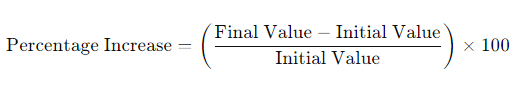2024 AI & SEO: Your 24-Expert Guide To Successful SERPs via @sejournal, @Conductor
Most people working in SEO will tell you that we have just been through an exceptional period of change and rapid learning required.
From the explosion of generative AI – first from ChatGPT and then Bard running to catch up.
The Google updates that were unrelenting.
And Universal Analytics finally being deprecated and switched off, with GA4 being a steep learning curve for anyone who wasn’t prepared in advance.
In 2024, as the dust settles around the introduction of gen AI, the predominant focus is going to be embracing the new tools to help as an assistant for workflow and productivity. For those who don’t take the time to experiment with AI and learn how to write prompts, there is a real threat of being left behind.
We don’t see AI replacing good quality writers or SEO, but we do see AI as an opportunity to enhance and augment what we already do.
[SEO Trends 2024] Download the free ebook →
What SEO Pros Should Focus On In 2024
As SEO is all about collaboration and sharing knowledge, we turned to some of the best minds in the industry to get their thoughts on where the industry is going and what might happen next.
1. Kevin Indig, Growth Advisor:
If Google’s frenzied algorithm updates in 2023 have shown us one thing, it’s that the bar for content and domain quality has risen faster than we thought. In 2024, we need to find ways to scale the production of high-quality content and groom our content portfolio.
The most obvious way is using AI, but we need to significantly increase the output quality and add human input. In some cases, AI might be the wrong content creator, but I think we underestimate how good it can really be.
2. Pedro Dias, Technical SEO and Growth Advisor, Visively:
This is a hard question to answer [What SEO pros should focus on in 2024]. Mostly because SEO is so driven by specific problems you need to solve at different levels of an online business. And every business may have different needs depending on the stage they’re in.
But, if I really have to pick a common issue I see across the board, it’s not really related to SEO tactics, or any specific search feature, but related to how SEOs and businesses are often misaligned with their expectations from search.
So, an actionable and practical take on this would mean that SEOs need to close the gap on what their businesses can expect from search and where they are in this path. Then, they need to communicate clearly what needs to be done and why – I’ve recently tweeted/posted on X (Twitter) about the issues around complex prioritization, and the lack of clarity around business-related problem-solving.
I think a lot of SEOs don’t do this well enough – probably because they lack the strategic vision of what the product they work for should look like in a search ecosystem in 2023 – and so, they often hit walls and don’t get the support they’d need to move ahead.
And it doesn’t matter how advanced or good you are at Python or AI, or how knowledgeable you are around specific search niches. If you can’t translate this to “business-related problem solving” speak, you’ll be stuck indefinitely.
3. Eli Schwartz, Author Of “Product Led SEO” And Growth Advisor:
With the launch of the generative experience, Google will now be taking the top of the funnel for itself, leaving SEO to the mid-funnel. To be fair, it isn’t really “taking” it; they are just answering what is essentially commoditized information.
To date, Google has only delved into short answers when it could rely on structured data that was more than likely to be accurate.
In this bucket would be topics such as population counts, sports scores, ticker symbols, heads of state, and all other kinds of results that we see today in knowledge graph answers.
Generative results in search mean that SEO moves from the top of the funnel to mid-funnel:
Instead of targeting keywords with the most search volume to hopefully peel off the maximum amount of clicks, SEO efforts will need to be more deliberate to target the right users with the right keywords.
- Make sure your content aligns with an actual buyer persona.
- Use modifiers on those head keywords you used to target, like “price,” “reviews,” and “features.”
- Lastly, write content that compares you to your competitors.
4. Shelley Walsh, SEO Content Strategist at SEJ and ShellShock:
With so much changing in SEO, now is the time to look at what is fundamental and never changes.
One of the foundations of good marketing is to put the user first.
Recently, it was revealed in Google’s antitrust lawsuit how user clicks are a factor that influences visibility. This highlights that Google does put emphasis on user signals. And why does Google do this – because they know that the user is central to everything.
If you can understand that SEO is structured around making it as frictionless as possible for a user to do what you want them to – then you have the right mindset to build your strategy.
