What is a redirect? Types, how to set them up, and impact on SEO
Ever clicked a link and landed on a “Page Not Found” error? Redirects prevent that. They send visitors and search engines to the right page automatically. Redirects are crucial for both SEO and user experience. For SEO, they preserve link equity and keep your rankings intact. Additionally, it enhances the user experience, as no one likes dead ends.
Key takeaways
- A redirect automatically sends users and search engines from one URL to another, preventing errors like ‘Page Not Found.’
- Redirects are crucial for SEO and user experience, preserving link equity and maintaining rankings.
- Different types of redirects exist: 301 for permanent moves and 302 for temporary ones.
- Avoid client-side redirects, such as meta refresh or JavaScript, as they can harm SEO.
- Use Yoast SEO Premium to easily set up and manage redirects on your site.
What is a redirect?
A redirect is a method that automatically sends users and search engines from one URL to another. For example, if you delete a page, a redirect can send visitors to a new or related page instead of a 404 error.
How redirects work
- A user or search engine requests a URL (e.g., yoursite.com/page-old).
- The server responds with a redirect instruction.
- The browser or search engine follows the redirect to the new URL (e.g., yoursite.com/page-new).
Redirects can point to any URL, even on a different domain.
Why redirects matter
Redirects keep your website running smoothly. Without them, visitors hit dead ends, links break, and search engines get lost. They’re not just technical fixes, because they protect your traffic, preserve rankings, and make sure users land where they’re supposed to. Whether you’re moving a page, fixing a typo in a URL, or removing old content, redirects make sure that nothing gets left behind.
When to use a redirect
Use redirects in these scenarios:
- Deleted pages: Redirect to a similar page to preserve traffic.
- Domain changes: Redirect the old domain to the new one.
- HTTP→HTTPS: Redirect insecure URLs to secure ones.
- URL restructuring: Redirect old URLs to new ones (e.g., /blog/post → /articles/post).
- Temporary changes: Use a 302 for A/B tests or maintenance pages.
Types of redirects
There are various types of redirects, each serving a distinct purpose. Some are permanent, some are temporary, and some you should avoid altogether. Here’s what you need to know to pick the right one.
Not all redirects work the same way. A 301 redirect tells search engines a page has moved permanently, while a 302 redirect signals a temporary change. Client-side redirects, like meta refresh or JavaScript, exist because they’re sometimes the only option on restrictive hosting platforms or static sites, but they often create more problems than they solve. Below, we break down each type, explain when to use it, and discuss its implications for your SEO.
Redirect types at a glance
| Redirect type | Use case | When to use | Browser impact | SEO impact | SEO risk |
| 301 | Permanent move | Deleted pages, domain changes, HTTP→HTTPS | Cached forever | Passes (almost) all link equity | None if used correctly |
| 302 | Temporary move | A/B testing, maintenance pages | Not cached | May not pass link equity | Can dilute SEO if used long-term |
| 307 | Temporary move (strict) | API calls, temporary content shifts | Not cached | Search engines may ignore | High if misused |
| 308 | Permanent move (strict) | Rare; use 301 instead | Cached forever | Passes link equity | None |
| Meta Refresh | Client-side redirect | Avoid where possible | Slow, not cached | Unreliable | High (hurts UX/SEO) |
| JavaScript | Client-side redirect | Avoid where possible | Slow, not cached | Unreliable | High (hurts UX/SEO) |
301 redirects: Permanent moves
A 301 redirect tells browsers and search engines that a page has moved permanently. Use it when:
- You delete a page and want to send visitors to a similar one.
- You change your domain name.
- You switch from HTTP to HTTPS.
SEO impact: 301 redirects pass virtually all link equity to the new URL. But be sure to never redirect to irrelevant pages, as this can confuse users and hurt SEO. For example, redirecting a deleted blog post about “best running shoes” to your homepage, instead of a similar post about running gear. This wastes link equity and frustrates visitors.
Example HTTP header:
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Location: https://example.com/new-page302 redirects: Temporary moves
A 302 redirect tells browsers and search engines that a move is temporary. Use it for:
- A/B testing different versions of a page.
