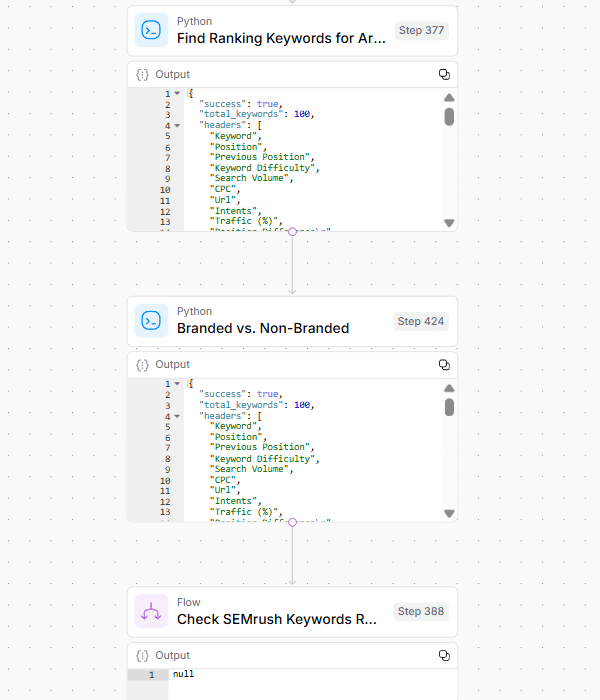
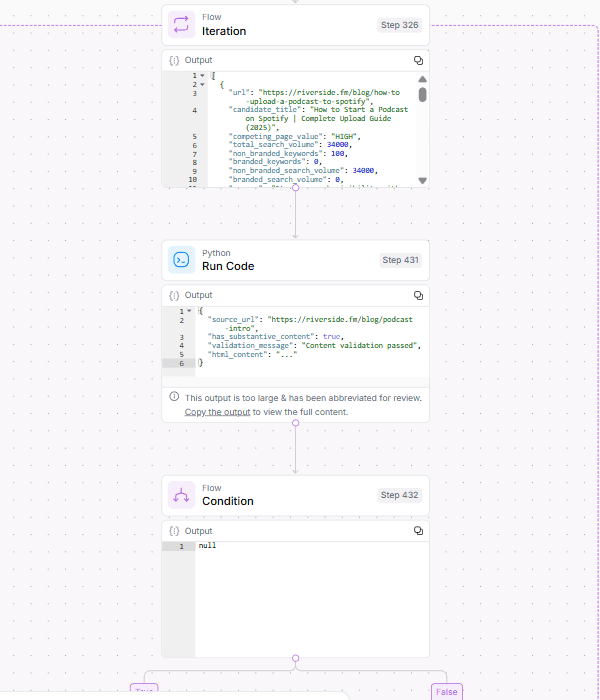
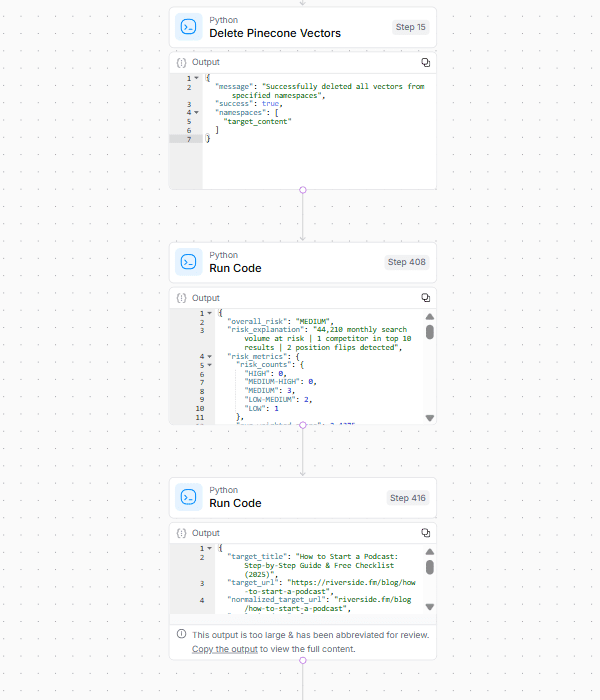
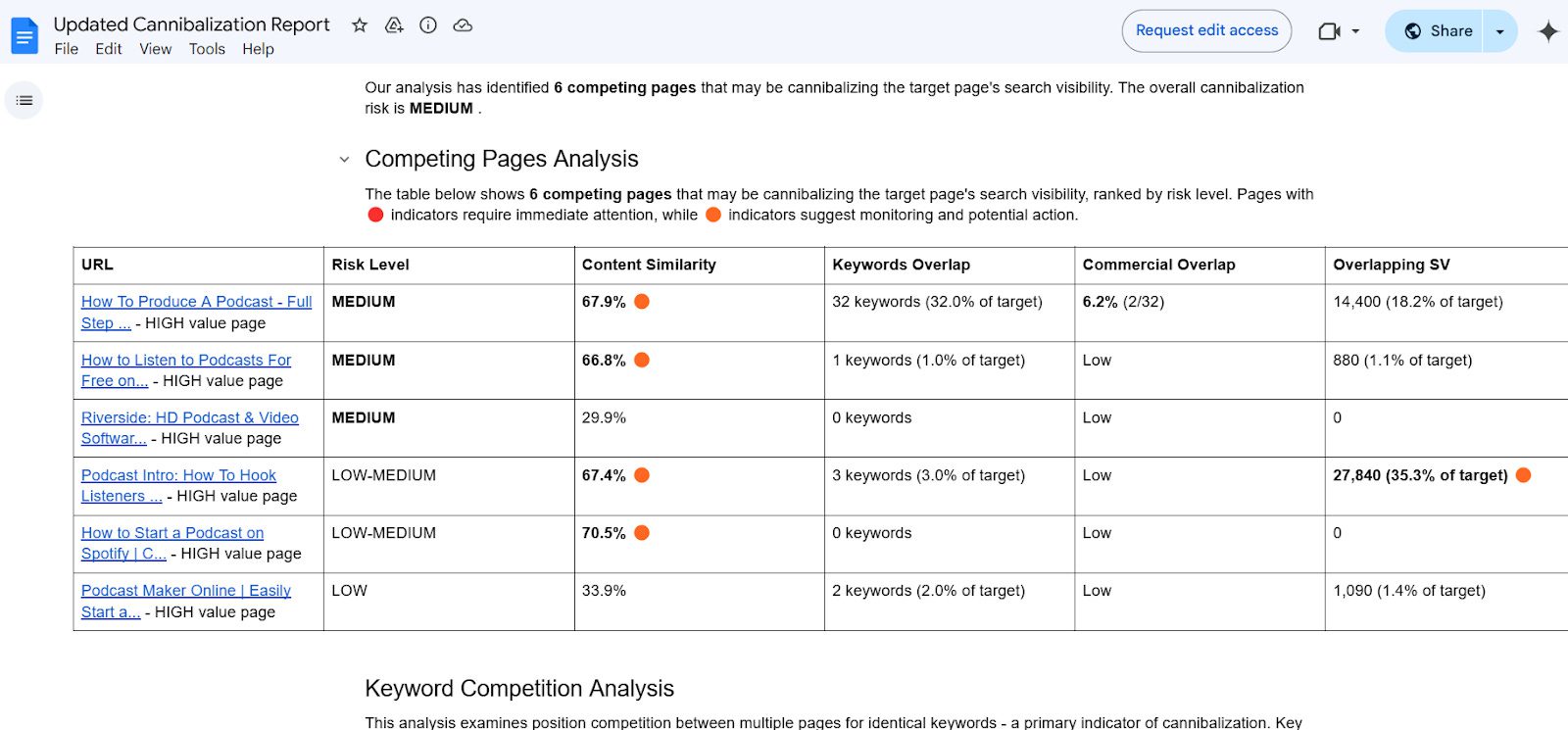
Social media offers a valuable channel for businesses to connect with their prospects and current customers.
A whopping 63.9% of the world’s population spends time on social media. Yet, social has also become an increasingly difficult forum to stand out in as more businesses continue to seek to capitalize on the opportunity that awaits.
The need for frequent updates, diverse content dependent on social media platforms, high-quality visuals, and compelling copy puts pressure on marketing teams to consistently deliver, often with limited time and resources.
This is where generative AI comes into play.
AI-powered tools can help automate many aspects of social media content creation, helping brands write witty captions, generate unique images, and even produce videos.
However, leaning on AI to help draft social media content comes with one notable dilemma: efficiency versus authenticity.
