What is Google AI Mode?
Google AI Mode is search with a brain. It uses AI to answer questions directly, so it’s no longer about just blue links. Type, talk, or upload a photo, and it gives you a useful summary plus follow-ups. Here’s how it works and why it matters.
Say hello to Google’s AI Mode
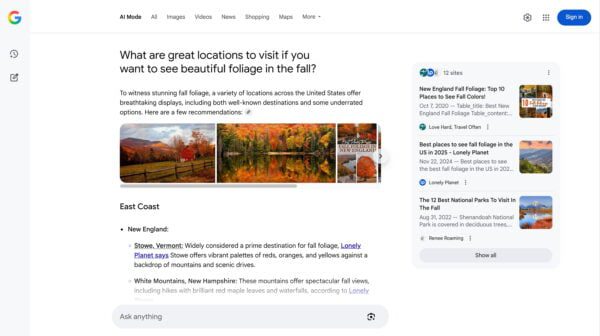
Google AI Mode is a feature in Search that uses generative AI to deliver full, conversational answers instead of just showing a list of links. It breaks questions into parts, pulls information from across the web, and presents a direct, useful response at the top of the results page.
This new feature doesn’t replace traditional search just yet, but it does build on it. As a result, it changes how people explore information and how content gets surfaced.
Are you curious about how this works? Check out the video below to see Google AI Mode in action while planning an autumn trip to Banff, Canada.
Search becomes a lot smarter
AI Mode handles different types of input, not just text. You can type a question, say it out loud, or upload a photo, and it works out what you mean. That flexibility makes it easier to search however and whenever it makes sense, whether you’re speaking into your phone, typing at your desk, or pointing your camera at something you want to learn more about.
It also uses what Google calls query fan-out. That means it quietly rewrites your question into a bunch of related ones and looks for answers across those variations. Ask something broad, like “best credit card for travel,” and the system may branch off behind the scenes, looking at fees, perks, user reviews, and so on.
AI Mode also pays attention to context. It keeps your previous queries in mind and follows the thread. You can ask follow-ups and get refined answers without starting from scratch.
How Google AI Mode works in practice
Using Google AI Mode feels different from standard search, and that shows up in how it delivers answers.
When someone asks a question, AI Mode doesn’t just take the words at face value—it tries to understand the intent behind them. It rewrites the query in several different ways behind the scenes, each one focused on a specific angle.
For example, a search like “what are the best places to travel in fall” might also trigger more specific questions in the background, like “pleasant weather and fewer crowds,” “fall foliage and scenic beauty,” or “unique experiences and cultural events.” AI Mode runs all of those in parallel, scans multiple online sources for useful information, and pieces together a response that covers what the user likely meant, even if they didn’t spell it out.
The response doesn’t look like a typical search results page. Instead of a list of links, users see a short summary stitched together from different sources. It reads more like an answer than a directory and can include images, maps, and more.
With AI Mode, you can also keep the conversation going. You could ask follow-up suggestions like “compare destinations in Canada,” “check visa requirements for Canada,” or “see average weather in British Columbia”. It helps users toward the next thing they might want to know without making them start over. The video at the top of this article shows this in practice.
Behind the scenes, AI Mode uses passage-level retrieval. Rather than ranking entire pages, it scans individual sections, like a single paragraph, list, or sentence, to find the parts that answer specific pieces of the question.
That means a well-written section buried halfway down a product guide or FAQ could be surfaced, even if the full page wouldn’t normally show up high in the results.
This alone could make us rethink visibility. It’s less about a page’s overall ranking and more about whether any part of it directly addresses what someone is asking.
The focus of content is changing
AI Mode shifts how content gets discovered. It’s less about ranking in the traditional sense and more about providing answers that are both useful and directly relevant to what someone is asking.
The system is looking for content that fits into a specific response. That means structure matters, like clear headings, focused sections, and formatting that makes key points easy to extract. But usefulness on its own doesn’t guarantee visibility. The content has to align with the intent of the query in a very specific way.
Covering a topic from different angles helps. It gives your content more chances to match how people frame their questions, even when those questions vary in wording, detail, or focus. Visibility often depends not just on quality, but on precision.



What does Google AI Mode mean for SEO?
Google AI Mode could shift what we aim for. Visibility now depends on whether your content can deliver value right away, often in small, specific pieces. Google’s pulling answers from across the web: a sentence from one page, a stat from another, maybe a checklist from a support article.
That might feel limiting, but it opens up opportunities. If others are still optimizing for old patterns, there’s space to improve. Recognizing this shift early can give your brand a real advantage.
It also rewards a stronger understanding of how people search. Pages, tools, and features that directly answer real questions and make that answer easy to find stand a better chance of getting picked up.
Find out how to optimize your content for AI LLM comprehension using Yoast’s tools.


Where it’s going
Google is folding AI Mode into regular search experiences. On some questions, especially ones that ask for a comparison, a definition, or a plan, it’s already showing AI-generated results first.
That approach is expanding. More queries will likely trigger this kind of response over time, which means the way content gets surfaced will keep shifting. Long, keyword-heavy pages won’t offer the same payoff they once did. What works now is content that’s clear, helpful, and flexible enough to match how people explore a topic.
Chances are, AI Mode isn’t a side feature for long. It’s looking more and more like the future of Google Search.
How to access Google AI Mode
AI Mode is rolling out now in the U.S. and India. If you’re using Google Search or the Google app, you’ll start to see a new AI Mode tab either at the top of the results page or right in the search bar. This gives you access to more advanced AI responses, improved reasoning, and a deeper view of web content through follow-up questions and linked sources.
If you don’t see AI Mode yet, it’s likely still rolling out. Expect it to appear automatically soon. Once it shows up, you can use it without any special sign-up or activation. Once Google figures out monetization, we’ll see it roll out AI Mode to more countries soon.
You can also access it from search results. If Google thinks your query fits, a “Try in AI Mode” option may appear automatically. Trying it out firsthand gives the clearest insight into how responses are built and how your content appears.
Meet Google’s AI Mode
Google AI Mode signals a shift in how search works. It’s not just about rankings anymore. It’s about how helpful your content is and how easily it can be used to respond to real questions.
This change gives SEO and content teams a reason to look at their work differently. Clear structure, focused writing, and alignment with how people search all play a bigger role in visibility.
It’s a good time to step back, reassess what’s working, and explore areas you may have overlooked. For many, this is a chance to improve useful content, refine formats, and meet search expectations in new ways.