This startup claims it can stop lightning and prevent catastrophic wildfires
On June 1, 2023, as a sweltering heat wave baked Quebec, thousands of lightning strikes flashed across the province, setting off more than 120 wildfires.
The blazes ripped through parched forests and withered grasslands, burned for weeks, and compounded what was rapidly turning into Canada’s worst fire year on record. In the end, nearly 7,000 fires scorched tens of millions of acres across the country, generated nearly 500 millions tons of carbon emissions, and forced hundreds of thousands of people to flee their homes.
Lightning sparked almost 60% of the wildfires—and those blazes accounted for 93% of the total area burned.
Now a Vancouver-based weather modification startup, Skyward Wildfire, says it can prevent such catastrophic fires in the future—by stopping the lightning strikes that ignite them. It just raised millions of dollars in a funding round that it plans to use to accelerate its product development and expand its operations.
Until last week the company, which highlights the role lightning played in the 2023 infernos, stated on its website that it has demonstrated technology capable of preventing “up to 100% of lightning strikes.”
It was an eye-catching claim that went well beyond the confidence level of researchers who have studied the potential for humans to suppress lightning—and the company took it down following inquiries from MIT Technology Review.
“While the statement reflected an observed result under specific conditions, it was not intended to suggest uniform outcomes and has been removed,” Nicholas Harterre, who oversees government partnerships at Skyward, said in an email. “In complex atmospheric systems, consistent 100% outcomes are not realistic, as the experts you spoke to rightly pointed out.”
The company now states it demonstrated that it “can prevent the majority of cloud-to-ground lightning strikes in targeted storm cells.” So far, Skyward hasn’t publicly revealed how it does so, and in response to our questions Harterre said only that the materials are “inert and selected in accordance with regulatory standards.”
But online documents suggest the company is relying on an approach that US government agencies began evaluating in the early 1960s: seeding clouds with metallic chaff, or narrow fiberglass strands coated with aluminum.
The military uses the material to disrupt radar signals; fighter jets, for example, deploy it during dogfights to throw off guided missile systems. Field trials conducted decades ago by US agencies suggest it could help reduce lightning strikes, at least to some degree and under certain conditions.
If Skyward could employ it reliably on significant scales, it might offer a powerful tool for countering rising fire risks as climate change drives up temperatures, dries out forests, and likely increases the frequency of lightning strikes.
“Preventing lightning on high-risk days saves lives, billions in wildfire costs, and is one of the highest-leverage and most immediate climate solutions available,” Sam Goldman, Skyward’s founder and chief executive, said in a statement posted on LinkedIn last year.
But researchers and environmental observers say there are plenty of remaining uncertainties, including how well the seeding may work under varying weather and climate conditions, how much material would need to be released, how frequently it would have to be done, and what sorts of secondary environmental impacts might result from lighting suppression on commercial scales.
Some observers are also concerned that the company appears to have moved ahead with weather modification field trials in parts of Canada without providing wide public notice or openly discussing what materials it’s putting into the clouds.
Given the escalating fire dangers, it’s “reasonable” to evaluate the potential for new technologies to mitigate them, says Keith Brooks, programs director at Environmental Defence, a Canadian advocacy organization.
“But we should be doing so cautiously and really transparently, with a robust scientific methodology that’s open to scrutiny,” he says.
Seeding the clouds
Skyward’s website offers few technical details, but the company says it worked with Canadian wildfire agencies in 2024 and 2025 to demonstrate its technology. The company also says it has developed AI tools to predict lightning strikes that could set off fires.
Skyward announced last month that it raised $7.9 million in Canadian dollars ($5.7 million), in an extension of a seed round initially closed early last year. Investors included Climate Innovation Capital, Active Impact Investments, and Diagram Ventures.
“Our first season demonstrated that prevention is possible at scale,” Goldman said in a statement. “This funding allows us to expand into new regions and support partners who need reliable, operational tools to reduce wildfire risk before emergencies begin.”
The company doesn’t use the term “cloud seeding” on its site or in its recent announcements. But a press release highlighting its selection as a finalist last year in a conservation group’s Fire Grand Challenge states that it suppresses lightning “by cloud seeding with safe, non-toxic materials to neutralize storm charges,” as The Narwhal previously reported.
