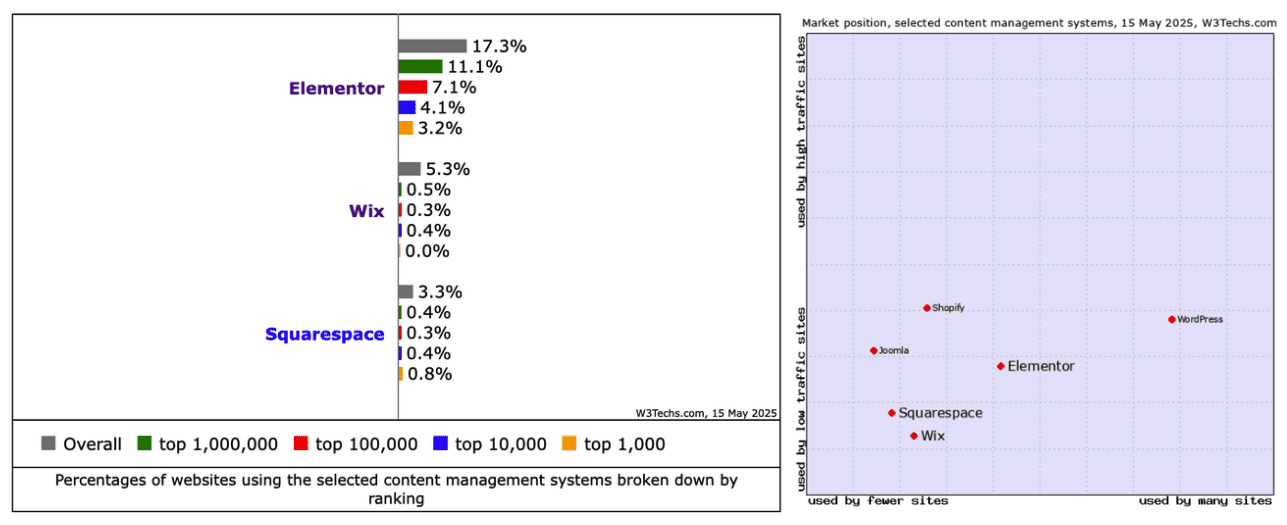
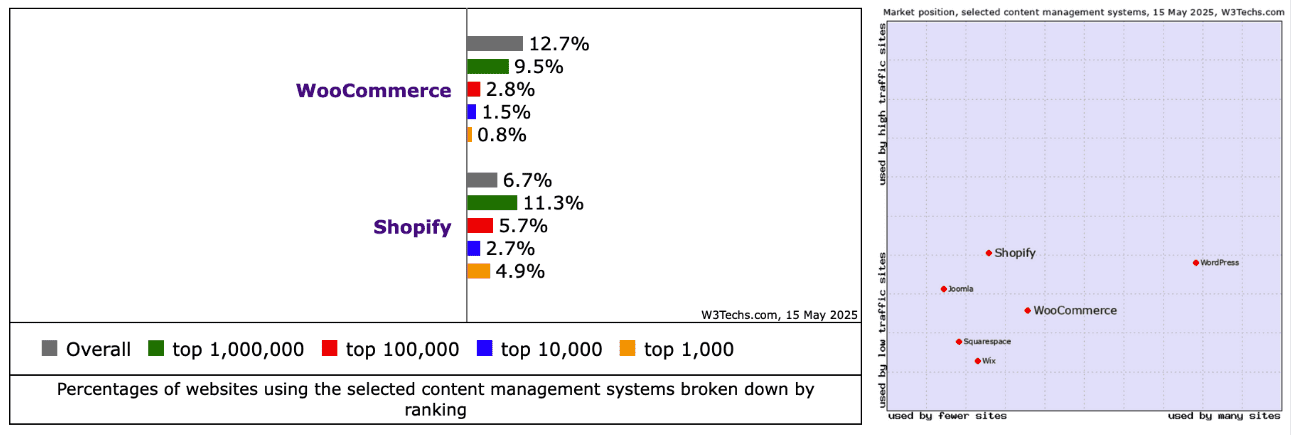
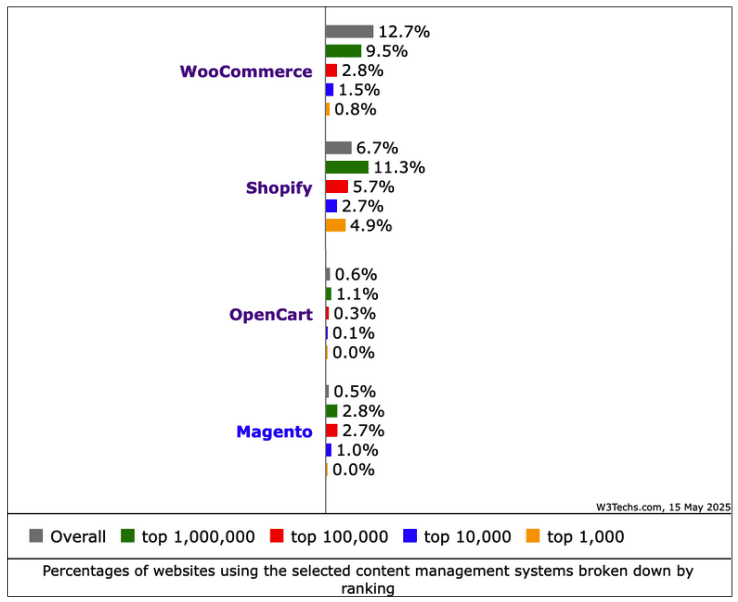
Google Claims AI Search Delivers ‘Quality Clicks’ Despite Traffic Loss via @sejournal, @MattGSouthern
Google executives are trying to reframe the conversation about AI-powered search features as industry data reveals significant website traffic reductions.
