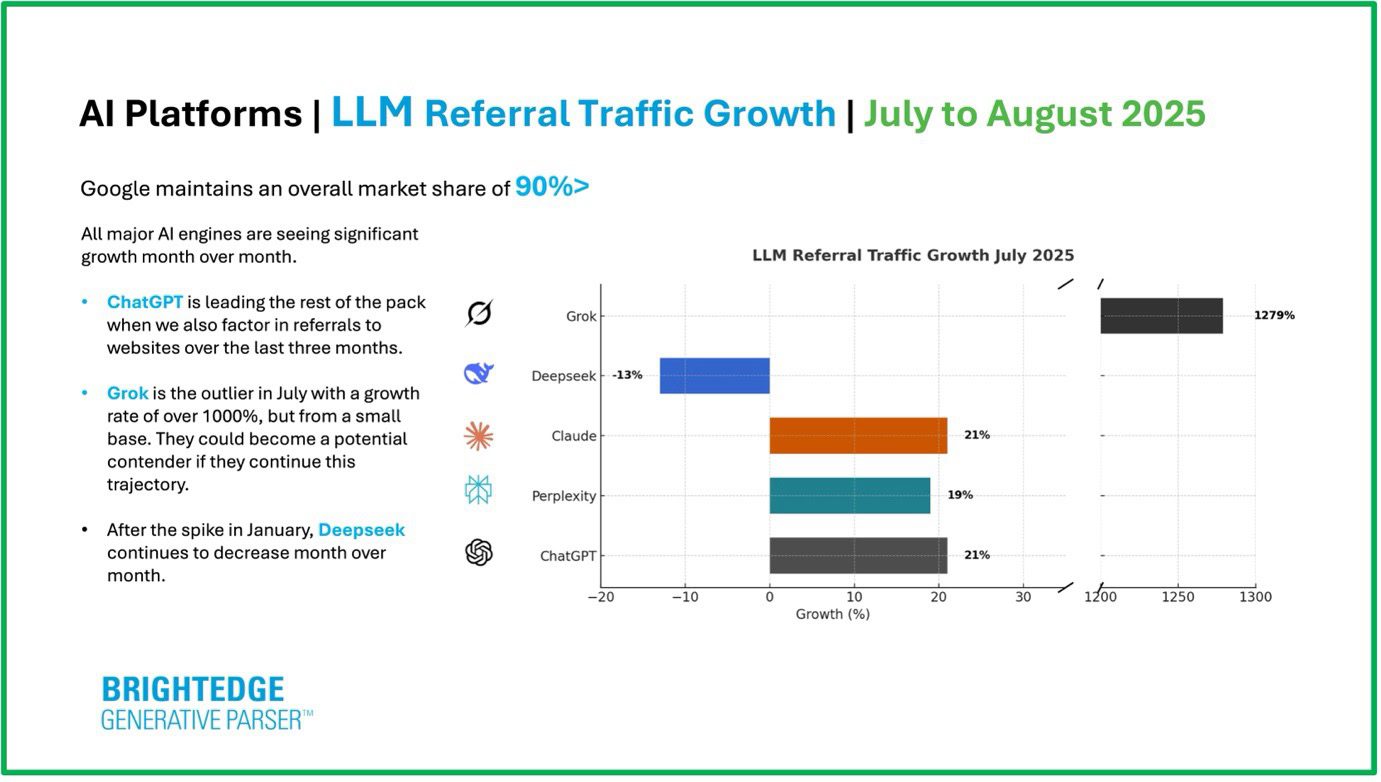
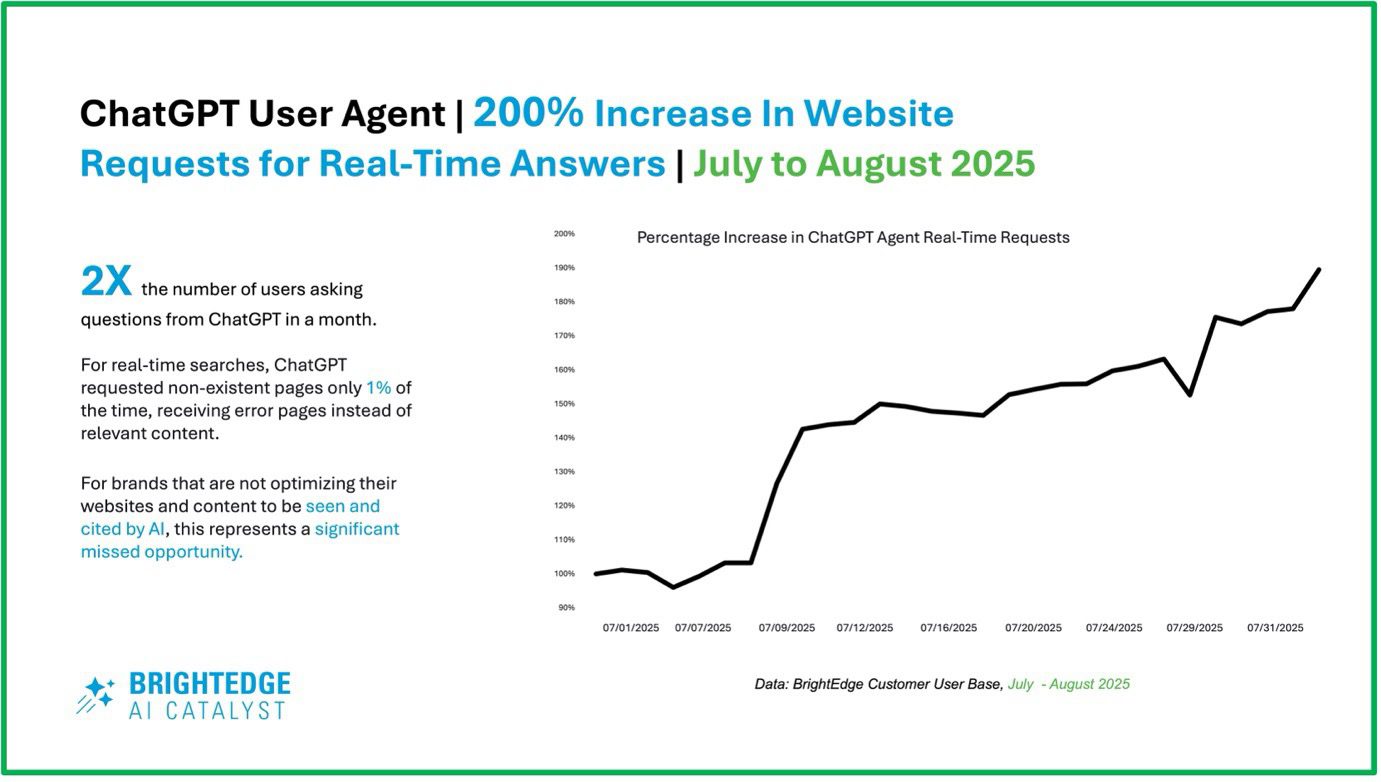
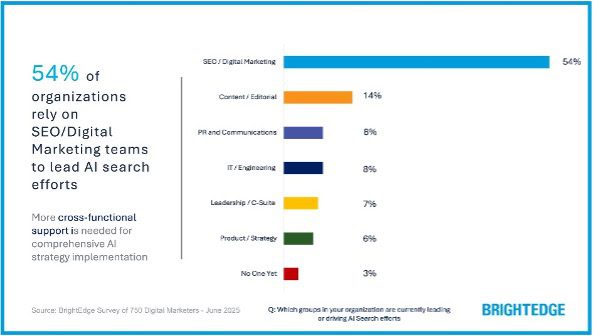
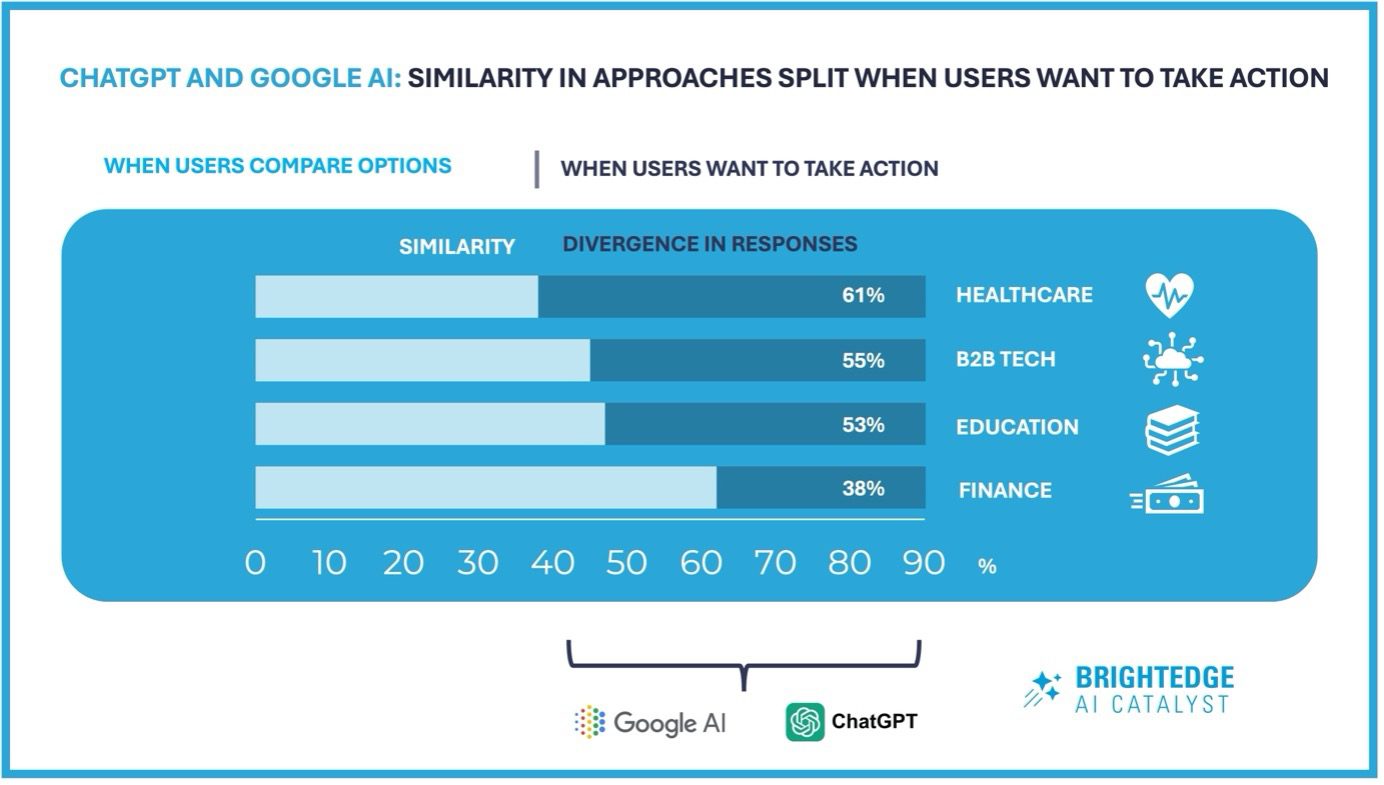
We’re more than halfway through 2025, and SEO has already changed names many times to take into account the new mission of optimizing for the rise of large language models (LLMs): We’ve seen GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) floating around, AEO (Answer Engine Optimization), and even LEO (LLM Engine Optimization) has made an apparition in industry conversations and job titles.
However, while we are all busy finding new nomenclatures to factor in the machine part of the discovery journey, there is someone else in the equation that we risk forgetting about: the end beneficiary of our efforts, the user.
