
Publisher Partnerships & Reactions
OpenAI reports collaborating with several publishers during the development of SearchGPT.
Nicholas Thompson, CEO of The Atlantic, provided a statement supporting the initiative, emphasizing the importance of valuing and protecting journalism in AI search development.
Robert Thomson, News Corp’s chief executive, also commented on the project, stressing the need for a symbiotic relationship between technology and content and the importance of protecting content provenance.
Limited Availability & Future Plans
Currently, SearchGPT is available to a restricted group of users and publishers.
OpenAI describes it as a temporary prototype, indicating plans to integrate features into their existing ChatGPT product eventually.
Why This Matters
The introduction of SearchGPT represents a potential shakeup to the search engine market.
This development could have far-reaching implications for digital marketing, content creation, and user behavior on the internet.
Potential effects include:
- Changes in content distribution and discovery mechanisms
- New considerations for search engine optimization strategies
- Evolving relationships between AI companies and content creators
Remember, this is still a prototype, and we have yet to see its capabilities.
There’s a waitlist available for those trying to get their hands on it early.
What This Means For You
AI-powered search might offer users more direct access to information. However, the accuracy and comprehensiveness of results may depend on publisher participation and content management choices.
For content creators and publishers, these new tools provide opportunities to have more say in how their work is used in AI search contexts.
While it may increase content visibility and engagement, it also requires adapting to new formats and strategies to ensure content is AI-friendly and easily discoverable.
As SearchGPT moves from prototype to integration with ChatGPT, it will be vital to stay informed about these developments and adapt your strategies.
The future of search is evolving, and AI is at the forefront of this transformation.