Track Santa On Christmas Eve 2025 (Via NORAD & Google) via @sejournal, @MattGSouthern
Santa’s coming!
The world waits with excitement and anticipation for the arrival of Santa Claus as he starts his world tour for 2025.
Children (and adults) everywhere are eager to track the man in the red suit as he defies the speed limit to make his journey across the globe in just one night.
To help you keep up to date on what time Santa will arrive in your neighborhood, there are now two portals you can use to follow the sleigh.
The original Santa tracker from NORAD tracks Santa’s sleigh as he starts his busy night shift at the International Date Line in the Pacific Ocean and heads across the world towards New Zealand and Australia.
Google also has an interactive website and mobile app so users can follow Old Saint Nick’s journey as he delivers presents worldwide until he finishes in South America after the world’s longest night shift.
NORAD Santa Tracker: A Holiday Tradition
For over 65 years, the NORAD Santa Tracker has helped families follow Santa’s whereabouts.
The NORAD Santa Tracker began in 1955 when a misprinted phone number in a Sears advertisement directed children to call NORAD’s predecessor, the Continental Air Defense Command (CONAD), instead of Santa.
Colonel Harry Shoup, the director of operations, instructed his staff to give updates on Santa’s location to every child who called.
NORAD continues the tradition to this day.

How To Track Santa With NORAD
- Visit the NORAD Santa Tracker website.
- On Christmas Eve, the live map will display Santa’s current location and next stop.
- For a more traditional experience, call the NORAD Tracks Santa hotline at 1-877-HI-NORAD (1-877-446-6723) to speak with a volunteer who will provide you with Santa’s current location.
- Follow NORAD’s social media channels for regular daily updates.
This year, NORAD has added an AI chatbot called Radar to help you get the latest updates.
The Evolution Of Google’s Santa Tracker
Since it launched in 2004, Google’s Santa Tracker has changed and improved. The team uses this project to try out new technologies and make design updates. Some of these new features, like “View in 3D,” are later added to other Google products and services.
What’s In The 2025 Google Santa Tracker
