An In-Depth Look At Google Spam Policies Updates And What Changed via @sejournal, @AlliBerry3
By now, you’ve likely seen the announcements about the March 2024 Core Update. This major update will roll out over the entire month and aims to reduce “unhelpful” content by 40%.
Interestingly, Google also updated its spam policies to call out some new types of spam it targets.
Let’s delve into what exactly changed in Google’s spam policies and what these changes mean for the future of SEO.
What’s Changed In The Spam Policies?
Google has introduced two new sections to its spam policies: “expired domain abuse” and “site reputation abuse.”
It also overhauled an existing section previously called “spammy auto-generated content,” now called “scaled content abuse.”
What I appreciate about these updates is that they all come with real-world examples within the spam policies, and it’s not difficult to figure out what situations these changes are stemming from.
All these three topics are pretty juicy, so let’s jump into each in more detail.
Expired Domain Abuse
Google has added “expired domain abuse” as a new type of spam it targets. Some people may know this tactic as domain squatting.
Google defines it as:
Where an expired domain name is purchased and repurposed primarily to manipulate search rankings by hosting content that provides little to no value to users.
Google previously denied that buying expired domains has any advantage. But that is not the case, or the search engine wouldn’t be taking more steps to combat it.
So, how did people manipulate search results by buying expired domains?
One method involves purchasing an expired domain in a related niche with valuable backlinks to speed up the process of building authority. People who do this will redirect pages from the expired domain to the relevant pages on the site for which they are trying to build authority.
Some will buy an expired domain and continue building the site, capitalizing on the authority others have built for it. There isn’t anything inherently wrong with this.
Google seems concerned with penalizing sites that use spammy tactics to build authority, such as generating AI content at scale or selling links or guest posts.
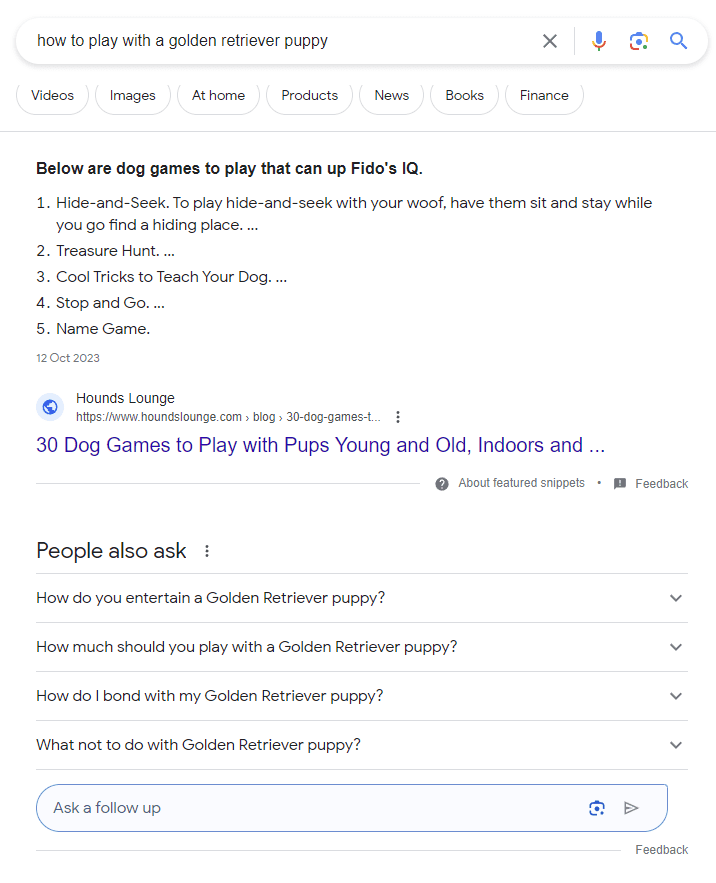
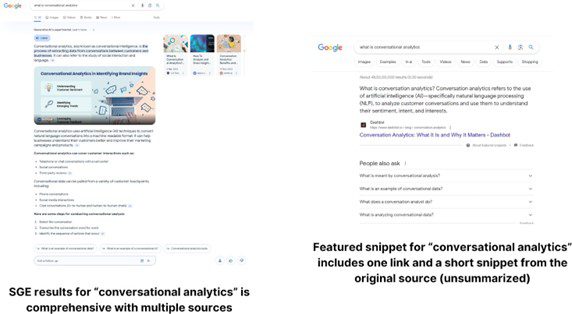
A quick search on Google for [buy expired domains] on Reddit reveals that this is a more common practice than people realize.