- Temporary promotions or sales pages.
- Maintenance pages.
SEO impact: 302 redirects typically don’t pass ranking power like 301s. Google treats them as temporary, so they may not preserve SEO value. For permanent moves, always use a 301 to ensure link equity transfers smoothly.
Examples of when to use a 301 and 302 redirect:
Example 1: Temporary out-of-stock product (302): An online store redirects example.com/red-sneakers to example.com/blue-sneakers while red sneakers are restocked. A 302 redirect keeps the original URL alive for future use.
Example 2: A permanent domain change (301): A company moves from old-site.com to new-site.com. A 301 redirect makes sure visitors and search engines land on the new domain while preserving SEO rankings.
307 and 308 redirects: Strict rules
These redirects follow HTTP rules more strictly than 301 or 302:
- Same method: If a browser sends a POST request, the redirect must also use POST.
- Caching:
- 307: Never cached (temporary).
- 308: Always cached (permanent).
When to use them:
- 307: For temporary redirects where you must keep the same HTTP method (e.g., forms or API calls).
- 308: Almost never, use a 301 instead.
For most sites: Stick with 301 (permanent) or 302 (temporary). These are for specific technical cases only.
What to know about client-side redirects:
Client-side redirects, such as meta refresh or JavaScript, execute within the browser instead of on the server. They’re rarely the right choice, but here’s why you might encounter them:
- Meta refresh: A HTML tag that redirects after a delay (e.g., “You’ll be redirected in 5 seconds…”).
- JavaScript redirects: Code that changes the URL after the page loads.
Why should you avoid them?
- Slow: The browser must load the page first, then redirect.
- Unreliable: Search engines may ignore them, hurting SEO.
- Bad UX: Users see a flash of the original page before redirecting.
- Security risks: JavaScript redirects can be exploited for phishing.
When they’re used (despite the risks):
- Shared hosting with no server access.
- Legacy systems or static HTML sites.
- Ad tracking or A/B testing tools.
Stick with server-side redirects (301/302) whenever possible. If you must use a client-side redirect, test it thoroughly and monitor for SEO issues.
How redirects impact SEO
Redirects do more than just send users to a new URL. They shape how search engines crawl, index, and rank your site. A well-planned redirect preserves traffic and rankings. A sloppy one can break both. Here’s what you need to know about their impact.
Ranking power
301 redirects pass most of the link equity from the old URL to the new one. This helps maintain your rankings. 302 redirects may not pass ranking power, especially if used long-term.
Crawl budget
Too many redirects can slow down how quickly search engines crawl your site. Avoid redirect chains (A→B→C) to save crawl budget.
User experience
Redirects prevent 404 errors and keep users engaged. A smooth redirect experience can reduce bounce rates.
Common redirect mistakes
Redirects seem simple, but small errors can cause big problems. Here are the most common mistakes and how to avoid them.
Redirect chains
A redirect chain happens when one URL redirects to another, which redirects to another, and so on. For example:
old-page → new-page → updated-page → final-page
Why it’s bad:
- Slows down the user experience.
- Wastes crawl budget, as search engines may stop following the chain before reaching the final URL.
- Dilutes ranking power with each hop.
How to fix it:
- Map old URLs directly to their final destination.
- Use tools like Screaming Frog to find and fix chains.
Redirect loops
A redirect loop sends users and search engines in circles. For example:
page-A → page-B → page-A → page-B...
Why it’s bad:
- Users see an error page (e.g., “Too many redirects”).
- Search engines can’t access the content, so it won’t rank.
How to fix it:
- Check your redirect rules for cblonflicts.
- Test redirects with a tool like Redirect Path (Chrome extension) or
curl -vin the terminal.
Using 302s for permanent moves
A 302 redirect is meant for temporary changes, but many sites use it for permanent moves. For example:
- Redirecting
old-producttonew-productwith a 302 and leaving it for years.
Why it’s bad:
- Search engines may not pass link equity to the new URL.
- The old URL might stay in search results longer than intended.
How to fix it:
- Use a 301 for permanent moves.
