A detailed guide to optimizing ecommerce product variations for SEO and conversions
Product variations are more than just an ecommerce feature. They give your customers choices, whether it’s size, color, style, or material, while helping your store stand out in competitive search results. When optimized correctly, product variations do more than display available options. They improve the customer experience by making shopping easier. At the same time, they boost conversions by catering to diverse needs and support your SEO strategy by targeting more keywords.
This guide will explain the best practices for product variations and show you how to optimize them for search engines and customers so your ecommerce site can grow in traffic, rankings, and sales.
What are product variations in ecommerce?
Product variations or product variants are different versions of the same product designed to give customers options. These variations can be based on attributes like size, color, material, style, or capacity. Instead of creating multiple product listings, variations group all options under a single product, making it easier for customers to browse and purchase.
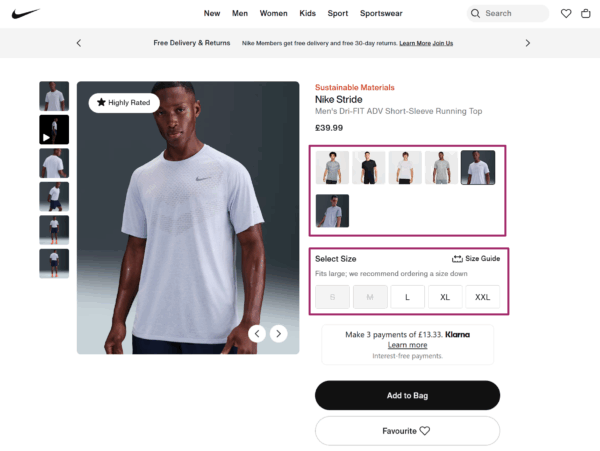
For example, when you search for an iPhone on Amazon, you’ll see options for different colors and storage capacities, all available on a single page. This setup lets customers explore multiple choices without leaving the main product page.
Managing product variations depends on the platform you use:
-
In WooCommerce, product variations are created using attributes such as size or color, and then assigning values to those attributes. Store owners can upload unique images, set prices, and adjust stock for each variation
-
In Shopify, variations are managed under the ‘Variants’ section of a product. You can add options like size, color, or material, and then assign values. Each variant can have its own price, SKU, and image, making it simple to customize how the variations appear in your store
Read more: Shopify Help Center – Adding variants
Why do product variations matter for customers?
Okay, now let’s see why you need product variants and not upload each option as a completely separate product. Think of it this way: customers don’t want to scroll through endless listings just to compare a black t-shirt with a white one or a 64GB phone with a 128GB version. Variations keep everything in one place, making shopping smoother and more intuitive.
Here’s why product variations are so important for your customers:
- Improved shopping experience: Variants reduce unnecessary clicks and allow customers to compare options side by side within a single product page. This saves time and makes decision-making easier
- Higher conversions and lower bounce rates: When customers find their preferred size, color, or feature right away, they are more likely to complete a purchase instead of leaving your store
- Reduced purchase anxiety: Variants ensure customers do not feel limited by stock. Seeing multiple choices available decreases the chance of cart abandonment
- Personalization and satisfaction: Offering customers options empowers them to choose a product that feels tailor-made for them, improving overall satisfaction
- Indirect SEO benefits: A better shopping experience often leads to longer session durations, fewer bounces, and more engagement. These signals may indirectly support stronger SEO performance, as they align with positive user experience metrics
How do product variations support your ecommerce SEO strategies?
Product variations are not just about creating a better shopping experience; they also bring direct ecommerce SEO benefits that can help your store attract more qualified traffic. When optimized correctly, variants can make your product pages richer, more discoverable, and more engaging.
Increase in keyword targeting
Variants allow you to target a wider range of long-tail keywords that reflect real customer search behavior. For example, instead of only competing for ‘men’s wallet,’ you can rank for ‘men’s black leather wallet’ or ‘slim men’s brown wallet.’ These specific keywords usually carry higher purchase intent and face less competition

Richer content for search engines and AI engines
Each variation allows you to add unique attributes, descriptions, and specifications. This creates a more detailed and content-rich product page that search engines and AI-driven engines (like ChatGPT or Google’s AI Overviews) value when surfacing answers and shaping brand perception.
