Building an MVP: Steps and Benefits
Building an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) is the first and most crucial step of creating a new digital platform. Before wasting your precious time and resources on developing all features and finished designs for your product, you should validate your idea. For that, building an MVP is the right solution for you.
If you’re thinking about building an MVP, we’re all ears and more than happy to help! Book a consultation with us and let’s discuss your goals.
In this article you’ll read about:
What is a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)?
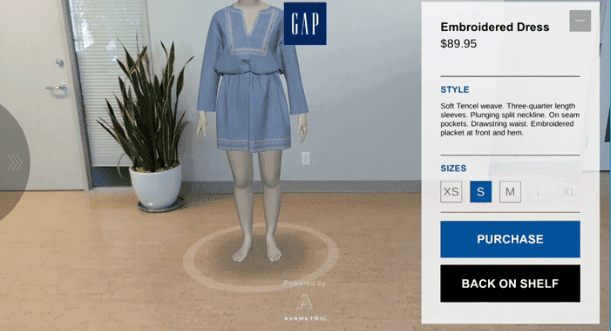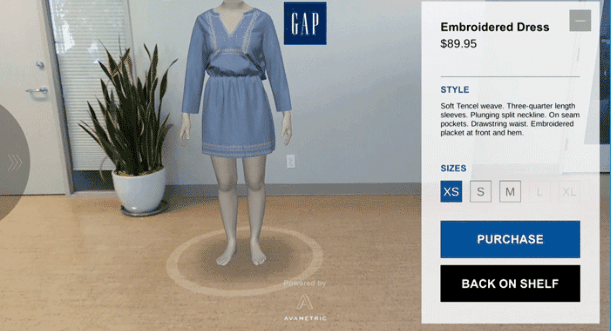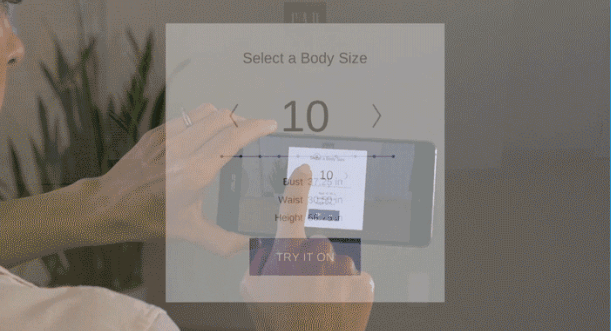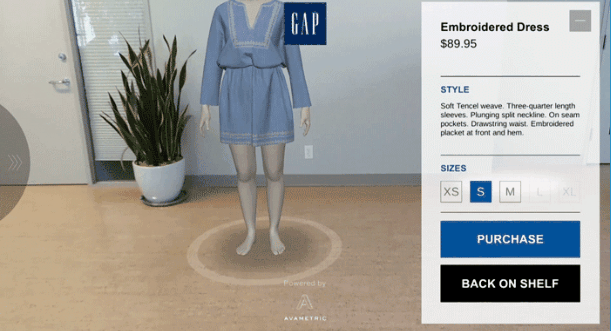
A digital product MVP is a UX/UI design and development method introducing it to the market only with its core features. It has enough functionalities and design solutions to get the attention of its target audience and customers and test the business model’s profitability.
Whether you’re planning to build up a platform from scratch or thinking of creating a new functionality/feature, building an MVP first will be on your side. It’ll help you to see and measure how your users react to it and what they think about your idea.
So the concept is quite straightforward: think of what would be your completely finished digital product as a whole. Then take away everything that wouldn’t be absolutely necessary for it to work or to serve its primary purpose. That will be your MVP.
Values and Benefits of Building MVP
First and foremost, the sole purpose and benefit of building an MVP can be different for a business, its users, or a design teams.
Generally, it’s beneficial when you’re planning to build something rather complex. Because this way you’ll be able to test the first and core version of your product. And with testing, you can launch something validated and valuable for the market without spending a lot of money.
But let’s see the benefits in a bit more detail.
Business value of an MVP
The most important business values and benefits of building an MVP:
- Save time and money
- Validate an idea or value proposition
- Test core features and user needs
- Launch as early as possible
- Attract customers at the earliest stage
You’ll also have the opportunity to test and measure the first version’s performance. Building an MVP will help to see if you need any changes or iterations in its current state – meaning your can already test your value proposition before putting more effort into additional features, designs, and development.