During a recent Google Marketing Live press session, executives indicated that while clicks may be down, the visits that do happen are supposedly of higher quality.
The session featured a panel including Jenny Cheng, Vice President and General Manager of Google’s Merchant Shopping organization; Sean Downey, President of Americas & Global Partners at Google; and Nicky Rettke, YouTube Vice President of Product Management.
 Photo: Matt G. Southern / Search Engine Journal
Photo: Matt G. Southern / Search Engine JournalTraffic Quality vs. Quantity Debate
Independent studies have documented that pages with AI overviews in search results receive significantly fewer clicks on organic listings than traditional search results.
When confronted with this issue, a Google executive sidestepped direct traffic concerns by shifting focus to user behavior, stating:
“What we’re seeing is people asking more questions. So they’ll ask a first question, they’ll get information and then go and ask a different question. So they’re refining and getting more information and then they’re making a decision of what website to go to.”
Google pointed to a 10% increase in queries from AI-enhanced search.
Google’s narrative suggests these changes benefit everyone:
“When they get to a decision to click out, it’s a more highly qualified click… What we hope to see over time—and we don’t have any data to share on this—is more time spent on site, which is what we see organically in a much more highly qualified visitor for the website.”
The notable admission that Google has “no data to share” on these quality improvements leaves their claims unverified.
Ads Perform Differently Than Organic Content
While publishers grapple with declining traffic, Google insists that ad performance remains largely unchanged in AI-enhanced search:
“When we run ads on AI overviews versus ads on standard search, we see pretty much the same level of monetization capabilities, which would indicate most factors are the same and they’re producing really the same results for advertisers to date.”
This favorable situation suggests that Google’s ad revenue may stay stable while organic traffic patterns shift, potentially pressuring more publishers to adopt paid strategies to maintain visibility.
New Search Patterns Demand Content Adaptation
Google executives characterized the evolution of search as a response to user preferences for more conversational and multimodal queries, stating:
“What we’re trying to do when we release things like AI overviews or AI mode is we’re trying to give consumers new ways to discover information and get answers to their most important questions… Most humans have unbound curiosity and their context strings or their query strings are much more conversational.”
For SEO professionals, Google recommends accommodating these changes by:
- Creating content that directly answers user questions
- Adding more video content
- Developing detailed FAQs and Q&A sections
AI Mode Creates New Discovery Opportunities?
Google also presented its AI mode as a potential way to increase content discovery through what they termed a “fanning technique.”
They explained:
“When we get into AI mode, it’s a similar functionality because we are also doing the fanning technique where you’re having many more queries go out. If you ask the question, it’s looking at a variety of different versions of that, which is giving more websites a chance to be considered.
We’re researching more sites, pulling in more information from more sites and summarizing. And that’s more linked opportunities for the publishers as well as the sites that are pushing the content to have access to it.”
Whether these theoretical opportunities translate to actual traffic remains to be seen.
Measurement Challenges
For marketers, the situation is complicated because Google’s reporting systems don’t differentiate between clicks from traditional search, AI overviews, and AI mode.
When asked if these different placements are shown separately in ad reporting, the Google representatives confirmed:
“We do not. Within the search term reporting, they’re not specifically broken out by the placement in that way. And that’s because the reporting is tied to what’s actionable for advertisers.”
This lack of transparency makes it impossible for publishers to verify Google’s claims independently.
The Road Ahead
While Google presents an optimistic view of traffic quality from AI-enhanced search, the lack of specific data places marketers in a precarious position.
Publishers and SEO professionals must now create their own measurement methods to assess whether these allegedly “more qualified clicks” truly offer greater value despite their reduced numbers.
For now, content creators are being asked to adjust their strategies to align with Google’s vision while having little choice but to accept the company’s quality claims on faith alone.