The Role Of E-E-A-T In AI Narratives: Building Brand Authority For Search Success via @sejournal, @cshel

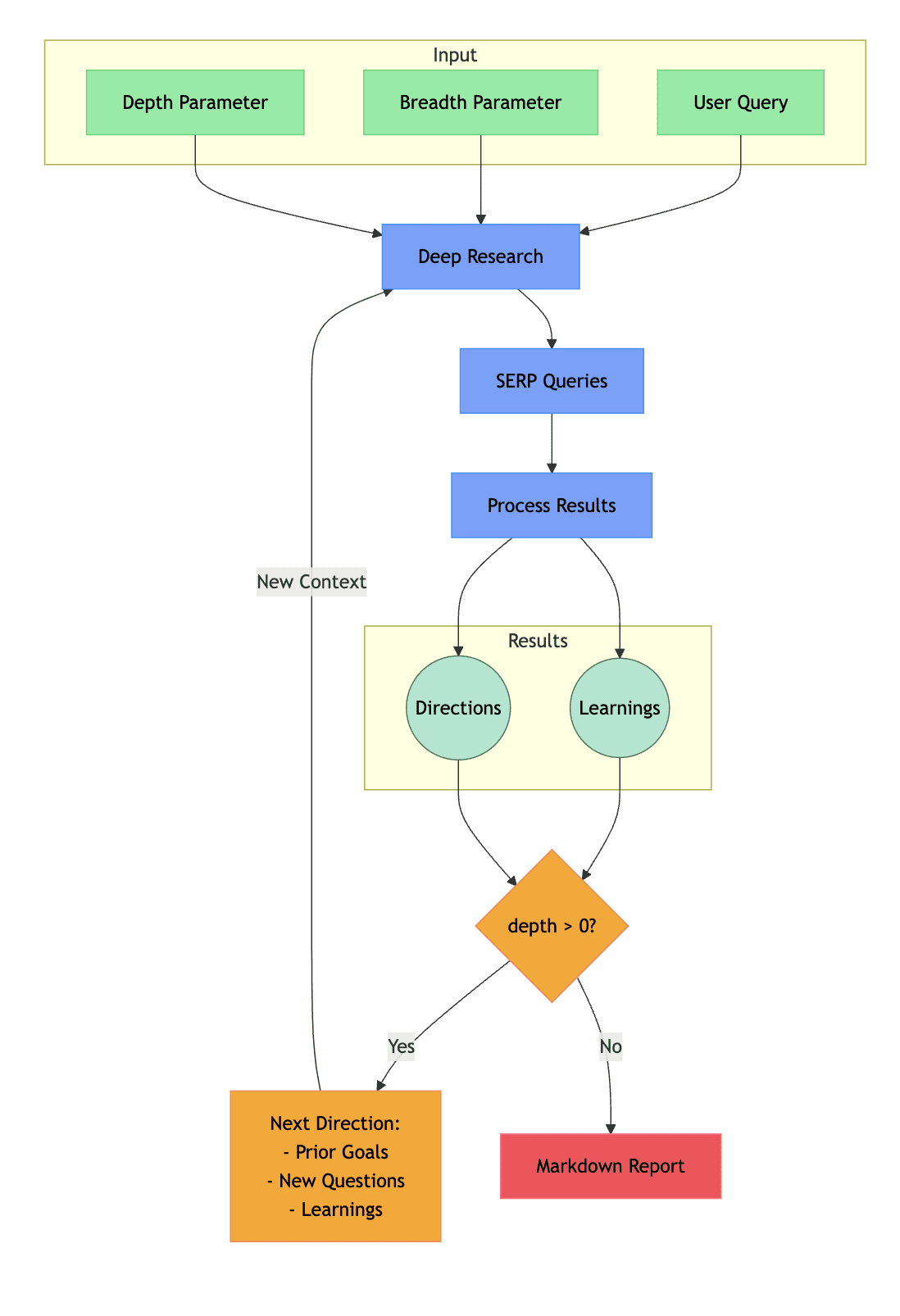
For over a decade, E-A-T (expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness) has played a role in search rankings, first introduced in Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines in 2014.