Why Do You Need Behavioral Data In Search?
Behavioral data is vital to understand what leads a user to a search journey, where they carry it out, and what potential points of friction might be blocking a conversion action, so that we can better cater to their needs.
And if we learned anything from the documents leaked from the Google trial, it is that users’ signals might actually be one of the many factors that influence rankings, something that was never fully confirmed by the company’s spokespeople, but that’s also been uncovered by Mark Wiliams Cook in his analysis of Google exploits and patents.
With search becoming more and more personalized, and data about users becoming less transparent now that simple search queries are expanding into full funnel conversations on LLMs, it’s important to remember that – while individual needs and experiences might be harder to isolate and cater for – general patterns of behavior tend to stick across the same population, and we can use some rules of thumb to get the basics right.
Humans often operate on a few basic principles aimed at preserving energy and resources, even in search:
- Minimizing effort: following the path of least resistance.
- Minimizing harm: avoiding threats.
- Maximizing gain: seeking opportunities that present the highest benefit or rewards.
So while Google and other search channels might change the way we think about our daily job, the secret weapon we can use to future-proof our brands’ organic presence is to isolate some data about behavior, as it is, generally, much more predictable than algorithm changes.
What Behavioral Data Do You Need To Improve Search Journeys?
I would narrow it down to data that cover three main areas: discovery channel indicators, built-in mental shortcuts, and underlying users’ needs.
1. Discovery Channel Indicators
The days of starting a search on Google are long gone.
According to the Messy Middle research by Google, the exponential increase in information and new channels available has determined a shift from linear search behaviors to a loop of exploration and evaluation guiding our purchase decisions.
And since users now have an overwhelming amount of channels, they can consult in order to research a product or a brand. It’s also harder to cut through the noise, so by knowing more about them, we can make sure our strategy is laser-focused across content and format alike.
Discovery channel indicators give us information about:
- How users are finding us beyond traditional search channels.
- The demographic that we reach on some particular channels.
- What drives their search, and what they are mostly engaging with.
- The content and format that are best suited to capture and retain their attention in each one.
For example, we know that TikTok tends to be consulted for inspiration and to validate experiences through user-generated content (UGC), and that Gen Z and Millennials on social apps are increasingly skeptical of traditional ads (with skipping rates of 99%, according to a report by Bulbshare). What they favor instead is authentic voices, so they will seek out first-hand experiences on online communities like Reddit.
Knowing the different channels that users reach us through can inform organic and paid search strategy, while also giving us some data on audience demographics, helping us capture users that would otherwise be elusive.
So, make sure your channel data is mapped to reflect these new discovery channels at hand, especially if you are relying on custom analytics. Not only will this ensure that you are rightfully attributed what you are owed for organic, but it will also be an indication of untapped potential you can lean into, as searches become less and less trackable.
This data should be easily available to you via the referral and source fields in your analytics platform of choice, and you can also integrate a “How did you hear about us” survey for users who complete a transaction.
And don’t forget about language models: With the recent rise in queries that start a search and complete an action directly on LLMs, it’s even harder to track all search journeys. This replaces our mission to be relevant for one specific query at a time, to be visible for every intent we can cover.
This is even more important when we realize that everything contributes to the transactional power of a query, irrespective of how the search intent is traditionally labelled, since someone might decide to evaluate our offers and then drop out due to the lack of sufficient information about the brand.
2. Built-In Mental Shortcuts
The human brain is an incredible organ that allows us to perform several tasks efficiently every day, but its cognitive resources are not infinite.
This means that when we are carrying out a search, probably one of many of the day, while we are also engaged in other tasks, we can’t allocate all of our energy into finding the most perfect result among the infinite possibilities available. That’s why our attentional and decisional processes are often modulated by built-in mental shortcuts like cognitive biases and heuristics.
These terms are sometimes used interchangeably to refer to imperfect, yet efficient decisions, but there is a difference between the two.