This underlines technical SEO and it underlines creating content that has a reason to exist.
If you understand how a website works, how a search engine works and how users behave online, then connecting the user to the action is common sense. It’s not complicated, but it is really hard to do this well.
Focus on the cross-section of usability, conversion, technical excellence and high-quality content output.
Generative AI tools are changing how the discipline of SEO will be applied, but they can’t change the fundamentals.
Tools are tools and should be treated as such. They can never replace applied knowledge, experience and expertise.
When everything is changing, hold on to what is timeless.
5. Jamie Indigo, Senior Technical SEO Lead, DeepCrawl:
Ecommerce SEOs need to look at how Google is changing their role in SERPs. The company no longer wants to be the search engine you use to find the sites with the products – they want to be where you shop for products.
SERPs will continue to cut out category and product listing pages in favor of showing product results directly in SERPs.
“Shop {categoryName}” is likely where your category and product listing page traffic has come from historically. Now “Shop” queries (and many other transactional intent keywords) trigger SERPs powered by Shopping Graph.
Everything from prices, product reviews, seller reviews, multiple images, and down to the last “Buy now click” can be facilitated without leaving Google. Google is using their new Notes feature to cultivate UGC social proof and facilitate quicker conversions.
Organic Shopping results (seen by filtering Search Appearance to Product Results) will continue to gain prominence. This means SEOs need to be the Merchant Center and optimize their feeds.
Some enhancements, like deals, can only be submitted with Free Feeds. Google will continue leveraging feed fields like “Discounts” to create SERP shopping pages that show both organic and paid feed results where that information is available.
Google will likely expand their learnings into other verticals as they refine and ⚡️syngerize⚡️
6. Mordy Oberstein, Head Of SEO Brand At Wix:
One of the interesting things I’ve seen is a huge surge in rank volatility circa Q3 of 2023 (per the Semrush data set). When you compare rank fluctuations to early in the year and even prior years, there is a clear divergence from the overall trends.
You don’t need to be a data scientist to see this. In the span of four months (less really), we had the August 2023 Core Update, the September 2023 HCU, the October 2023 Link Spam Update, the October 2023 Core Update, the November 2023 Core Update, and then the November 2023 Reviews Update.
The obvious question is: What role does AI play in this? Is AI content behind all of these rank fluctuations?
Yes and no.
The scenario reminds me of COVID. When COVID hit, rankings went berserk. Old queries had new intents, and new queries had to be understood and processed by the algorithm. What’s happening now reminds me of that. And I think part of the reason is AI, but I think it goes beyond AI.
Look at some of the things Google has recently announced, from Notes [an experimental feature in Search Labs] to saying they are trying to reward more content that rests on firsthand knowledge to the perspectives filter to even the additional “E” for experience in E-E-A-T.
I’ve been on a soapbox about this for years: We don’t appreciate how fast content consumption trends change and how impactful those changes are. The web is undergoing a fundamental shift.
Yes, a big part of that is AI-written content, which opens the floodgates. (I know Google has said they are not targeting AI content, just low-quality content. However, to quote Animal House, “What’s the difference?”)
But a lot of that is just how fast content trends are changing. The proof is in the announcements I just mentioned and the theme you see within them. Namely, a focus on information that rests on actual experience and people – not just brands or authors who seemingly only exist in the ethers of the internet.
So what should SEOs focus on in 2024?
Not AI. Not SGE – content trends.
The advent of AI has reignited the conversation around what content users want, how they want to consume it, and how skeptical they are about it (I will tell you this is very much part of the conversation I have with my team at Wix when we create content). To the latter point, the more specific, nuanced, and targeted the content is – the more the consumer will trust it.
Google knows this. And while it has focused on the great AI race to nowhere, I think seeing any lack of growth in Bing’s market share will be taken as a strong signal that AI is not what the user ultimately wants (although it’s probably what the shareholders want, so don’t expect it go anywhere).
Increased topical parsing, increased relevancy, and increased quality (which, for these purposes, I am going to define qua the content’s ability to offer an authentic experience) will circle back around to coming into Google’s primary focus.
Simply, Google, as it usually is (I say usually to factor in the AI wars), is focused on emerging user trends and consumption preferences.