In this article, we’ll explore how brands can make the most of generative AI while still adhering to brand standards, diving into how AI can be put to work for social media marketers in an ethical and authentic way that captures customer interest.
What Is Generative AI In Social Media?
Generative AI enables social media marketers to quickly and nearly effortlessly generate different types of content, such as text, images, videos, and even audio.
AI learns patterns from vast datasets and can translate this vast amount of information into content that aligns closely with what a human could create.
Unlike traditional automation, which follows pre-set templates, generative AI generates new content based on the prompts the end user provides.
AI is becoming widely adopted, as 75% of marketers are either testing the waters with AI or have fully implemented AI in their operations.
For social media marketers specifically, AI is being used to help generate post copy, reply to comments, create AI images, and much more.
How AI Works For Social Media Content
Generative AI has changed the game for content creation and impacted the way social media marketers engage with their followers and analyze insights across their social media channels.
However, it’s important to note that human creativity remains a must. AI is paramount to incorporate into every marketer’s day-to-day efforts, but it must be used wisely.
Here are a few ways social media marketers use AI to automate routine tasks.
AI For Text Generation
Perhaps one of the primary uses for AI-powered language models is to create engaging content for a variety of divergent social media formats, including:
- Photo and Reels Captions: AI can generate catchy, concise, and engaging captions tailored to different platforms.
- Responses: AI can suggest follow-up replies to comments and feedback, helping brands create engaging threads that encourage participation and further conversation.
- Thought Leadership: AI can help businesses discover ideas and angles for longer-form content like blog posts or content for LinkedIn, helping brands establish and position themselves as thought leaders.
- Ad Copy: AI can help generate ideas for succinct yet meaningful ad copy, providing several options for A/B testing to see what resonates best.
- Hashtags: Need help crafting the right hashtags? AI can help generate hashtags related to your business and what people are looking for to help boost visibility.
In order to create relevant content that converts, AI tools analyze what content performs best and what gets customers to engage.
As with any AI-generated content, it’s imperative to have human oversight to ensure your message aligns with brand voice and tone and is factual.
Here’s an example of AI in action.
Consider a travel brand that wants to encourage people to travel to a new destination. It might use AI to create a few different versions of a caption. Here are a few different examples of captions AI created:
- Casual: “Looking for your next adventure? 🏝️ Book your dream trip today!”
- Luxury: “Indulge in an unforgettable getaway at our exclusive beachfront resort. 🌊✨”
- Call to Action (CTA) Focused: “Flights are filling up fast! Book now and escape to paradise. ✈️🌴”
With a few versions to choose from, brands can quickly tailor their messaging for different audiences and can pick the one that will resonate most with their potential customers.
AI For Image And Video Creation
Visual content is growing increasingly popular, given the rise of TikTok and Instagram.
A recent study found that nearly 22% of marketers reported that over 75% of their content this year was visual content.
The same study found that 34.3% of marketers said that visual content made up at least 20-50% of their overall content marketing strategy.
Given the high demand for engaging visual content, marketers are tasked with finding the resources (and time) to create high-quality visuals.
Bandwidth constraints and a lack of creatives can lead to marketers producing solely text-based content. Enter Generative AI.
Generative AI can now produce high-quality graphics, illustrations, and videos without requiring a human designer. Below are a few ways AI is reshaping how visual content is made:
- AI-Generated Images: Tools like DALL·E, MidJourney, and Canva AI allow marketers to create custom graphics based on text prompts.
- AI Video Generation: Platforms like Runway ML and Synthesia allow marketers to create short promotional videos, product showcases, or AI-powered explainer videos without the need for a videographer or video editing.
- Smart Image Editing: AI tools can make images look better by boosting certain elements like brightness and saturation, removing backgrounds, and enhancing low-resolution graphics. This helps to ensure that every visual your business publishes is high-quality and up to brand standards.
Consider a beauty brand that plans to launch a new skincare product. The beauty brand could use AI to:
- Generate realistic AI-created images of the product, such as on a bathroom counter, on different skin tones, or in a model’s hand.
- Create a short promotional video that introduces the product, explains its benefits, and gives tips for application.
- Modify user-generated content (UGC) by removing cluttered backgrounds or enhancing lighting for a more professional look.
AI visuals help businesses save on labor like production costs and editing fees while allowing brands to generate unique visuals at scale.