Cognitive Biases
Cognitive biases are systematic, mostly unconscious errors in thinking that affect the way we perceive the world around us and form judgments. They can distort the objective reality of an experience, and the way we are persuaded into an action.
One common example of this is the serial position effect, which is made up of two biases: When we see an array of items in a list, we tend to remember best the ones we see first (primacy bias) and last (recency bias). And since cognitive load is a real threat to attention, especially now that we live in the age of 24/7 stimuli, primacy and recency biases are the reason why it’s recommended to lead with the core message, product, or item if there are a lot of options or content on the page.
Primacy and recency not only affect recall in a list, but also determine the elements that we use as a reference to compare all of the alternative options against. This is another effect called anchoring bias, and it is leveraged in UX design to assign a baseline value to the first item we see, so that anything we compare against it can either be perceived as a better or worse deal, depending on the goal of the merchant.
Among many others, some of the most common biases are:
- Distance and size effects: As numbers increase in magnitude, it becomes harder for humans to make accurate judgments, reason why some tactics recommend using bigger digits in savings rather than fractions of the same value.
- Negativity bias: We tend to remember and assign more emotional value to negative experiences rather than positive ones, which is why removing friction at any stage is so important to prevent abandonment.
- Confirmation bias: We tend to seek out and prefer information that confirms our existing beliefs, and this is not only how LLMs operate to provide answers to a query, but it can be a window into the information gaps we might need to cover.
Heuristics
Heuristics, on the other hand, are rules of thumb that we employ as shortcuts at any stage of decision-making, and help us reach a good outcome without going through the hassle of analyzing every potential ramification of a choice.
A known heuristic is the familiarity heuristic, which is when we choose a brand or a product that we already know, because it cuts down on every other intermediate evaluation we would otherwise have to make with an unknown alternative.
Loss aversion is another common heuristic, showing that on average we are more likely to choose the least risky option among two with similar returns, even if this means we might miss out on a discount or a short-term benefit. An example of loss aversion is when we choose to protect our travels for an added fee, or prefer products that we can return.
There are more than 150 biases and heuristics, so this is not an exhaustive list – but in general, getting familiar with which ones are most common among our users helps us smooth out the journey for them.
Isolating Biases And Heuristics In Search
Below, you can see how some queries can already reveal subtle biases that might be driving the search task.
| Bias/Heuristic |
Sample Queries |
| Confirmation Bias |
• Is [brand/products] the best for this [use case]?
• Is this [brand/product/service] better than [alternative brand/product service]?
• Why is [this service] more efficient than [alternative service]? |
| Familiarity Heuristic |
• Is [brand] based in [country]?
• [Brand]’s HQs
• Where do I find [product] in [country]? |
| Loss Aversion |
• Is [brand] legit?
• [brand] returns
• Free [service] |
| Social Proof |
• Most popular [product/brand]
• Best [product/brand] |
You can use Regex to isolate some of these patterns and modifiers directly in Google Search Console, or you can explore other query tools like AlsoAsked.
If you’re working with large datasets, I recommend using a custom LLM or creating your own model for classifications and clustering based on these rules, so it becomes easier to spot a trend in the queries and figure out priorities.
These observations will also give you a window into the next big area.
3. Underlying Users’ Needs
While biases and heuristics can manifest a temporary need in a specific task, one of the most beneficial aspects that behavioral data can give us is the need that drives the starting query and guides all of the subsequent actions.
Underlying needs don’t only become apparent from clusters of queries, but from the channels used in the discovery and evaluation loop, too.
For example, if we see high prominence of loss aversion based on our queries, paired with low conversion rates and high traffic on UGC videos for our product or brand, we can infer that:
- Users need reassurance on their investment.
- There is not enough information to cover this need on our website alone.
Trust is a big decision-mover, and one of the most underrated needs that brands often fail to fulfill as they take their legitimacy for granted.
However, sometimes we need to take a step back and put ourselves in the users’ shoes in order to see everything with fresh eyes from their perspective.