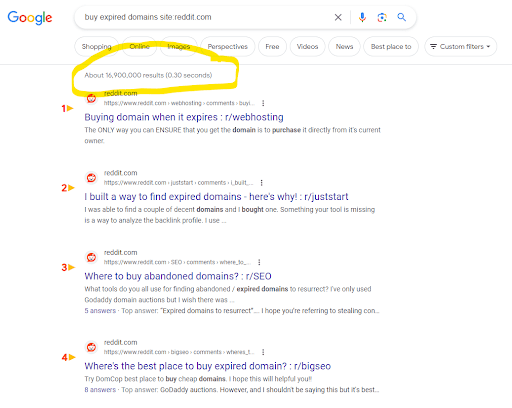 Screenshot from search for [buy expired domains site:reddit.com], Google, March 2024
Screenshot from search for [buy expired domains site:reddit.com], Google, March 2024Google provides a few examples of expired domain abuse:
- Affiliate content on a site previously used by a government agency.
- Commercial medical products being sold on a site previously used by a non-profit medical charity.
- Casino-related content on a former elementary school site.
These are egregious examples, and I couldn’t find the real-world scenario for any of them. If you know of any, feel free to leave them in the comments.
An issue I can recall is The Hairpin case, which had a viral moment earlier this year thanks to Wired’s Confessions of an AI Clickbait Kingpin.
The Hairpin was a once-beloved, women-run indie website. It ceased publication in 2018, and the domain expired in 2023.
It was promptly purchased by a Serbian DJ named Nebojsa Vujinovic, who then transformed the site into an AI-generated content farm.
Some original content remains with new formatting, but the author names were replaced with male names without any online presence.
It’s a pretty obvious example of expired domain abuse, and Vujinovic even admitted to Wired that he bought the domain for its authority and reputation.
Thankfully, The Hairpin website was recently de-indexed; may its original content RIP.
![Screenshot from Google for [site:thehairpin.com], March 2024](https://ecommerceedu.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/the-hairpin-deindexed.png)
![Screenshot from Google for [site:thehairpin.com], March 2024](https://ecommerceedu.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/the-hairpin-deindexed.png)
![Screenshot from Google for [site:thehairpin.com], March 2024](https://ecommerceedu.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/the-hairpin-deindexed.png)
Site Reputation Abuse
The other type of spam added to Google’s spam policies is site reputation abuse, also sometimes called Parasite SEO or pSEO.
Google defines it as:
When third-party pages are published with little or no first-party oversight or involvement, where the purpose is to manipulate search rankings by taking advantage of the first-party site’s ranking signals.
Of particular interest, it specifies that this includes:
Sponsored, advertising, partner, or third-party pages that are typically independent of a host site’s main purpose or produced without close oversight or involvement of the host site, and provide little to no value to users.
Google goes on to provide some examples. My personal favorite:
A sports site hosting a page written by a third-party about “workout supplements reviews,” where the sports site’s editorial staff had little to no involvement in the content and the main purpose of hosting the page is to manipulate search rankings.
This is likely in response to Sports Illustrated’s AI scandal that went viral in November 2023. Futurism discovered that there were AI-generated product reviews written in Sports Illustrated with fake authors.
It blew the whistle on these nonsensical reviews that said things like, “Volleyball can be a little tricky to get into, especially without an actual ball to practice with.”