Benefits of an MVP for the users
For your users, an MVP helps to get familiar with the core idea of the whole application, website, or web application. Users tend to enjoy products that are not too complex or overwhelming with too many features and options to choose from.
So there is a great chance that building an MVP first will also serve the user’s needs better. They can get familiar with it more easily and most likely will keep using it with more features and designs added later.
Benefits of an MVP for design teams
As for UX/UI designers and UX researchers, building an MVP is about creating a bridge between business goals and the user’s needs at the earliest possible opportunity.
They need to figure out the most essential features for the users. And how to offer solutions for these needs with the MVP. Meanwhile, design teams also need to keep in mind the product’s primary purpose and business objectives.
A business either works with its internal product team or can join forces with an experienced UX agency like UX studio. We support all sizes of companies and businesses building an MVP and have impactful and successful platforms.
When we work with our clients, our main goal is to build the strongest MVP possible. Our designers and researchers work closely together with stakeholders and developers to make sure that every party’s – including the user’s – needs are met and the early launch is successful.
Our team has all the experience and knowledge you need to build your MVP. And we always take the extra mile to make your product as successful as possible. Want to know how we collaborate with businesses? Book a free consultation with us and let’s get to know each other!
Until then, let’s go through the most important know-hows and best practices for designing an MVP.
What to Do Before Building an MVP
For an early-stage product definition and MVP, the very first step should always be to create a strategic UX/UI design roadmap. It helps you think through the project plan and see it as a whole in its timeline. A roadmap includes what tasks you and your team have and when those tasks are due.
When creating a roadmap, there are four main phases you need to keep in mind for an MVP plan:
- Preparation and Discovery – to gather valuable data and insights before making design decisions
- Ideation and User Journey – to map out your user flow and platform architecture.
- Prototyping and Testing – to validate your ideas and solutions
- Launch – to release your product to the market
Steps of Building an MVP
Sure, it seems like a waste of time when you could just go and create your product in one sitting, but trust us, you won’t regret building an MVP.
Any product, digital or otherwise, that is not subjected to extensive ideation, research, prototyping, testing, and validation is almost guaranteed to experience later problems that could have been prevented.
With product ideation, research, prototyping, testing, and validation, you can avoid issues that could come up later. Which are, to be honest, usually complicated and expensive to fix.
So let’s see how you can successfully build an MVP:
1. Do market and competitor research
When you’re building an MVP or any other digital platform, looking around your target market will help to position your service.
- Analyze your industry,
- Study the target market,
- Check your competitors, and
- Find a competitive gap.
All-in-all see what and how the market does, how penetrated it is, and what problems your product could solve.
Ultimately, you need to offer a unique solution to your future customers. And, of course, stand out from your competitors with it.
2. Create a value proposition
A value proposition reflects the value your services or platform can deliver. Creating one is pretty tricky. It needs to be as simple as possible yet expressive. It has to tell your customers why they should try it, buy it, and commit to it. It’s your unique offer to your audience.
When you work and ideate on your value proposition, you should focus on three main areas:
- What does it do?
- Why would it be useful for its users?
- What makes it unique?
Core features should be aligned with your value proposition – but not only that. Users should instantly understand what they will get and how your product will serve their goals and needs. Even before they start using any of its features.
3. Know your users and their needs
Understanding your users and their needs is crucial in 2022. They’ll be grateful and loyal to your brand if you can meet their expectations. And loyal customers who stick with you are pretty profitable in the long term.
But what’s the best way to know more about them? Of course, via UX research. Talking with them, listening to them, and getting information about their opinions, expectations, and experiences. That’s how you’ll get from assumptions to validated data.
The most important steps for this in UX research are:
- Create an assumptive persona(s) that describes your ideal target users, their most important attributes, and motivations
- Find people who fit your set criteria list
- Create a script that includes the questions you’d like to ask
- Have in-depth interviews with them for qualitative data
- Send out surveys to get quantitative data
- Analyze your insights to validate your assumptive persona.
This step-by-step process will help you validate your value proposition, develop better features, and design solutions for your future customers.
Good products are best built with data-driven approaches that back up your hypotheses.
At UX studio, we always make sure not to skip this part of any collaboration or product design development process, as this is a crucial part of a good and well-functioning platform.
Drop us a line if you would like us to help you understand your users and audience better!
4. Create a User Journey for your MVP
Before jumping into designing screens one by one, make sure to create a user journey first.