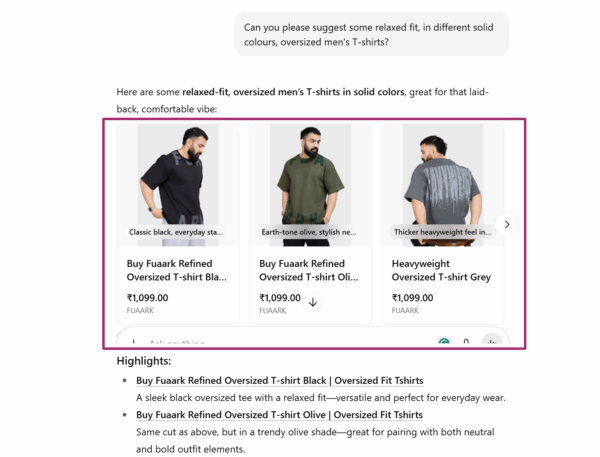


Improved user engagement and longer sessions
A well-structured page that clearly displays variations keeps users from bouncing to competitor sites when they don’t immediately find their preferred option. Instead, they spend more time exploring, comparing, and interacting with your store, which indirectly supports SEO through stronger engagement signals.
Better structured data for enhanced search results
When product variants are properly marked up with structured data, search engines can display rich snippets that include price ranges, availability, color options, and reviews. This not only makes your listings stand out but also boosts click-through rates (CTRs) from search results.
Yoast SEO’s Structure data feature describes your product content as a single interconnected schema graph that search engines can easily understand. This helps them interpret your product variations more accurately and increases your chances of getting rich results, from product details to FAQs.
In short, optimized product variants make your product pages more keyword-diverse, content-rich, and engaging while also improving how your store is presented in search results and generative AI chat replies.
Blueprint for optimizing your product variations
Here’s the part you’ve been waiting for: how to optimize your product variations for SEO, conversions, and user experience. In this section, we’ll cover the right technical implementation, smart SEO tactics, and the common mistakes you’ll want to avoid.
Technical implementation of product variations
Getting the technical setup right is the foundation for optimizing your product variations for both ecommerce SEO and user experience. Poor implementation can lead to crawl inefficiencies, duplicate content, and a confusing buyer journey.
Here’s how to approach it effectively:
Handling variations in URLs
One of the biggest decisions you’ll make is how to structure URLs for your product variations:
- Parameters (e.g.,
?color=red&size=12): Good for filtering and faceted navigation, but they can create crawl bloat if not managed properly. Always define URL parameters in Google Search Console and use canonical tags to consolidate signals - Separate pages for each variation (e.g.,
/red-dress-size-12): This can be useful when specific variations have significant search demand (like ‘iPhone 15 Pro Max 512GB Blue’). However, it requires careful duplication management and unique, optimized content for each page - Single product page with dropdowns or swatches: The most common approach for ecommerce stores, as it consolidates SEO signals into one canonical page while providing users with all available variations in one place
Takeaway: Use a hybrid approach. Keep a single master product page, but only create dedicated variation URLs for high-demand search queries (with unique descriptions, images, and structured data).
Note: only create dedicated variation URLs if you can add unique value (content/images), otherwise, it risks duplication
Internal linking best practices
Internal linking is crucial in helping search engines understand the relationships between your main product page and its variations.
- Always link back to the parent product page from any variation-specific pages
- Ensure your category pages link to the main product page, not every single variation (to prevent diluting crawl equity)
- Use descriptive anchor text when linking internally, e.g., ‘men’s black leather wallet’ rather than just ‘wallet’
The Internal linking suggestions feature in Yoast SEO Premium is a real time-saver. As you write, it recommends relevant pages and posts so you can easily connect variations, parent products, and related content. This not only strengthens your site structure and boosts SEO but also ensures visitors enjoy a seamless browsing experience.
A smarter analysis in Yoast SEO Premium
Yoast SEO Premium has a smart content analysis that helps you take your content to the next level!
Takeaway: Build a clean hierarchy where category pages → main product pages → variations, ensuring both users and crawlers can navigate easily.
Managing faceted navigation and filters
Filters (like size, color, brand, or price) enhance user experience but can create SEO challenges if every filter combination generates a new crawlable URL.
- Use
noindexfor low-value filter pages (like ‘price under $20’ if it doesn’t add SEO value) - Block irrelevant filter parameters in robots.txt to prevent crawl bloat
- For valuable filters (e.g., ‘red running shoes’), allow them to be indexed and optimize the content
Takeaway: Conduct a filter audit in Google Search Console. Identify which filtered URLs actually drive impressions and clicks, and only allow those to be indexable.