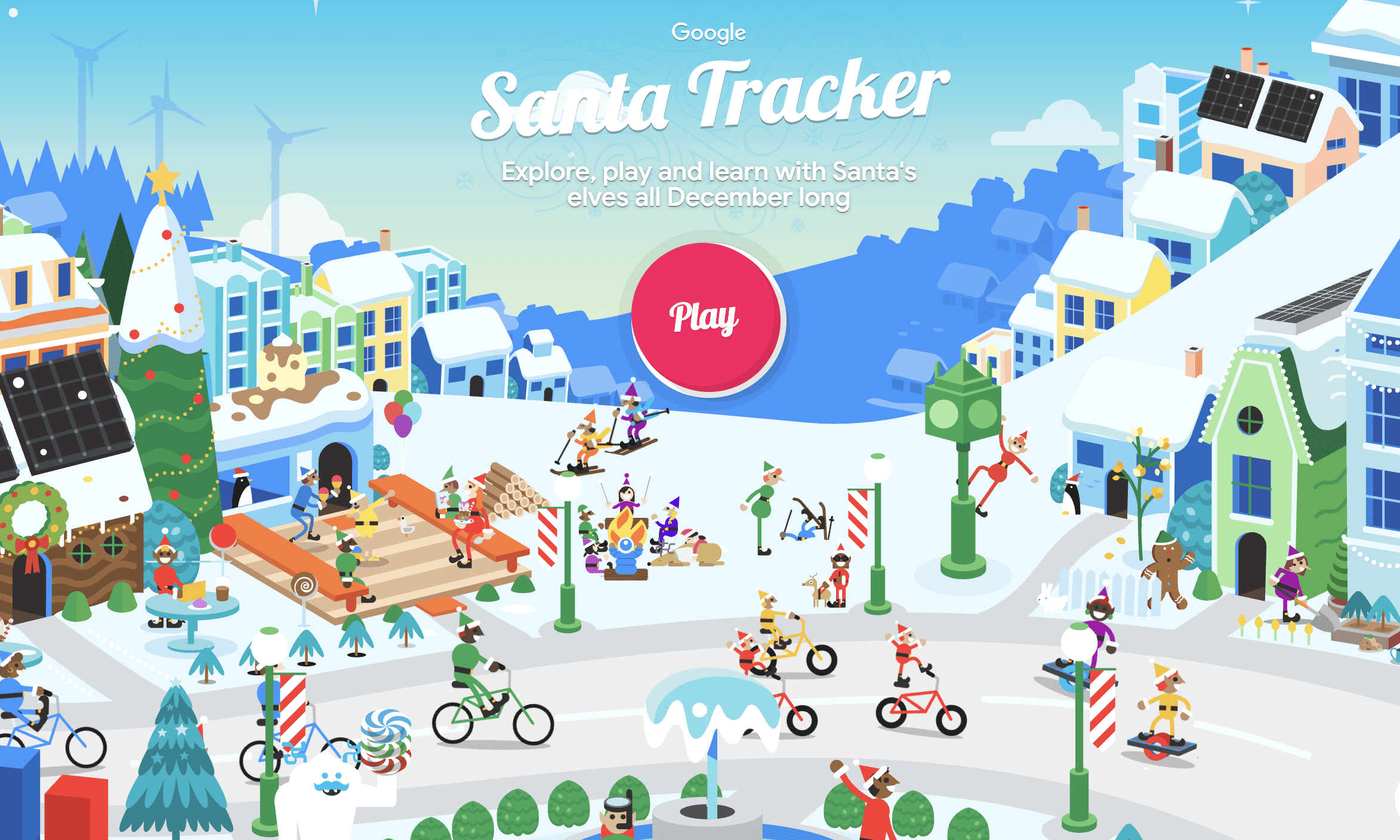


Google’s Santa Tracker returns for its 21st year with the familiar village experience you know and love. The site features games, videos, and activities throughout December, with the live tracker launching on Christmas Eve.
This year’s collection includes classics like Elf Ski and Penguin Dash alongside creative activities like Santa’s Canvas and Code Lab. Google uses the Santa Tracker project to test new technologies that often make their way into other Google products.
On Christmas Eve, the live map shows Santa’s current location, where he’s heading next, his distance from your location, and an estimated arrival time. The tracker begins at midnight in the furthest east time zone (10:00 a.m. UTC) as Santa starts his journey at the International Date Line in the Pacific Ocean.
For each city Santa visits, the tracker displays Wikipedia excerpts and photos, turning the experience into a geography lesson wrapped in Christmas magic.
How To Use The Google Santa Tracker
- Visit the Google Santa Tracker website or download the mobile app for Android devices.
- On Christmas Eve, the live map will show Santa’s current location, the number of gifts delivered, and his estimated arrival time at your location.
- Explore the map to learn more about the 500+ locations Santa visits, with photos and information provided by Google’s Local Guides.
Extra Features & Activities
Beyond games, the platform showcases detailed animated environments ranging from cozy kitchens where elves prepare holiday treats to snowy outdoor scenes filled with winter activities.
The experience is wrapped in Google’s characteristic bright, cheerful art style, with colorful illustrations that bring North Pole activities to life.
Whether practicing basic coding concepts or learning holiday traditions from around the world, kids (and big kids) can explore while counting down to Christmas.
To All, A Good Night
Settle down for the evening tonight with your choice of favorite Christmas snack and follow Santa’s journey with either Google or NORAD.
Santa has an estimated 2.2 billion homes to visit, so it’s going to be a busy night tonight! Don’t forget to leave out your carrots and mince pies.
Happy holidays from all of us at Search Engine Journal!
Featured Image: Roman Samborskyi/Shutterstock