In 2024, I think SEOs should take a step out of the algorithmic bubble and start looking at the content trends that Google themselves are focused on.
7. Katie Morton, Senior Managing Growth Editor, Search Engine Journal
Adaptability and evolving strategy are essential in 2024 and beyond.
With the release of AI, the one thing we can all predict from now until the end of time is exponentially faster technological innovation. This will result in near-constant changes in how we think about and work in an SEO industry that will be marked by—dare I say—upheaval.
While 2023 was stunning in the number of major algorithm updates by Google, we haven’t seen anything yet. SEO pros need to get used to the one-two-punch of constant algorithm updates.
To stay competitive in SERPs, SEO pros and content strategists need to embrace a strategy that involves the creation and optimization of multimodal content—that is, content that includes video, audio, and images, as well as text.
The ability to optimize multimedia content to stay competitive in SERPs will soon dominate the SEO landscape in a big way.
As AI evolves to improve its ability to create content, it makes sense that Google’s own algorithmic AI improves right alongside these developments.
With AI’s growing capability of understanding audio, video, and images, Google’s algorithm will get better at accurately indexing and serving multimedia content. This will add competitive pressure to SEOs who are stuck in a text-only content environment.
Helpful content is king. Google has made it clear that, when it comes to content, helpfulness is more important than ever. Users are increasingly listening to and watching content, and marketers are finding that use of video increases sales.
With the helpfulness of multimodal content, along with Google’s increasing ability to understand video, audio, and images, it stands to reason that multimedia content will begin to play a bigger part in SERPs in 2024.
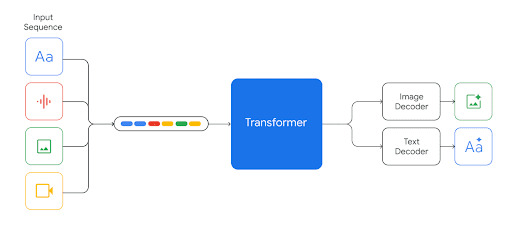
Google recently announced its multimodal AI model, Gemini:
“Gemini is built from the ground up for multimodality — reasoning seamlessly across text, images, video, audio, and code.”
Google promises integration of Gemini in Search, Ads, Chrome, and Duet AI.
Using prompts, Gemini can generate code, and text and images combined. It can also understand, reason and offer insights into vast amounts of data and multimodal inputs.
[Free Download:] Top SEO trends to shape your 2024 strategy
While Google’s launch demo caught flak for being contrived as opposed to an authentic demo, I think that’s a minor point. Gemini is touted as being a significant advancement in large language models (LLMs) and MMLU (massive multitask language understanding).
After its full release, beginning with Gemini Pro on December 13, 2023 and additional version releases staggered in the coming months in 2024, we will have to wait and see whether Gemini lives up to the hype.
It’s likely Gemini’s reputation will remain in flux as it’s benchmarked against the advancements of competitors, and as the AI model continues to learn, and learn faster in the wake of its public deployment.
As if that’s not enough to keep you busy, it will also be key to business success to deepen your symbiotic relationships with marketing, sales, and your product and web development teams.
In the face of ongoing economic challenges, Return on Investment (ROI) is mission-critical. The best SEO pros have business strategy on lock. They have a deep understanding of various revenue streams feeding the different business units they serve, and how to attract those customers organically for maximum revenue generation.
It will be more important than ever for SEO pros to work closely with marketing, sales, product managers, and web developers to capture highly-qualified leads. User Experience (UX), content design, and conversion rate optimization (CRO) will be key to capturing the traffic SEO pros bring to business websites and platforms.
The coming harsh economic realities of 2024 will necessitate a holistic approach to digital strategy—to ensure traffic is not only driven to the website, but also converted into meaningful leads, revenue, and business growth.
In 2024 and beyond, the only constant in SEO will be change. The continual development, training, and integration of AI into the SEO industry; plus, changes in how we create content and what makes it “helpful” in Google’s eyes; and increased economic vulnerability on a global scale will all demand adaptability and strategic foresight.
8. Motoko Hunt, President, International Search Marketing:
As SEO professionals, we tend to focus on the search engine algorithms and rankings/visibilities.