A user journey will be the path your users will go through using your digital platform. It starts when they open your platform and ends at the point when they reach their goal or finish their task.
Your users’ path includes several small steps toward their ultimate goal. And a user journey can help you map out these steps. Each step gets some kind of emotion out of the users — for example, excitement to start something or confusion when not understanding a function.
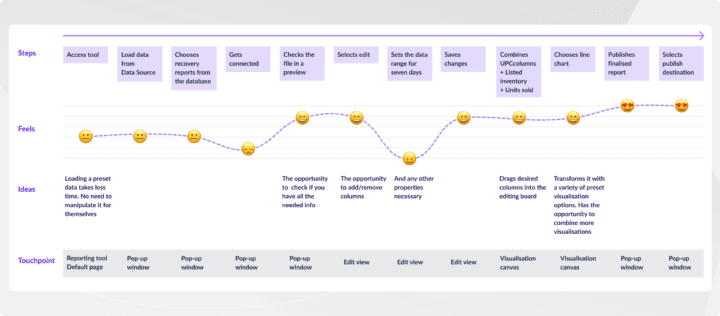


When creating a user journey, you need to make sure that it reflects your user’s needs. Offers a solution that will ease their pain points. In an ideal user journey, all steps and functions should be intuitive and easy to understand.
5. Prioritize features
Features are tools that get users to reach their goals. Every feature belongs to a bigger functionality. Map out what functionalities and features your audience will need. Knowing your value proposition, user pain points, and user journey can help you with that.
But what are functionalities and features? Imagine that you’re on an e-commerce website. You’ll need to go through a couple of steps to buy a product. For example, reviewing products and filtering based on your preferences. This is a functionality. In this functionality features will help you to go through and ease the review and selection process.
You can categorize features into these main groups:
- High priority,
- Medium priority, and
- Low priority
You should focus on the high-priority category when building an MVP. With this in mind, you will be able to deliver only must-have features for your early launch.
6. Prototype, test, repeat
Before deciding on final designs, you can test your ideas with a clickable product version. This way, you’ll quickly get early feedback from actual potential users. During these testing phases, you’ll get actionable insight on what to improve, how to change some solutions, or what to keep.
At UX studio, we always encourage an agile way of thinking and working. With an agile design approach, you break down your process into more digestible design cycles. In each cycle, you focus on 2-3 features and functions. This process will allow you to deliver and develop faster.
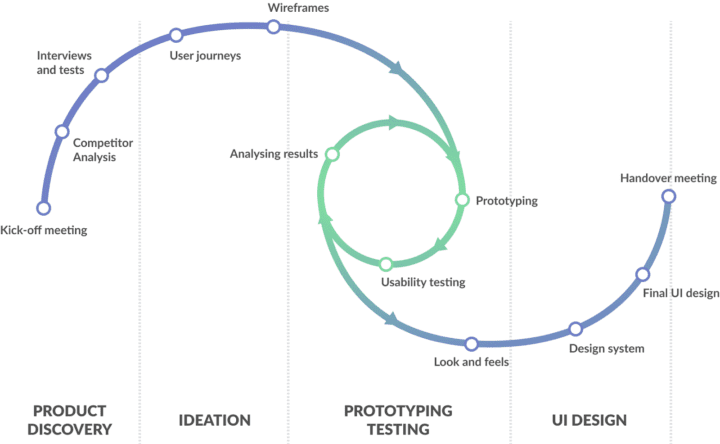


The main advantage of any agile method is constant iteration. With iterations, you can test the changed version again. Repeating these steps will guarantee that you will make data-driven design decisions.
7. Launch your MVP
Congrats! You reached the end of the first part of your MVP project. It’s not a small task to manage building an MVP. Take a moment and enjoy the fruit of your labor.
Based on your research, tests, and interviews, you have a clear idea if your MVP fills the gap for your user’s need. Now you just have to soft launch it to get more feedback and measurements before moving on to additional features.
But soft launch is another story for another article.
Why choose UX studio for building an MVP?
At UX studio, we’re a trusted choice for building MVPs. We’ve worked with many startups and industry leaders worldwide, like Google, Netflix, and Zignaly.
Still not sure? Let’s talk! We’re happy to help you figure things out.







![Ranking Factors: Fact Or Fiction? Let’s Bust Some Myths! [Ebook]](https://ecommerceedu.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/rf-ebook-download-banner-62e8c6126ffe8-sej.jpg)