Media content optimization for ecommerce product variations
When it comes to product variations, visuals and supporting media play a critical role in both SEO and conversions. Shoppers often make purchase decisions based on how well they can visualize a specific variation. In fact, 75% of online shoppers rely on product images when making purchasing decisions.
Also read: Image SEO: Optimizing images for search engines
Here’s how you can optimize media content for ecommerce product variations:
Use unique images for each variation
Avoid using the same generic image across all variations. Display each color, size, material, or feature with its own high-quality image set. For example, if you sell a t-shirt in six colors, show each color separately to help customers make confident choices.
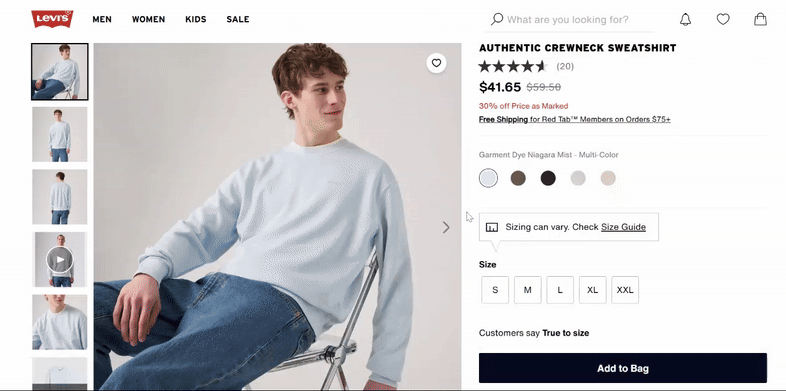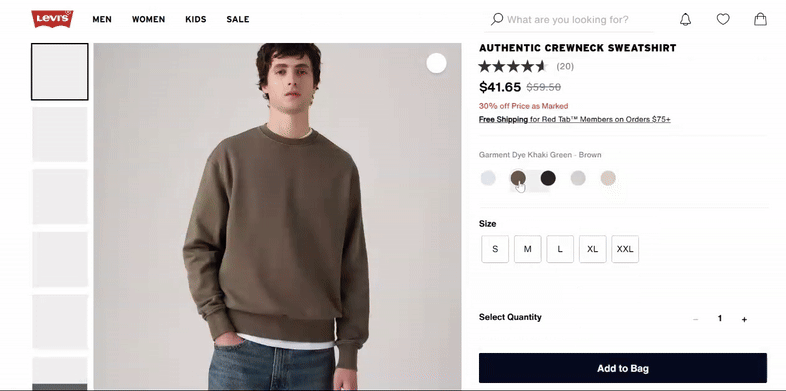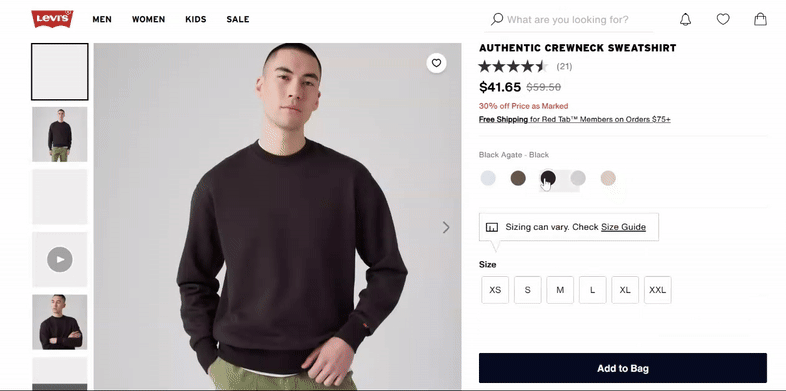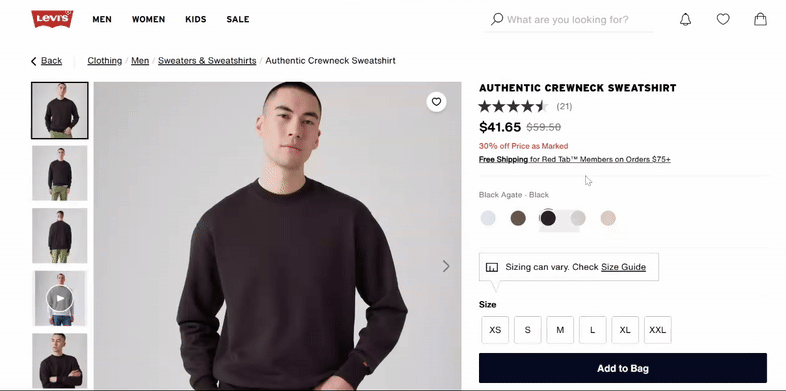


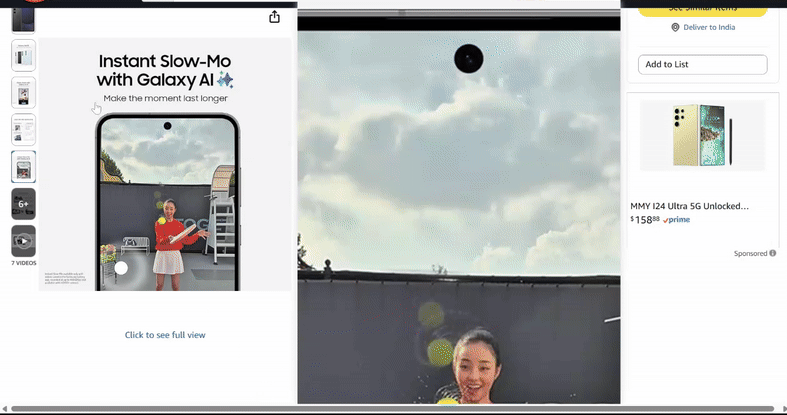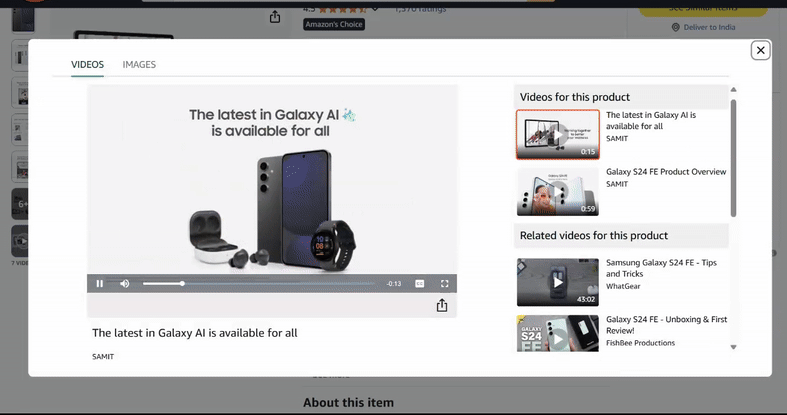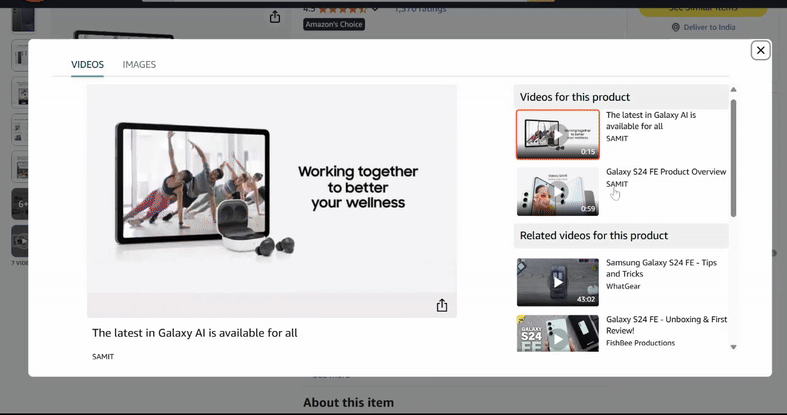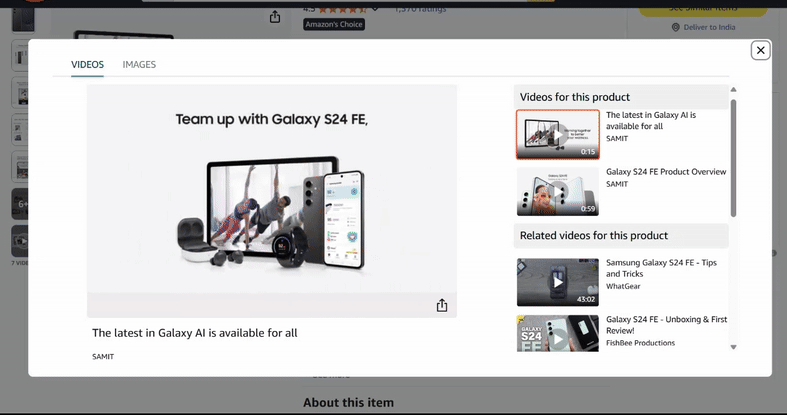
Leverage 360° views and videos
Showcase variations with interactive media like 360° spins or short product videos. For example, a ‘black leather recliner’ video demonstrates texture and function more effectively than a static image, leading to higher engagement and conversions.