In 2024, I wish more SEOs would pay attention to clients’ business goals and provide the SEO recommendations that help them achieve their goals. It’s one thing to send a list of 100 action items, but it won’t help them unless the items are implemented.
Oftentimes, the delay with the implementation is not that they are not interested in fixing the issues. Each company has different processes, resources, budgets, etc., as well as higher priority items. Try to understand how a client’s SEO/IT/Content processes are set up and how they operate.
If you can prioritize the action items in smaller batches, it usually gets fixed gradually. Things move even quicker if you can create a business case of how a company can benefit from fixing each issue.
We SEOs live deeply in the SEO world, but our clients are not SEO experts. The people who need to discuss (negotiate) the SEO fixes are definitely not SEO experts. By breaking your recommendations down into smaller action items, it’s easier for them to understand what they need to do.
We are in a good time when most businesses understand the importance of SEO. There’s no need to convince them about SEO. At the same time, there are millions of SEOs out there to choose from.
Besides the SEO skills, how you work with clients could separate you from other SEOs in 2024.
9. Suganthan Mohanadasan, Co-founder and product lead, Snippet Digital:
SEO experts should pay attention to changes in how people search online, especially when it comes to new demographics like millennials. It’s worth noting that not everyone relies solely on Google for their online searches anymore.
Social media platforms have become significant search engines for many people, particularly when they’re looking for information about experiences like travel, holidays, or the latest trends.
On the other hand, topics related to medical and financial matters still tend to be searched for on Google. So, it’s important to figure out where your target audience is searching and adjust your content strategy accordingly.
This might mean creating content specifically for certain social media platforms or adapting and sharing existing content in the right channels to connect with your audience effectively.
10. Duane Forrester, VP, Industry Insights, Yext:
I have been doing SEO since 1998, so I’m basing my opinions here on an entire career’s worth of knowledge, learnings, and insights. It’s a constantly evolving space, which makes it challenging to get these predictions right, but always fun to try.
In November of 2022, OpenAI launched ChatGPT broadly. It’s safe to say that at that point, most of us didn’t fully grasp the changes it would bring in such a short time. Yet, we’ve adapted, and I expect more adaptation through 2024.
One key area people will need to focus on and get right is structured data. With the advent of generative AI-powered systems, more and more crawlers are scouring data to feed systems where consumers are turning for answers.
That structured data helps ALL systems better understand content. It’s not just a “Google Thing,” so skipping this, or lagging behind, opens a gap that competitors can move through. Close the door, get it done.
Tight on the heels of this, I expect we’re going to see an entirely new understanding of what it means to be “useful” when it comes to content and customer journeys. Sure, the search engines have been talking to us for years about the importance of “being useful,” but SEO teams still focus on keyword research, producing pages that fill content gaps, and getting it all published.
And while those should remain part of a robust SEO program, teams need to add customer listening, sentiment extraction, and intent understanding into the mix, as well. Keyword research equalling content is an old playbook and one being eclipsed by businesses that effectively listen to customers and give them exactly what they’re looking for.
One prediction close to my heart is that marketing, content, and SEO teams will realize the need for closer collaboration with all teams and put systems into place to break down the silos that have historically existed across these groups. The SEO program needs to understand what’s happening in the social spaces.
Paid needs to share precisely what is and isn’t converting so that SEO can refine strategies with relevant content. There are many more examples, but I’m hopeful that 2024 is the year we start to see this change truly take root in businesses. 2024 is the year of meaningful, cross-team conversations: buy the pizza, invite your teammates, and align on shared goals.
Ending on an AI-related note, I’m predicting that 2024 will be the year when personal agents begin to be widely adopted, reaching a scale of use that has real implications.
We’re on the cusp of a new era in search technology that will be built on a foundation of user confidence in platforms that not only secure their personal information but also take direction from personalized search tools.
These tools, be they virtual characters or GPT-style programs, will conduct searches as effectively as users themselves – and as they become more mainstream, businesses will need to pivot, focusing on structured data and user value to stay relevant.
11. Dan Taylor, Partner & Head of Technical SEO, SALT.agency:
Google’s efforts to surface “hidden gems” in search is going to be something we have to factor into how we structure and portray our webpage’s value propositions and beneficial purposes.