AI For Automated Engagement And Customer Interaction
Social media marketers know that engagement is key to growing a business’s social media presence.
AI-powered technology can now manage customer engagement, responding to social media comments and direct messages in real-time.
This helps brands boost engagement while also ensuring customers receive timely, thoughtful responses.
- AI Chatbots: Platforms like Drift and ManyChat allow businesses to automate FAQs, product recommendations, and customer service questions through social media messaging.
- AI-Driven Comment Moderation: AI can analyze and respond to user comments, helping brands respond quickly to customer feedback.
- Real-Time Sentiment Analysis: AI tools track user sentiment, identifying positive engagement opportunities and potential PR risks.
For example, a restaurant brand can use AI automation to:
- Respond instantly to frequently asked questions like “Are you open for brunch on the weekends?” with pre-programmed answers.
- Automatically direct users to a reservation link when they ask, “How can I book a table?”
- Flag and escalate negative reviews or complaints for human customer service intervention.
For example, a popular fast-casual restaurant revamped its customer experience by mining through a plethora of customer feedback to identify areas of improvement.
The restaurant found it could improve its ordering and delivery systems by mining for common negative feedback.
By proactively addressing this feedback and making swift changes, the restaurant was able to boost its Google star rating from 4.2 to 4.4.
The Benefits Of AI In Social Media
A recent global survey found that 38% of professionals in marketing, PR, sales, and customer service identified increased efficiency as the top advantage of using generative AI for social media marketing.
The same report found that 34% of respondents highlight easier idea generation as a key benefit of generative AI, showcasing the technology’s growing role in streamlining content creation and strategy.
Generative AI has many potential use cases such as allowing brands to seamlessly create, manage, and optimize content at a rapid pace that would be difficult to replicate with a human touch alone.
The following are other major advantages of AI in social media.
Speed And Efficiency
AI produces content with just a few clicks. Enter a prompt and users will receive a response nearly in an instant.
Social media marketers have turned to AI to help generate captions, posts, responses, and more to help streamline work.
This reduction in time allows social media marketers to focus on actual strategy, drive revenue, and grow the brand’s social media presence.
Social media marketers no longer need to invest time in brainstorming the perfect hashtags, a catchy caption, or relevant copy as AI can generate multiple diverse content variations in seconds.
Responding to comments is an equally essential task and AI enables personalized responses to customer feedback rapidly.
Scalability
For some brands, their target audience’s frequent different social media platforms. Each platform requires a different content strategy.
For example, longer-form content typically performs well on LinkedIn, whereas shorter-form content is necessary for X (Twitter) given its character limit.
Lean marketing teams may find value in using AI to scale content production to remove some of the burden of work from the team.
- AI-generated content allows brands to post frequently without the need to come up with fresh ideas for each channel.
- AI-driven scheduling tools automatically determine when the ideal posting times and dates are based on engagement trends.
- AI can adjust content formats dependent on the channel, such as lengthening a short-form Instagram caption into a long-form LinkedIn post.
For example, an agency running multiple client accounts might use AI to help generate content or brainstorm potential content ideas without hiring additional writers.
Personalization
AI is able to review a wealth of information in a matter of seconds, analyzing user behavior and preferences to help create relevant content for different audience segments.
AI-driven audience insights enable brands to understand what type of content resonates most.
It can also translate and adapt messages to fit regional preferences as well, adhering to that region’s unique tone and other popular nomenclature.
For example, a fitness brand creating targeted messaging for individual locations across the country might use AI to adjust language, tone, and services based on regional audience behavior.
Cost Savings
Prior to AI, copywriting, graphic design, and video editing were left solely to the professionals.
Now, AI tools can present significant cost savings, reducing the need to rely entirely on professionals, if needed.
AI-generated images and videos can eliminate the need for costly video and photo creation and reduce reliance on external agencies.
For example, a small business that may have previously spent thousands on its creative needs can now use AI tools to create ads with minimal effort or expertise.