But with the rise of AI-generated content and AI-synthesized answers, E-E-A-T (now including experience) is no longer just a good idea. It has become the defining factor in determining which sources AI-driven search results consider authoritative enough to cite and include in their synthesized narratives and responses.
AI Overviews and other AI-generated search features don’t just favor sites that “align with E-E-A-T principles” – they favor recognized experts.
To be cited in AI-driven answers, a brand needs to demonstrate undeniable expertise and establish itself as the authority in its field.
This means consistently producing original research, providing real-world insights, and gaining industry-wide (or broader) recognition.
In this article, we’ll explore how E-E-A-T determines visibility in AI-driven search and AI-generated answers, what challenges brands face in maintaining credibility, and strategies for ensuring that AI models and search engines rely on your content as a trusted source.
The Intersection Of E-E-A-T And AI-Generated Answers
The rise of AI-generated search results presents both opportunities and challenges for brands.
AI-powered features like Google’s AI Overviews, ChatGPT search integrations, and Perplexity AI are synthesizing answers instead of just returning traditional blue links.
This means that appearing in AI-driven answers requires more than just good SEO – it requires E-E-A-T-backed authority.
Key considerations for ensuring visibility in AI search features:
- Experience: AI models favor content backed by first-hand knowledge. Brands that demonstrate real-world expertise through case studies, original research, and hands-on experience have a greater chance of being cited.
- Expertise: AI-generated answers prefer sources with clear subject matter expertise. Author bylines, credentials, and expert contributions all signal trustworthiness to AI-driven search.
- Authoritativeness: AI Overviews and LLM-generated answers prioritize brands that own their knowledge graph, are widely referenced, and are recognized leaders in their industry.
- Trustworthiness: AI-generated content is acceptable to use (in that it is not inherently “bad” or penalized) but must be factually accurate and verifiable. Content backed by reliable sources, citations, and transparent authorship is more likely to surface in AI-generated search features.
Read More: A Candid Assessment Of AI Search & SEO
AI Overviews And E-E-A-T: What Google’s Latest Research Reveals
Google’s recent post on AI Overviews and AI Mode highlights how AI-generated search experiences are evolving and underscores the importance of E-E-A-T in shaping AI-driven responses.
Here are key takeaways that reinforce the role of E-E-A-T:
Google Integrates E-E-A-T Into AI Overviews
- AI Overviews leverage Google’s ranking systems and Knowledge Graph to determine which sources are most authoritative. (Hint: Ensure your Knowledge Graph exists and is accurate!)
- E-E-A-T signals directly influence which websites AI Overviews pull from, reinforcing the need for brands to establish themselves as leading authorities.
High-Quality Sources Are A Requirement
- AI Overviews corroborate AI-generated summaries with top-ranked content, (theoretically) ensuring the information is reliable.
- For Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) queries, the bar for trustworthiness is even higher, emphasizing the importance of expert-driven content. (This is why author biographies with CVs, other credentials, and proof of expertise are necessary.)
AI Overviews Increase Engagement With High-Quality Content
- Google reports that users who interact with AI Overviews visit a greater diversity of websites and that click-throughs from AI Overviews are of higher quality.
- This presents an opportunity for brands with strong E-E-A-T signals to attract engaged visitors who trust the AI-curated results (but click through to verify).
Manual And Algorithmic Safety Checks Reinforce E-E-A-T’s Importance
- Google’s Search Quality Raters, adversarial testing, and fact-checking systems ensure AI Overviews prioritize reliable information.
- Brands that lack E-E-A-T credentials (specifically Knowledge Graphs and other key indicators that your brand is considered authoritative) may struggle to appear in AI-generated search experiences.