In my opinion, this effort to surface “authentic content” is also, in part, why Reddit has seen such an increase in search visibility – because despite our opinions on how useful or “quality” a lot of content is on the platform, it’s definitely authentic, genuine, and full of first-hand knowledge. This could also be an initial “over-correction”
Doing this scalably across large websites will be a challenge. Still, it is achievable – and one way to develop this within any organization is to leverage content with your evangelists and create “we experience content.”
For ecommerce businesses, this can be as simple as identifying your most loyal customers (sales, lifetime value) and reaching out to engage them in producing content either at a specific product or category level, or content for the wider brand.
This content can add value to product listing pages (PLPs) and product description pages (PDPs), giving them a unique proposition to other brands with the same generic, optimized ecommerce landing pages.
SaaS companies can do this through community-led content by facilitating product and tangential topic conversations in their own environment, taking them away from third-party forums that open the door for competitors to engage.
12. Navah Hopkins, Optmyzr:
This might seem really simple and basic, but there are still folks who don’t have a solid UTM strategy and cookie consent baked into their marketing operations. This is going to come back to bite folks as the privacy first web gets stricter on what can be tracked.
The reason why both cookie consent and UTM parameters are important is attribution is constantly shifting, and if you don’t have a solid UTM strategy, odds are there will be misattributed traffic.
Additionally, with the depreciation of some tracking IDs (like the gclid and fbclid), having a uniform UTM system will ensure PPC and SEO can exist side by side without reporting anomalies. Make sure that naming schemes are the same throughout your organization.
Cookie consent has been a critical item for the EU for years and some parts of the US. In 2024, this is expanding to other US states, and so folks who put it on the back burner or didn’t want to risk visibility now will be playing catch-up.
Cookie consent doesn’t need to be complicated, and you don’t need to make it obtrusive. You do need to make it an opt-in conversation, as well as let folks have the option to select which cookies they’re willing to let you track.
13. Ross Tavendale, Managing Director, Type A:
In 2024, SEOs should be getting to grips with AI. Not as something to create content or to do all your work for you, but as a gateway to massive amounts of computing power that your laptops and even virtual desktops have never seen.
In 2024, SEOs should be zooming out of their campaigns and thinking about deliverables as ‘input databases’ and understanding how they are all connected.
For example, a technical audit is an input database, GSC is an input database, and content gaps are an input database, all joined together with a simple joining key – the URL.
With this in mind, we should be examining how we interact with these deliverables and what outputs we are looking to achieve and use data explorer in GPT to merge, clean, and wrangle this data together.
We should also be thinking about how we can turn John Mueller and Matt Cutts into robots. Getting creative by downloading the transcripts of everything they have ever written and creating a custom GPT bot that can answer your SEO questions for you based on 10 years of their videos, podcasts, and articles.
14. Gianluca Fiorelli, International And Strategic SEO Consultant:
Concentrate on analyzing the search journeys… Using Google as a tool.
We live in the era of Messy Middle; the search results pages bloated with search features and the related increase of the so-called “0 click SERP” are the consequence of how Google is dealing with the Messy Middle.
Therefore, it is even more important now to understand what could be the potential search journey path a person may take starting from an initial “germinal” query.
We can conduct this research with the help of focus groups and audience analyses. However, while this is correct and should not be quit as a procedure to follow, it misses one important thing: what we discover may not necessarily align with what Google thinks the same audience may search for.
So, how can we see the search journeys Google considers the most probable?
Looking at a search feature that has existed practically since the beginning of Google and that has been updated this year: the search menu, which now presents Filters and Topics (see here).
Ok, but how can we use them?
We can use them as a sort of People Also Ask for search journeys. If we can use People Also Ask as a way to discover potential topics for the creation of informational content hubs, we can do something similar with the Topics presented in the Search Menu.
Example: “Painting Warhammer minis” because you are passionate about the Games Workshop game, have a website, and want to be the most visible possible on Google.
[Recommended Read] → SEO Trends 2024
The topics Google presents to us are:
- 40K.
- For Beginners.
- Guide PDF.
- For money.
- Guide book.
- Service.
If we click on them, we are directed to a new SERP showing us the results of the corresponding rewritten query search:
- Painting Warhammer minis 40k.
- Painting Warhammer minis for beginners.