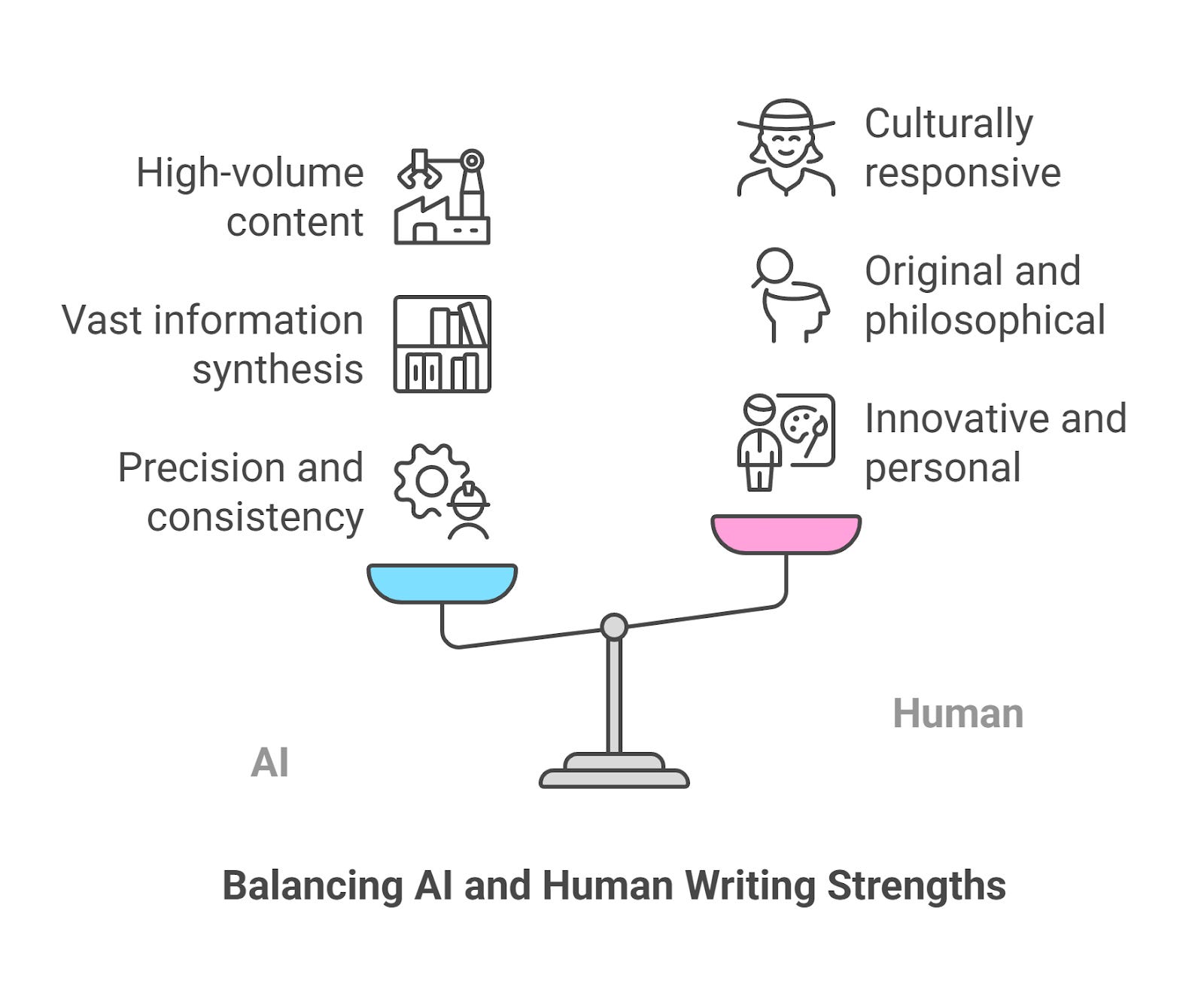
Maintaining Brand Authenticity With AI Content
One of the biggest concerns surrounding the use of generative AI in social media marketing is the risk of losing the brand’s individuality and unique voice.
In turn, the brand can be seen as disingenuous and inauthentic, both of which greatly erode brand trust.
Consumers have become accustomed to AI and are getting smarter at detecting AI-generated content. This is why it’s essential to have a high level of human oversight.
A human must be tasked with reviewing any and every piece of content that gets published, ensuring content matches brand voice and tone.
While AI-generated content can be a game-changer for streamlining work, over-reliance on it and leaving it unchecked can lead to misinformation, impersonal messaging, and generic content that fails to connect with audiences.
To maintain brand authority in the AI era, brands must be deliberate and strategic in their usage of AI.
Creative storytelling and quality content continue to reign supreme.
Only humans can truly discern whether messaging aligns with brand voice standards and will land right with their audience.
