Checking In: Where Are We With The Google Lawsuits? via @sejournal, @Kevin_Indig
We’ve been focused on the impact of AI on Search and how to still make gains in this competitive and volatile SEO world.
It’s easy to forget that two big lawsuits are deciding potential remedies against Google soon, which could affect organic traffic and the search landscape.
I know most of you don’t spend your free time reading up on antitrust law – I certainly don’t.
But the truth is, the rulings in these Google cases could impact your website’s traffic – which is a big deal for any business trying to grow online.
On one hand, a weakened Google could open the door for AI chatbots and other new players to shake up the landscape.
On the other, a strengthened Google would solidify its position as the gatekeeper of customer acquisition.
 Image Credit: Lyna ™
Image Credit: Lyna ™Boost your skills with Growth Memo’s weekly expert insights. Subscribe for free!
Context
There are many lawsuits against Google, some of which come with the territory of being one of the biggest companies in the world.
However, two prominent cases stand out because they have the power to transform the company:
1. “Search Monopoly Lawsuit: United States v. Google LLC (2020)”
- The claim: Google unlawfully maintains monopolies in the search and search advertising markets by using exclusive agreements (e.g., with Apple) and paying device manufacturers to make Google the default search engine.
- Demanded remedies: Google should divest Chrome and Android (or remove mandatory Google services from Android), terminate exclusive agreements, add choice screens, and share data with competitors. Important: the judgment would last 10 years from its effective date, with the potential for early termination under certain circumstances.1
- Expected judgment: August 2025.
2. “Digital Advertising Lawsuit: United States v. Google LLC (2023)”
- The claim: Google has unlawfully monopolized key digital advertising technologies and markets, including ad exchanges and publisher ad servers. Google engages in exclusionary practices that stifle competition, such as acquiring competitors, manipulating auctions, and restricting publishers from using rival technology platforms.
- Demanded remedies: Google should sell Google Ad Exchange and Ad Publisher Server, allow advertisers and publishers to pick other services, and make auctions more transparent.
- Expected judgment: Early to mid-2025.
Each case will significantly change Google’s position if the remedies (consequences) come into rule. They already attract other lawsuits.
As I mentioned in my article, the Chegg lawsuit might have been strategically filed to build on top of these two DoJ lawsuits.
Two reasons: Trump and AI.
1. Administration
The Trump administration has cut the already dull teeth of many antitrust government bodies and runs a mafia/kleptocracy, which introduces a significant wildcard into both lawsuits.
- Even though the first Google lawsuit started in Trump’s first term, Google understands that there is a chance the Trump administration will stop the DoJ lawsuit or weaken remedies and will do everything in its power to lobby for the outcome. Google tried to persuade Trump with a one-million-dollar gift from Sundar PichAI and complied with an executive Trump order to remove DEI programs and hiring goals for federal contractors.
- Trump has spoken out against a break-up at an event in Chicago in October: “If you do that, are you going to destroy the company? What you can do without breaking it up is make sure it’s more fair.”2
- Trump appointed Republican Andrew Ferguson as the new chairman of the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), making it more likely to steer the outcome in his favor. However, in March, the DoJ reaffirmed its position on divesting Chrome despite pulling back its ask for Google to divest its investments in AI (e.g., Anthropic).3
2. Competition From AI
AI hasn’t just threatened Google Search but also leveled the playing field.
Many products, from meta AI to ChatGPT & Co to Copilot, can answer questions now and are basically a search engine, which means Google’s monopoly position could be questioned.
- Judge Mehta, who rules in the Search Monopoly case, addressed this point: “AI cannot replace the fundamental building blocks of search, including web crawling, indexing, and ranking.”
- However, he could change his mind based on the rapid growth of many AI chatbots and the fact that so many new ones pop up left and right.
Conclusion: A Small Chance For The Open Web
Google is doing well: Search revenue has grown to almost $200 billion in 2024, up from $175 billion the year before.
Search ads still make up over 50% of Alphabet’s revenue, YouTube is stable, and Cloud offsets the dropping Network revenue.
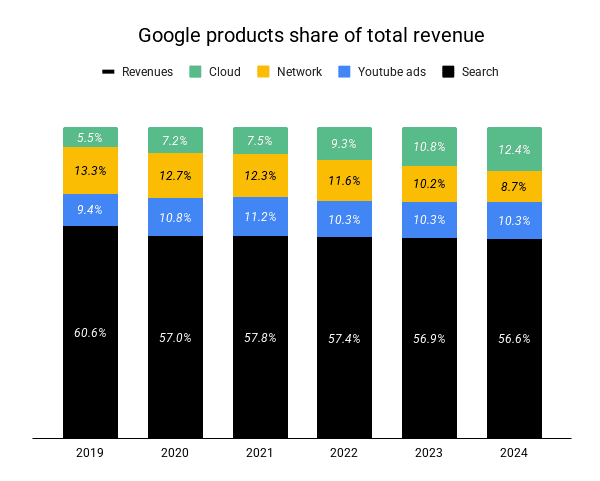


- Is Google doing well because people use it more or because advertisers have no alternative? Probably both: Sparktoro found that Google searches grew by 20% YoY in 2024. At the same time, “42% said Google and search engines are becoming less useful.” Maybe the explanation of the paradox is that more searches result from users not finding what they want.
- Google is still the biggest source of traffic by a big margin, even if AI would mean 20-30% less referral traffic.
The lawsuit matters because if it goes through, it could accelerate or decelerate traffic from Google.
How the search ecosystem would change if the remedies went through as proposed:
- Google will lose a significant data advantage from Chrome and competitors will benefit big time from Google’s data. I reported how Ecosia and QWANT are building their own search index to become independent of Google and Bing. Enforced data sharing would support this process and inspire competitors like DuckDuckGo.
- Google would encounter a big hit in mobile traffic from Apple devices, similar to how it already sees a weakened market share in the EU (see the above article as well). Device manufacturers could pre-install different search engines, adding to the pain.
- Google might make search better to compete harder, benefitting users. But it could also push Google to be even more aggressive about AI and send even less traffic to websites.
I concluded that one scenario is most likely to happen in my last post on the Search Monopoly case Monopoly:
Google must end its exclusivity deals immediately. Apple needs to let users choose a default search engine when setting up their devices. Google could get hefty fines for every year they keep the contract with Apple going.
Realistically, that still seems to be the most likely outcome. But for the web economy, it would be best if the judges in both lawsuits ruled against Google.
1 Source
2 Trump expected to shift course on antitrust, stop Google breakup
3 Trump’s Justice Department still wants to break up Google
Featured Image: Paulo Bobita/Search Engine Journal