In addition, Unorthodox Philanthropy, a foundation that provided a grant to support Skyward’s efforts “to test and deploy” the technology, offered more detail in an awardee write-up about Goldman.
It states: “The Skyward team … settled on an inert substance consisting of aluminum covered glass fibers, which is regularly used in military operations to intercept and confuse enemy radar and can also dis-charge clouds.”
Additional details were disclosed in a document marked “Proprietary and Confidential,” which the World Bank nonetheless released within a package of materials from companies developing means of addressing fire risks.
Skyward’s diagrams show planes dropping particles into clouds to prevent cloud-to-ground lightning strikes in “high risk areas.” The company also notes in the document that it uses artificial intelligence for a number of purposes, including forecasting lightning storms, prioritizing treatments, targeting storm cells, and optimizing flight paths.
Harterre stressed that the company would deploy the technology judiciously and reserve it for storm events with elevated wildfire risk, adding that such storms account for less than 0.1% of lightning activity in a given area.
“Our objective is to reduce the probability of ignition on the limited number of extreme-risk days when fires threaten lives, critical infrastructure, and ecosystems, and when suppression costs and impacts can escalate rapidly,” he said.
The document posted by the World Bank states that Skyward partnered with Alberta Wildfire in August of 2024 to “prove suppression by plane and drone,” and that its process produced a “60-100% reduction” in lightning compared with “control cells” (which likely means storm cells that weren’t seeded).
The document added that the company would be carrying out additional field trials in the summer of 2025 with the wildfire agencies in British Columbia and Alberta to “provide landscape level solutions with more advanced aircraft, sensors and forecasting.”
“BC Wildfire Service is aware that Skyward is developing technology that aims to reduce instances of lightning in targeted situations,” the British Columbia agency acknowledged in a statement provided to MIT Technology Review. “Last year, preliminary trials were conducted by Skyward to gain a better understand [sic] of the technology and its applicability in B.C. Should a project/technology like this move forward in B.C., we would engage with the project team in an effort to learn and ensure we’re using every tool available to us to respond to wildfire in B.C.”
The BC agency declined to make anyone available for an interview and didn’t respond to questions about what materials were used, where the tests were carried out, or whether it provided public disclosures or required the company to. Alberta Wildfire didn’t respond to similar questions from MIT Technology Review.
Rising lightning risks
Clouds are just water in various forms—vapor, droplets, and ice crystals, condensed enough to form the floating Rorschach tests we see in the sky. Within them, snowflakes and tiny ice pellets known as graupel rub together, causing atoms to trade electrons. This process creates highly reactive ions with negative and positive charges.
Updrafts separate the light snowflakes from the graupel, building up larger differences in the charges across the electrical field until … crack! An electrostatic discharge occurs in the form of a lightning strike.
The 2023 fire season wasn’t a particularly big year for lightning strikes in Canada—but then it didn’t have to be. It was so hot and dry that every bolt that struck the surface had a better than usual chance of igniting a fire, says Piyush Jain, a research scientist at the Canadian Forest Service and lead author of a study published in Nature Communications that analyzed the year’s fires.