How To Use AI Ethically And Effectively In Social Media Marketing
Generative AI can best be seen as an assistant, a tool that helps marketers streamline work but still requires editing and oversight.
Left unchecked, it can lead to false information, poor user experiences, and, in extreme cases, lost sales.
To ensure you’re using generative AI in a way that’s ethical, responsible, and meaningful for your target audience, avoid the following tactics:
- Overreliance: Avoid using AI excessively and look at it more as a tool for idea generation.
- Lack of Human Editing: Ensure AI-generated content has human oversight. The future of AI will still require a level of human intervention to ensure authenticity and accuracy.
- Generic Content: Humans crave connection. AI models, while sophisticated, can lack human emotion. This can lead to less engaging content or content that relies heavily on clichés, buzzwords, or generic phrasing that every other brand is using. Use AI-generated content as a starting point and refine it with human expertise.
- Inconsistent Voice: AI finds information from a variety of sources, which can translate to diverse tones and voices in the content it returns. Train AI tools to understand your brand’s unique voice and tone by sharing past content with them. Have a human editor review each piece of content to ensure it aligns with brand guidelines and standards.
- Forgetting the Power of UGC: Brand content is great, but the power of user-generated content can’t be forgotten. UGC can help tell your brand’s story from a customer’s point of view. Potential customers often rely on testimonials to convince them to convert.
- Lack of Transparency: The future of AI will call for even greater transparency for disclosing when brands are using AI. Ethical concerns have already been raised about what’s real and what’s artificially created, and these concerns will only continue to grow in the future.
- Only Using AI Visuals: AI-generated visuals can be high-quality and cost-effective, but brands should try to incorporate their own images and UGC as well. Customers are growing to accept AI visuals, but in the future, they’ll likely still welcome company-owned and produced images and videos.
The Future AI For Social Media
The current frontier of AI is exciting, presenting myriad opportunities to scale content at a rapid pace.
However, as exciting an opportunity AI may seem, it doesn’t and can’t replace humans.
Only humans have the expertise and emotion necessary to connect with other humans. Striking a balance between automation and authenticity is a must.
Social media marketers who successfully harness AI will strategically use the technology to assist, rather than replace, human creativity.
Those that can strike a balance will be able to take advantage of AI’s myriad benefits while also maintaining meaningful connections with their audiences.
More Resources:
Featured Image: ImageFlow/Shutterstock
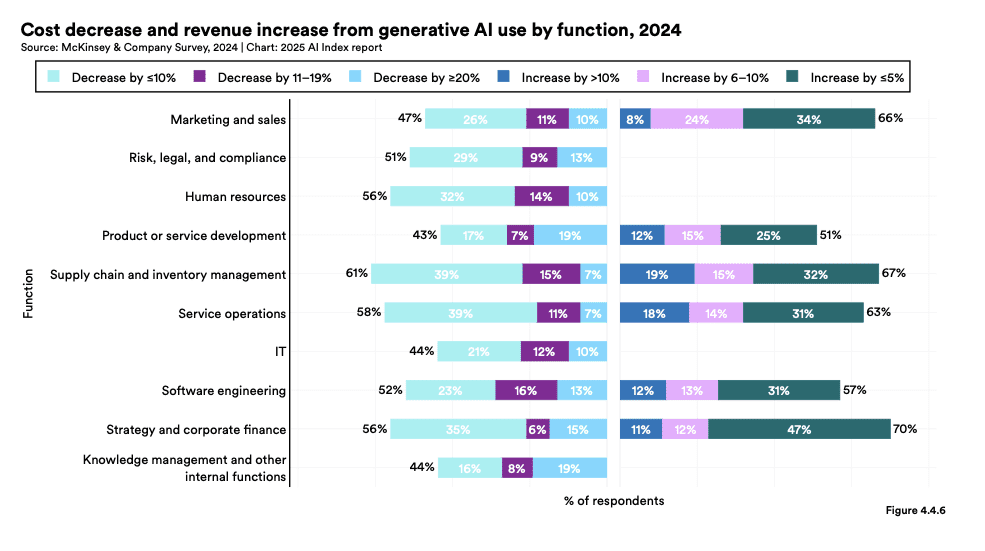 Source: McKinsey & Company Survey, 2024 | Chart: 2025 AI Index report
Source: McKinsey & Company Survey, 2024 | Chart: 2025 AI Index report