- If you accidentally used a 302, switch it to a 301 as soon as possible.
Redirecting to irrelevant pages
Redirecting a page to unrelated content confuses users and search engines. For example:
- Redirecting a blog post about “best running shoes” to the homepage or a page about “kitchen appliances”.
Why it’s bad:
- Users land on content they didn’t expect, increasing bounce rates.
- Search engines may ignore the redirect or penalize it for being manipulative.
- Wastes ranking power that could have been passed to a relevant page.
How to fix it:
- Always redirect to the most relevant page available.
- If no relevant page exists, let the old URL return a 404 or 410 error instead.
Ignoring internal links after redirects
After setting up a redirect, many sites forget to update internal links. For example:
- Redirecting
old-pagetonew-pagebut keeping links toold-pagein the site’s navigation or blog posts.
Why it’s bad:
- Internal links to the old URL force users and search engines through the redirect, slowing down the experience.
- Wastes crawl budget and dilutes ranking power.
How to fix it:
- Update all internal links to point directly to the new URL.
- Use a tool like Screaming Frog to find and fix outdated links.
Not testing redirects
Assuming redirects work without testing can lead to surprises. For example:
- Setting up a redirect but not checking if it sends users to the right place.
- Missing errors like 404s or redirect loops.
Why it’s bad:
- Broken redirects frustrate users and hurt SEO.
- Search engines may drop pages from the index if they can’t access them.
How to fix it:
- Test every redirect manually or with a tool.
- Check Google Search Console for crawl errors after implementing redirects.
Redirecting everything to the homepage
When a page is deleted, some sites redirect all traffic to the homepage. For example:
- Redirecting
old-blog-posttoexample.cominstead of a relevant blog post.
Why it’s bad:
- Confuses users who expected specific content.
- Search engines may see this as a “soft 404” and ignore the redirect.
- Wastes ranking power that could have been passed to a relevant page.
How to fix it:
- Redirect to the most relevant page available.
- If no relevant page exists, return a 404 or 410 error.
Forgetting to update sitemaps
After setting up redirects, many sites forget to update their XML sitemaps. For example:
- Keeping the old URL in the sitemap while redirecting it to a new URL.
Why it’s bad:
- Sends mixed signals to search engines.
- Wastes crawl budget on outdated URLs.
How to fix it:
- Remove old URLs from the sitemap.
- Add the new URLs to help search engines discover them faster.
Using redirects for thin or duplicate content
Some sites use redirects to hide thin or duplicate content. For example, redirecting multiple low-quality pages to a single high-quality page to “clean up” the site.
Why it’s bad:
- Search engines may see this as manipulative.
- Doesn’t address the root problem, which is low-quality content.
How to fix it:
- Improve or consolidate content instead of redirecting.
- Use canonical tags if duplicate content is unavoidable.
Not monitoring redirects over time
Redirects aren’t a set-it-and-forget-it task. For example:
- Setting up a redirect and never checking if it’s still needed or working.
Why it’s bad:
- Redirects can break over time (e.g., due to site updates or server changes).
- Unnecessary redirects waste crawl budget.
How to fix it:
- Audit redirects regularly (e.g., every 6 months).
- Remove redirects that are no longer needed.
How to set up a redirect
Setting up redirects isn’t complicated, but the steps vary depending on your platform. Below, you’ll find straightforward instructions for the most common setups, whether you’re using WordPress, Apache, Nginx, or Cloudflare.
Pick the method that matches your setup and follow along. If you’re unsure which to use, start with the platform you’re most comfortable with.
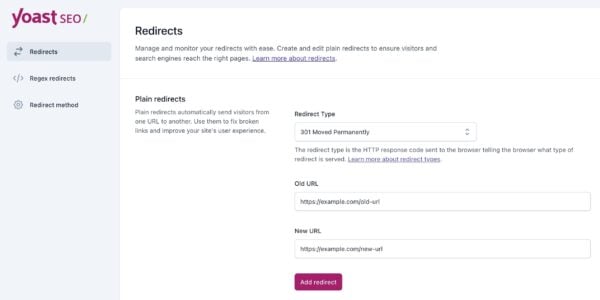
WordPress (using Yoast SEO Premium)
Yoast SEO Premium makes it easy to set up redirects, especially when you delete or move content. Here’s how to do it:
Option 1: Manual redirects
- Go to Yoast SEO → Redirects in your WordPress dashboard.