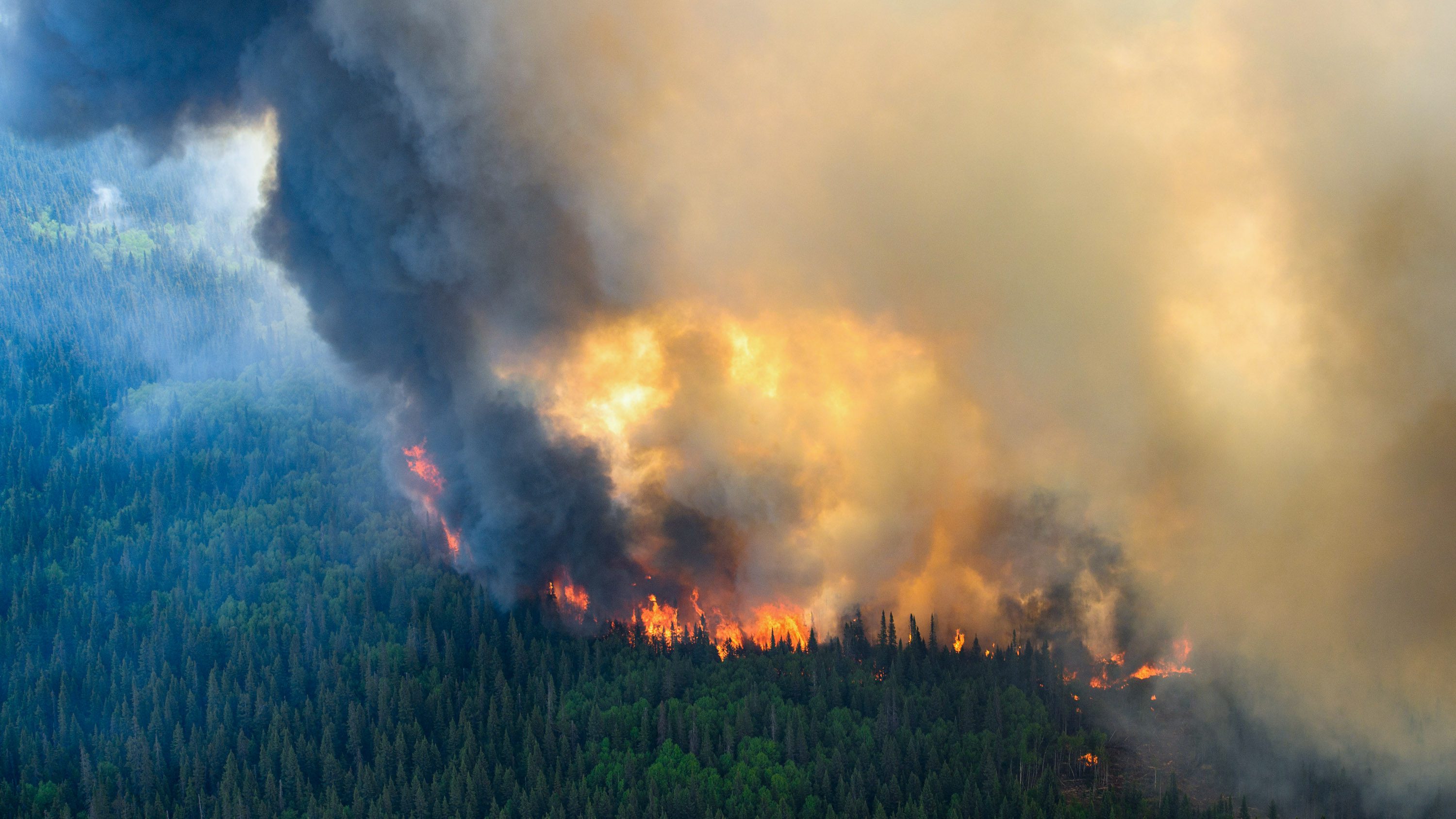

Climate change is, however, likely to produce more lightning strikes, if it hasn’t started to already. Warmer air holds more moisture and adds more convective energy to the atmosphere, which drives the vertical movement of air that forms clouds and stirs up lightning storms.
“So the conditions are there, and the conditions are likely to increase,” Jain says.
Different models arrive at different lightning forecasts for some regions of the world. But a clearer trend is already emerging in the northernmost latitudes, where the planet is warming fastest. Studies show that lightning-ignited fires have substantially increased in the Arctic boreal region, and predict that they will continue to rise.
This combines with other growing risks like longer fire seasons, warmer temperatures, and drier vegetation, together raising the odds of more severe fires and more greenhouse-gas emissions, says Brendan Rogers, a senior scientist at the Woodwell Climate Research Center who studies the effect of fires on permafrost thaw.
In fact, Canada’s emissions from the 2023 fires were more than four times its emissions from fossil fuels.
Midcentury field trials
Scientists have conducted a variety of experiments exploring the possibility of preventing lightning, but most of it happened in the later half of the last century.
Amid the cultural optimism and booming economy of the postwar period, US research agencies and corporations went on a tear of cloud seeding experiments aimed at conquering nature—or at least moderating its dangers. Research teams launched or dropped materials like dry ice and silver iodide into clouds in attempts to boost rainfall, reduce hail, dissipate fog, and redirect hurricanes.
“Cloud seeding activity was so intensive that at its peak in the early 1950s, approximately 10% of the US land area was under some kind of weather modification program,” wrote MIT’s Phillip Stepanian and Earle Williams in a 2024 history of lightning suppression efforts in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. (MIT Technology Review is owned by MIT but is editorially independent.)