By mapping biases and heuristics to specific users’ needs, we can plan for cross-functional initiatives that span beyond pure SEO and are beneficial for the entire journey from search to conversion and retention.
How Do You Obtain Behavioral Data For Actionable Insights?
In SEO, we are used to dealing with a lot of quantitative data to figure out what’s happening on our channel. However, there is much more we can uncover via qualitative measures that can help us identify the reason something might be happening.
Quantitative data is anything that can be expressed in numbers: This can be time on page, sessions, abandonment rate, average order value, and so on.
Tools that can help us extract quantitative behavioral data are:
- Google Search Console & Google Merchant Center: Great for high-level data like click-through rates (CTRs), which can flag mismatches between the user intent and the page or campaign served, as well as cannibalization instances and incorrect or missing localization.
- Google Analytics, or any custom analytics platform your brand relies on: These give us information on engagement metrics, and can pinpoint issues in the natural flow of the journey, as well as point of abandonment. My suggestion is to set up custom events tailored to your specific goals, in addition to the default engagement metrics, like sign-up form clicks or add to cart.
- Heatmaps and eye-tracking data: Both of these can give us valuable insights into visual hierarchy and attention patterns on the website. Heatmapping tools like Microsoft Clarity can show us clicks, mouse scrolls, and position data, uncovering not only areas that might not be getting enough attention, but also elements that don’t actually work. Eye-tracking data (fixation duration and count, saccades, and scan-paths) integrate that information by showing what elements are capturing visual attention, as well as which ones are often not being seen at all.
Qualitative data, on the other hand, cannot be expressed in numbers as it usually relies on observations. Examples include interviews, heuristic assessments, and live session recordings. This type of research is generally more open to interpretation than its quantitative counterpart, but it’s vital to make sure we have the full picture of the user journey.
Qualitative data for search can be extracted from:
- Surveys and CX logs: These can uncover common frustrations and points of friction for returning users and customers, which can guide better messaging and new page opportunities.
- Scrapes of Reddit, Trustpilot, and online communities conversations: These give us a similar output as surveys, but expand the analysis of blockers to conversion to users that we haven’t acquired yet.
- Live user testing: The least scalable but sometimes most rewarding option, as it can cut down all the inference on quantitative data, especially when they are combined (for example, live sessions can be combined with eye-tracking and narrated by the user at a later stage via Retrospective Think-Aloud or RTA).
Behavioral Data In The AI Era
In the past year, our industry has been really good at two things: sensationalizing AI as the enemy that will replace us, and highlighting its big failures on the other end. And while it’s undeniable that there are still massive limitations, having access to AI presents unprecedented benefits as well:
- We can use AI to easily tie up big behavioral datasets and uncover actionables that make the difference.
- Even when we don’t have much data, we can train our own synthetic dataset based on a sample of ours or a public one, to spot existing patterns and promptly respond to users’ needs.
- We can generate predictions that can be used proactively for new initiatives to keep us ahead of the curve.
How Do You Leverage Behavioral Data To Improve Search Journeys?
Start by creating a series of dynamic dashboards with the measures you can obtain for each one of the three areas we talked about (discovery channel indicators, built-in mental shortcuts, and underlying users’ needs). These will allow you to promptly spot behavioral trends and collect actions that can make the journey smoother for the user at every step, since search now spans beyond the clicks on site.
Once you get new insights for each area, prioritize your actions based on expected business impact and effort to implement.
And bear in mind that behavioral insights are often transferable to more than one section of the website or the business, which can maximize returns across several channels.
Lastly, set up regular conversations with your product and UX teams. Even if your job title keeps you in search, business success is often channel-agnostic. This means that we shouldn’t only treat the symptom (e.g., low traffic to a page), but curate the entire journey, and that’s why we don’t want to work in silos on our little search island.
Your users will thank you. The algorithm will likely follow.
More Resources:
Featured Image: Roman Samborskyi/Shutterstock