- Enter the old URL (the one you want to redirect from).
- Enter the new URL (the one you want to redirect to).
- Select the redirect type:
- 301 (Permanent): For deleted or permanently moved pages.
- 302 (Found): For short-term changes.
- Click Add Redirect.
Option 2: Automatic redirects when deleting content
Yoast SEO can create redirects automatically when you delete a post or page. Here’s how:
- Go to Posts or Pages in your WordPress dashboard.
- Find the post or page you want to delete and click Trash.
- Yoast SEO will show a pop-up asking what you’d like to do with the deleted content. You’ll see two options:
- Redirect to another URL: Enter a new URL to send visitors to.
- Return a 410 Content Deleted header: Inform search engines that the page is permanently deleted and should be removed from their index.
- Select your preferred option and confirm.
This feature saves time and ensures visitors land on the right page. No manual setup required.
Need help with redirects? Try Yoast SEO Premium
No code, no hassle. Just smarter redirects and many other invaluable tools.
Apache (.htaccess file)
Apache uses the .htaccess file to manage redirects. If your site runs on Apache, this is the simplest way to set them up. Add the rules below to your .htaccess file, ensuring it is located in the root directory of your site.
Add these lines to your .htaccess file:
# 301 Redirect
Redirect 301 /old-page.html /new-page.html# 302 Redirect
Redirect 302 /temporary-page.html /new-page.htmlNginx (server config)
Nginx handles redirects in the server configuration file. If your site runs on Nginx, add these rules to your server block and then reload the service to apply the changes.
Add this to your server configuration:
# 301 Redirect
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}# 302 Redirect
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location = /old-page {
return 302 /new-page;
}
}Cloudflare (page rules)
Cloudflare allows you to set up redirects without modifying server files. Create a page rule to forward traffic from one URL to another, without requiring any coding. Simply enter the old and new URLs, select the redirect type, and click Save.
- Go to Rules → Page Rules.
- Enter the old URL (e.g., example.com/old-page).
- Select Forwarding URL and choose 301 or 302.
- Enter the new URL (e.g., https://example.com/new-page).
Troubleshooting redirects
Redirects don’t always work as expected. A typo, a cached page, or a conflicting rule can break them, or worse, create loops that frustrate users and search engines. Below are the most common issues and how to fix them.
If something’s not working, start with the basics: check for errors, test thoroughly, and clear your cache. The solutions are usually simpler than they seem.
Why isn’t my redirect working?
- Check for typos: Ensure the URLs are correct.
- Clear your cache: Browsers cache 301 redirects aggressively.
- Test with curl: Run
curl -v http://yoursite.com/old-urlto see the HTTP headers.
Can redirects hurt SEO?
Yes, if you:
- Create redirect chains (
A→B→C) - Use 302s for permanent moves
- Redirect to irrelevant pages
How do I find broken redirects?
- Use Google Search Console → Coverage report.
- Use Screaming Frog to crawl your site for 404s and redirects.
What’s the difference between a 301 and 308 redirect?
- 301: Most common for permanent moves. Broad browser support.
- 308: Strict permanent redirect. Rarely used. Same SEO impact as 301.
What is a proxy redirect?
A proxy redirect keeps the URL the same in the browser but fetches content from a different location. Used for load balancing or A/B testing. Avoid for SEO, as search engines may not follow them.
Conclusion about redirects
Redirects are a simple but powerful tool. A redirect automatically sends users and search engines from one URL to another. As a result, they keep your site running smoothly and preserve SEO value and ranking power. Remember:
- Use 301 redirects for permanent moves.
- Use 302 redirects for temporary changes.
- Avoid client-side redirects, such as meta refresh or JavaScript.
Need help? Try Yoast SEO Premium’s redirect manager.