Harry Gisborne, then chief of the division of fire research at the US Forest Service, wondered if the technique could be used to trigger downpours that might extinguish hard-to-reach wildfires on public lands. But when he put the question to Vincent Schaefer of General Electric, who had done pioneering research in cloud seeding, Schaefer thought they could perhaps do one better: prevent the lighting that sparked the fires in the first place.
The conversations kicked off what would become Project Skyfire, a multiagency private-public research program that carried out a series of experiments through the 1950s and 1960s. Research teams seeded clouds over the San Francisco Peaks of Arizona, the Bitterroot Mountains at the edge of Idaho, and the Deerlodge National Forest in Montana, among other places.
After comparing treated and untreated storm clouds, the researchers concluded that seeding decreased cloud-to-ground lightning by more than half. But as MIT’s Stepanian and Williams noted, the sample sizes were small, and questions remained about the statistical significance of the findings.
(Soviet scientists also carried out some field experiments on lightning suppression in the 1950s, as well as some related research that involved using rockets to launch lead iodide into thunderstorms in the 1970s, but it’s difficult to find further details about those programs.)
A near tragedy reignited US government interest in the possibility of lightning suppression in 1969, when lightning struck the Apollo 12 space shuttle twice within seconds of launch. The astronauts were able to reset their systems and successfully complete their mission to the moon, but it was a very close call.
In the aftermath, NASA and NOAA teamed up on what became known as Project Thunderbolt, which relied on the metallic chaff normally used in military countermeasures.
Researchers at the US Army Electronics Laboratory had previously proposed the possibility of suppressing lightning by deploying this material, which a handful of defense contractors manufacture. The idea is that chaff acts as a conductor in a forming electrical field, stripping electrons from some oxygen and nitrogen molecules and adding them to others. The mismatched electrons already collecting in cloud water molecules, thanks to all that rubbing between snowflakes and graupel, can then leap over to those newly charged atoms. That, in turn, should reduce the buildup of static electricity that otherwise results in lightning.
“By continuously redistributing—and thereby neutralizing—charges within the storm in a weak electric field, the strong electric fields required to produce lightning would never develop,” Stepanian and Williams wrote.
NASA and NOAA carried out a series of experiments seeding clouds with chaff from the early to mid 1970s, over Boulder, Colorado, and later at the Kennedy Space Center. Here, too, the experiments showed “generally promising field results.” But NASA eventually grew concerned about the possibility that chaff could affect radio communications and shuttered the program.
“Lightning suppression research was once again abandoned, and the responsibility for mitigating lightning hazards reverted to weather forecasters,” Stepanian and Williams concluded.
‘Hard to draw conclusions’
So what does all this tell us about our ability to prevent lightning?
“In my opinion, it’s unambiguously true that this technique can be used to reduce lightning strikes in a storm,” says Stepanian, a technical staff member at MIT Lincoln Laboratory’s air traffic control and weather systems group. “With some major caveats.”
For example, it’s not clear how much material you would need to release, how long it would persist, and how the effectiveness might change under different climate and weather conditions.
(Stepanian consulted with Skyward in its early stages, and he declined to discuss the startup.)
His coauthor on the history of lightning suppression seems a tad more skeptical. In an email, Williams, a research scientist at MIT who studies physical meteorology and atmospheric electricity, said there’s unmistakable evidence that chaff “has an impact on the electrification of thunderstorms.” But in email responses, he said its effectiveness in reducing or eliminating lighting activity “remains controversial” and requires further testing. (Williams says he did not consult for Skyward.)
In his own written reviews, he’s highlighted a number of potential shortcomings with earlier research, including unaccounted-for differences in cloud heights between treated and untreated storms. In addition, he’s noted that some studies used detection systems that pick up only cloud-to-ground strikes, not intracloud lightning, which is far more common.
He also points to the results of a more recent study that he and Stepanian collaborated on with researchers at New Mexico Tech. They relied upon data from weather radars in Tampa and Melbourne, Florida, located on opposite sides of the state, to detect the presence of chaff released over the central part of the state during military training and testing exercises.
They compared 35 storms during which chaff was clearly detected in clouds with 35 instances when it wasn’t.