- Warhammer painting guide PDF.
- Painting Warhammer miniatures for money.
- Warhammer 40k painting guide Book.
- Warhammer miniatures painting service.
We already have great insights about three potential search journeys:
- Practical guides about how to paint Warhammer minis: 1) per type of Warhammer game (40K, but it could also be Age of Sigmar or Blood Bowl or any other game). 2) per level (beginners but also medium and advanced painters).
- Painting guides, both as downloadable PDFs (for us, this could be a lead generation goal) and books (affiliate? It could be).
- Warhammer painting marketplace (“painting Warhammer miniatures for money” and “Warhammer miniatures painting service”), which could be our real source of revenue if we want to create a business around the passion and the fans of Warhammer.
This is just a little example of the insights we can think about the potential search journeys our users may take inside Google, during which we should always be visible.
We could – as we can with People Also Ask – dig further by clicking the Topics of the Topics we have just seen above. And they are there, hidden in plain sight.
15. Jono Alderson, Independent Technical SEO Consultant:
As ever, SEO seems to be going through an existential and identity crisis. It’s clear that Google (and others) are continuing to reinvent what a “search” is, and they’re continuing to change the relationship between searches and publishers in the process.
As the internet fills up with near-infinite amounts of derivative, generated content (thanks, SEO industry), Google is understandably becoming pickier about what they ingest and what they return to users.
So it’s no longer enough to produce content, get links, and have a strong technical foundation; that’s not even going to get you indexed in many verticals. And if you do get indexed, there’s no guarantee that your content will turn up on any of Google’s surfaces or send any traffic to your website.
So, what do we do, as a discipline that is fundamentally one that produces content (which Google no longer wants or needs), chases coverage (as the traditional PR industry out-performs us as the role of websites and links diminishes), and improves websites (which play an increasingly passive role in Search)?
I think there are a few practical things we can do.
We can evaluate our content marketing machines with a critical eye (and surveying and feedback tools) to validate that they’re actually designed to help audiences, and not just to try to sell to solution-aware buyers.
We can invest our link-building budgets in training our call center staff, reviewing our user experience, and improving our accessibility.
We can make sure that our senior execs are media trained, on hand to give interviews and quotes to the media, and that they’re producing short-form video that shares and showcases their expertise.
We can give away our best resources for free to win hearts and minds higher up the funnel.
We can choose to stop being a discipline whose job is to produce content, get links, and improve websites. We can be an industry that improves how helpful businesses are to their audiences, using a breadth of domain expertise that no other industry can compare with.
16. Sherry Bonelli, Owner Of Early Bird Digital Marketing:
In 2024, SEOs need to forget about writing “SEO-optimized” content and instead focus on writing helpful content for their readers if they want to rank high on Google. With Google’s Helpful Content System, Google has made it clear that they will reward content that is written for the end user – not content written for search engines.
Google’s Helpful Content System generates a signal used by their automated ranking systems to better ensure people see original, helpful content written for people in search results.
This means that SEOs need to think differently about how they write and optimize content.
First, you must think about the questions that your customers are asking about the products or services you offer and then write authoritative and informative content around those topics. Forget about focusing on keywords and instead focus on answering the questions people have about the topic.
Try to answer the specific questions about the topic as early as possible in the content – don’t write long, flowery paragraphs just to try and get more words into your content. Get to the point and answer the questions.
Also, be sure to add unique content – like research you’ve done, case studies, surveys, a unique perspective from the author, or some other exclusive content that isn’t found in all the other content about the topic. (That means you need to really evaluate competing pages!)
Think about what will make your content stand out among all the other content about the same subject. What does your content have to offer that’s different?
Ensure that the author is writing from experience and that the writer’s experience is clearly demonstrated in the content. Google is looking for expert perspectives from people with true experience about the subject matter – so make sure that the experience is evident in the content.
For example, would you trust content written by a certified LEED Green Associate or someone who is just passionate about using recycled materials to build a building? Which one has more authority and expertise? Google would see the LEED Green Associate as having more authority and expertise if the content is written correctly.
Next, ensure that you are building “writing authorities” at your company – people who are recognized as experts who are knowledgeable about the topics they are writing about.