Optimize alt text, file names, and metadata
Every image should have descriptive, keyword-rich alt text that specifies the variation. Instead of writing ‘red shoe,’ use ‘women’s red running shoe size 8.’ File names (e.g., womens-red-running-shoe-size8.webp) and captions should also reinforce the variation for better indexing.
Implement structured data for media
Use the Product schema to explicitly define images and videos for each variation. Including structured data ensures that Google and AI-driven engines like ChatGPT can clearly interpret your variation visuals and display them in rich results or AI summaries.
For instance, assigning images to specific SKUs (via image markup) makes it easier for search engines to show the correct variation in shopping results.
SEO tips for product variations
Optimizing product variations for SEO requires more than attractive visuals and solid descriptions. You need to apply some proven SEO techniques to ensure search engines correctly interpret your product pages and users get the best possible experience.
Here are a few key practices every ecommerce store owner should follow:
Use canonical tags to avoid duplicate content issues
Product variations often generate multiple URLs, which can cause duplicate content problems. Canonical tags help solve this by pointing to the primary version of a page, consolidating ranking signals, and avoiding internal competition.
Yoast simplifies this process by automatically inserting canonical URL tags on your product pages. This ensures search engines know which version to prioritize, prevents diluted link equity, and even consolidates social shares under the original page. For store owners, this means less technical overhead and stronger, cleaner rankings.
Apply global product identifiers (GTIN, MPN, ISBN) where relevant
Global product identifiers like GTINs, MPNs, and ISBNs act as unique fingerprints for your products. They help Google and other search engines correctly match your items in their vast index, which improves the accuracy of search listings and reduces confusion with similar products. They also add credibility, since customers can cross-check these identifiers before purchase.
With Yoast WooCommerce SEO, adding these identifiers becomes much easier. The plugin reminds you to fill in missing SKUs, GTINs, or EANs for each product variation and automatically outputs them in structured data. This not only helps your products qualify for rich results but also ensures that no variant is left incomplete from an SEO standpoint.
Buy WooCommerce SEO now!
Unlock powerful features and much more for your online store with Yoast WooCommerce SEO!
Regularly audit Google Search Console data to track performance
Google Search Console is a goldmine for understanding how product variations are performing. By monitoring which variant pages are driving impressions, clicks, and conversions, you can refine your SEO strategy.
For example, if certain variants attract little traffic but consume crawl budget, it might be better to consolidate them under canonical tags.
Regular audits also help you detect indexing issues, thin content problems, or underperforming structured data. This keeps your product catalogue lean, crawl-efficient, and focused on driving meaningful organic traffic.
Also read: How to check the performance of rich results in Google Search Console
Common product variation ecommerce errors to avoid
Even if you’ve implemented the right technical setup, added structured data, and optimized your media content, a few small mistakes can undo all that effort. To make sure your product variations support SEO and conversions instead of hurting them, here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Duplicate content: Creating separate standalone pages for each variation (like size or color) without consolidation leads to content duplication. This confuses search engines and dilutes rankings across multiple weak pages
- Poor user experience: If your variation options are hidden, unclear, or slow to load, users struggle to make choices. This friction reduces conversions and increases bounce rates
- Incorrect structured data: Applying schema inaccurately can cause search engines to display the wrong product details in search results, damaging credibility and visibility
- Thin content: Not providing unique descriptions, images, or metadata for each variation leaves the page with little value. Search engines tend to down-rank such content, reducing discoverability
- Crawl bloat: Generating too many low-value variation URLs (like separate pages for every minor option) wastes crawl budget and prevents high-priority pages from being indexed efficiently. Additionally, it could dilute internal link equity
By keeping these errors in check, you’ll ensure your product variation strategy strengthens your SEO and user experience instead of working against them.
Ready to unfold all variations?
Product variations are not just small details hidden in your catalogue. They play a major role in how both search engines and shoppers experience your store. When done right, they prevent duplicate content issues, improve crawl efficiency, deliver richer search results, and create a seamless journey for your customers.
The key is to treat product variations as part of your overall SEO strategy, not as an afterthought. Every unique image, structured snippet, and clear variation option makes your store more visible, more reliable, and more profitable.
This is where Yoast SEO becomes a game-changer. With automatic structured data, smart handling of canonical URLs, and advanced content optimization tools, Yoast helps you get product variations right the first time.