According to an abstract of the paper—which hasn’t been peer-reviewed or published but was presented at the American Geophysical Union conference in December—storms that occurred when chaff was present were generally “smaller and shorter-lived.”
But the number of total flashes—which includes ground strikes as well as lightning within and between clouds and the air—was actually significantly higher in clouds carrying chaff: 62,250 versus 24,492.
“In summary, so far, it is hard to draw any conclusion about lightning suppression using chaff,” the authors wrote.
Williams says their results and other studies suggest that large chaff concentrations may be needed to suppress lightning. That could be because there’s a strong tendency for the ions released from the chaff fibers to be captured by cloud droplets before they reach the charged particles that would need to be neutralized.
But that may also present a significant deployment challenge, since chaff quickly becomes dilute once it’s released into the midst of turbulent storm clouds, Williams adds.
Skyward’s Harterre said he couldn’t comment on the results of the Florida study but noted that storms in the state are very different from those that occur in the Canadian provinces where his company operates.
“Our work to date has focused on regions where operational feasibility has been evaluated and wildfire risk is highest,” he wrote.
‘Unintended consequences’
The possibility of releasing more chaff into the air also raises the questions of what else it could do in the atmosphere, and what will happen once it lands.
The US military has produced a number of studies exploring the environmental and health effects of chaff and found that it disperses widely, breaks down in the environment, and is “generally nontoxic.”
For instance, a Naval Health Research Center report assessing environmental impacts from decades of training exercises near Chesapeake Bay concluded that “current and estimated use of aluminized chaff by American forces worldwide” will not raise total aluminum levels above the Environmental Protection Agency’s established limits.
But a US Government Accountability Office report in 1998 raised a few other flags, noting that chaff can also affect civilian air traffic control radar and weather forecasts. It also highlighted a “potential but remote chance of collecting in reservoirs and causing chemical changes that may affect water and the species that use it.”
Stepanian says that if lightning suppression efforts require more chaff than the military currently releases, further studies may be needed to properly evaluate the environmental effects.
Brooks of Environmental Defence Canada says he wants to know more about what materials Skyward is using, where they’re sourced from, what the effort leaves behind in the environment, and what the impacts on animals could be. He is also wary of the possible secondary effects of intervening in storms.
“I just think there’s the potential for unintended consequences if we start to mess with a complex system, like weather,” Brooks says, adding: “It makes me nervous to think there are pilots going on without people knowing about them.”
Harterre said that the company abides by any applicable regulations, and that it conducts its field activities “in coordination with relevant authorities and with appropriate authorization.”
He added that it releases seeding materials at lower volumes and concentrations than those associated with defense use and that deployments “are limited to defined high-wildfire-risk storm conditions.”
Remaining doubts
It’s not clear whether or to what degree Skyward has meaningfully advanced the science of lightning suppression or cleared up the questions that have lingered since the studies from the last century.
The company hasn’t released data from its field trials, published any papers in peer-reviewed literature, or disclosed how its tests were performed, as far as MIT Technology Review was able to determine.
Without such information it’s impossible to assess its claims, Williams says. He and two of his New Mexico Tech coauthors—associate professor Adonis Leal and master’s student Jhonys Moura—had all expressed skepticism about the company’s previous claim of “up to 100%” lightning prevention.
Harterre said Skyward intends to release more technical information as its programs mature.
“We look forward to the opportunity to share more detailed information,” he wrote.
In the meantime, Skyward’s investors have high hopes for the company and see “tremendous opportunity” in its potential ability to counteract fire dangers.
“Mitigating the exponentially increasing risk of wildfires can only happen if we shift from reactive suppression to proactive prevention,” Kevin Kimsa, managing partner of Climate Innovation Capital, said in a statement when the company’s recent funding was announced.
Rogers, of the Woodwell Climate Research Center, has spoken with Skyward several times but hasn’t worked with them. He also stressed that it’s crucial to understand potential environmental impacts from lightning suppression and to consult with citizens in affected areas, including Indigenous communities.
But he says he’s “optimistic” about the role that lighting suppression could play, if it works effectively and without major downsides.
That’s because preventing wildfires is far cheaper than putting them out, and it avoids risks to firefighters, ecosystems, infrastructure and local communities.
“If you’re able to go after fires before they’ve even ignited, you remove a lot of that from the equation,” he says.