The Arena Group (the company that owned the publishing rights to Sports Illustrated at the time) issued a statement that the articles were created by a partner called AdVon, which runs ecommerce product reviews across a number of its web properties, and that it was unaware that AdVon was using AI-generated content.
Google’s spam policy update essentially flags this as a site reputation abuse. The Arena Group and other large publishers who engage in such practice need to end these partnerships or de-index these pages, or they’ll be penalized.
Plus, the lack of oversight or involvement in the partner content strategy is irrelevant if it’s on your domain.
Another example Google gave that sparked discussion in the SEO community is:
A news site hosting coupons provided by a third-party with little to no oversight or involvement from the hosting site, and where the main purpose is to manipulate search rankings.
Gannett’s USA Today has a surprisingly robust coupon network hosted on a subdomain. I suspect it isn’t the only one, but it may be the biggest.
It’ll be interesting to see what it does in response to being called out. Clearly, Google is trying to get news publishers to stay in their lane because it’s hard to argue that coupons provide no value to users.


Google’s site reputation abuse penalties aren’t going into effect until May 2024, so publishers have time to get their ducks in a row and adjust their strategies. They have to decide whether to de-index pages that could violate this policy, end partnerships, or (I suppose) take their chances and forge ahead.
In the spam policies, Google links to a page explaining how to de-index content.
Scaled Content Abuse
The last area of change in Google’s spam policies is rebranding “spammy automatically generated content” as “scaled content abuse” and broadening its definition with examples.
In a previous version of the spam policies in January 2024, Google defines “spammy automatically generated content” as:
Content that’s been generated programmatically without producing anything original or adding sufficient value; instead it’s been generated for the purpose of manipulating search rankings and not helping users.
Today, Google has rebranded this to “scaled content abuse” and defines it as:
When many pages are generated for the primary purpose of manipulating search rankings and not helping users. This abusive practice is typically focused on creating large amounts of unoriginal content that provides little to no value to users, no matter how it’s created.
The past definition specifically targets programmatic content, whereas this new definition says it doesn’t matter how the content is generated.
What matters is that the content is unoriginal and does not add value, regardless of how it’s created – programmatically, AI-generated, or low-quality human-created.
The old version also contains six examples, all of which start with “text,” indicating that they are targeting words on the page. In this new version, formats are not mentioned at all.
The implication is that scaled content abuse could also involve a broader array of formats like images or videos.
In the scaled content abuse definition, Google provides these five examples:
- Using generative AI tools or other similar tools to generate many pages without adding value for users.
- Scraping feeds, search results, or other content to generate many pages (including through automated transformations like synonymizing, translating, or other obfuscation techniques), where little value is provided to users.
- Stitching or combining content from different webpages without adding value.
- Creating multiple sites with the intent of hiding the scaled nature of the content.
- Creating many pages where the content makes little or no sense to a reader but contains search keywords.
An example: In August 2023, Time exposed an urgent care clinic called Nao Medical, which was found flooding the internet with nonsensical AI-generated posts about topics like what happens when unicorns consume ketamine or a medical condition called “Derek Jeter Herpes Tree.”
These pages are no longer live and have seemingly been removed from the Internet Archive.
Conclusion
Of everything that’s in this March 2024 core update, I am most curious about what falls under scaled content abuse.
Plenty of large brands are utilizing programmatic templates to build out content on their higher-value transactional pages. Take any ticketing marketplace website, for example.
The below page for Colorado Rapids tickets has all of the appropriate content for purchasing tickets.
But further down the page, there is lower-quality programmatic content, presumably to try to rank for more related keywords.
So, would a page like this get dinged even though it’s a transactional page, and this programmatic content isn’t the focus?


Obviously, several content publishers have scaled their content strategy utilizing a large staff of freelance writers who crank out daily articles to rank in Google News and Top Stories.
The quality of this content varies considerably, but most of it gets pretty repetitive. Will that get penalized? It seems unlikely.
Time will tell what happens, but I am definitely ready to see some shake-ups.
More resources:
Featured Image: YoloStock/Shutterstock