Future AI Search Innovations Will Reward E-E-A-T Signals
- Google’s experimental AI Mode in Search expands AI-generated responses using multimodal data and real-time corroboration with authoritative sources.
- Brands with verified expertise, structured citations, and widespread recognition will have an advantage in AI-driven search.
This reinforces the need for brands to proactively establish E-E-A-T authority to maintain visibility in AI-driven search features.
Read More: AI Search Optimization: Data Finds Brand Mentions Improve Visibility
Challenges In Applying E-E-A-T To AI-Generated Search
Despite its benefits, AI-driven search presents several challenges for brands trying to maintain visibility:
1. AI Prioritizes Recognized Authorities: Simply optimizing for E-E-A-T is not enough. Brands must become the trusted source that AI search engines consistently reference.
It’s easy to optimize for or align with E-E-A-T in principle, but much more difficult to achieve in reality because some of the requirements simply aren’t within your control.
2. Potential For Misinformation: AI-generated search results can fabricate statistics, misquote sources, or create misleading narratives. Brands must actively monitor AI-generated mentions for accuracy.
3. Duplicate And Unoriginal Content: AI often pulls from widely cited knowledge bases, meaning brands that don’t produce original insights and research risk being ignored.
4. Algorithmic Bias And Filtering: AI search models prioritize widely referenced sources, which can disadvantage emerging brands. Overcoming this requires strategic partnerships, citations, and broad industry engagement.
AI’s Tendency To Be “Confidently Wrong”
A March 2025 study by the Columbia Journalism Review found that AI-powered search tools frequently provide incorrect answers with “alarming confidence.”
The study tested eight major AI search engines and found that chatbots collectively provided inaccurate answers more than 60% of the time, nearly always without acknowledging uncertainty.
Most interesting finding: Premium AI models were even more prone to confidently incorrect responses than their free counterparts, contradicting the assumption that paid AI services are more reliable.
ChatGPT, in particular, only indicated uncertainty in its wrong answers 7.5% of the time. Which means that 92.5% of the times it was wrong, it was confident it was correct.
If ChatGPT’s success rate at indicating uncertainty were a batting average, it would be .075.
John Vukovich, known for recording the lowest ever MLB batting average (for non-pitchers with more than 500 at bats), had a career BA of .161 – which is still 100% better than ChatGPT’s ability to acknowledge it might not be right.
The findings in this report only underscore the need for careful, attentive human oversight when producing content and active reputation management to ensure accuracy in AI-generated search environments.
Read More: The Impact Of AI And Other Innovations On Data Storytelling
Strategies For Strengthening E-E-A-T In AI-Driven Search
To ensure visibility in AI-generated search results, brands must prioritize establishing true authority, not just optimizing content.
1. Own And Optimize Your Knowledge Graph
- Ensure Google’s Knowledge Graph accurately represents your brand.
- Claim your entity in Google Search and establish schema markup for credibility.
2. Demonstrate Real-World Expertise
- Publish original research, case studies, and expert insights.
- Engage in media interviews, guest contributions, and speaking engagements.
3. Become The Primary Source Of Industry Insights
4. Monitor And Influence AI Search Results
- Actively track how AI-generated answers represent your brand.
- Engage with AI search models via feedback loops and corrections.
5. Leverage Thought Leadership Beyond Your Website
- Be featured on authoritative platforms, podcasts, and news outlets.
- Participate in peer-reviewed research and industry collaborations.
Read More: What 7 SEO Experts Think About AI Overviews And Where Search Is Going
Becoming The Source AI Can’t Ignore
E-E-A-T is the key to visibility in AI-driven search – but it’s not just about optimization.
Brands must become the expert sources AI models trust, reference, and cite.
Those who invest in credibility, expertise, and real-world authority will survive in AI-powered search landscapes, and those who don’t will fade into irrelevance.
More Resources:
Featured Image: insta_photos/Shutterstock