This needed expertise falls in line with E-E-A-T (Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trust), which is discussed at length in the newly updated Quality Raters Guidelines (which every SEO should become familiar with).
You can do this by having your writers write guest blog posts on leading industry websites, give webinars, speak at events and conferences, be expert panelists, guests on podcasts, etc. Be sure and promote all these things on the author’s bio page on your website and include backlinks to the articles, webinars, podcasts, etc.
Once you have a solid, helpful piece of content written for the reader, then you can optimize the headers, alt tags, title, and description tags — and do the rest of the SEO basics.
In 2024, content is going to be all about the end user. Get started writing helpful content today.
17. Alli Berry, SEO & Content Consultant:
Heading into 2024, I would recommend being dialed into the ongoing antitrust lawsuit against Google and any future lawsuits ahead. It seems likely that this is only the beginning for Google and other big tech companies.
Thanks to the Department of Justice (DOJ), we’ve learned a lot of juicy information about Google’s algorithm, relevant to anyone working in SEO.
For example:
We’ve learned that there are three pillars of rank: on-page (what the document says about itself), links + anchors (what the web says about the document), and user interactions (what users say about the document).
While we have known about on-page and links + anchors for years, the user interactions part has been more of a mystery. In the past, Google has denied using things like click data for rank.
But we’ve now learned that Google is measuring user interactions in four ways:
- Hover/mouse movement.
- Clicks.
- Scrolls.
- Whether the user enters a new query.
While some of the documents revealed with this information are from 2016, we now know how Google has been using click data, and based on some of the information they’ve redacted, they likely still are.
This is actual proof that your metadata needs to do more than contain the right keywords. It should show immediate value to the user, be informative (and compelling), and establish trust to get those clicks. And once you’ve got the click, you need to retain the searcher with content that meets those criteria as well.
Nothing we didn’t necessarily think before – but now we know.
We all should be tuning in to see what else we learn in 2024 from this case.
You can keep tabs on trial documents here.
18. Cyrus Shephard, Founder and Head of Strategy at Zyppy SEO:
So, I hate to say it, but in light of evidence pouring out of the US vs. Google antitrust trial, it’s become surprisingly clear how much Google relies on user behavior data to shape actual web rankings.
For years, Google has told SEOs to “focus on the user,” but we never understood the secret reason that was true: rankings wholly rely on user behavior via clicks, scrolls, additional searches, and more.
What does focusing on the user mean besides the typical empty platitudes? For most, it starts with having a title, description, and favicon that users want to click above all others. But it’s more than that. It showcases a navigation that highlights your Expertise, Authority, and Trust.
Working as a Google Quality Rater, I only have a short time to evaluate each page, and so do users. Is your subject matter expertise clearly obvious on the page? Or do users need to click and hunt it out? Does your logo clearly communicate what you do?
Google can’t likely read your logo, but users can, and Google can read users. Likewise, if you label your blog “Blog” in your navigation, how about labeling it something to show your expertise, such as “Protein Research,” “Tennis News,” or “Coffee Blog.”
Finally, make sure to answer users’ questions as quickly and directly as possible. Google is very good at figuring out when a user is satisfied. These may sound like tired and trite pieces of advice, but we are starting to learn there is a lot of real Google science behind it.
19. Dixon Jones, CEO, Inlinks:
Find a Data Layer of your own!
It is clear that AI is going to make big inroads. We can fight it, but I think that is a bit like burning books or banning the printing press. It is coming anyway, which will herald a new dawn of what may largely be regurgitated junk.
If you have some unique data of your own, then you may be able to leverage this to be one step ahead of the pack.
A great example might be some statistical data of your own. This can be used to generate interesting takes and analyses.
The AI can still help you quickly interpret the data, but if the data is yours and yours alone, then you get something unique and, hopefully, something that people want. Something helpful.
20. Fabrice Canel, Principal Product Manager – Microsoft Bing:
Take control of your SEO game with real-time indexing by adopting IndexNow.
IndexNow is the free protocol empowering websites to take control of their own content indexing instead of depending on unpredictable traditional crawl methods. With a simple ping, websites can now update multiple search engines with their content changes as soon as they happen.
Whether you’re adding, updating, or deleting content, search engines quickly reflect your changes in their search results – giving consumers access to the most relevant information on your website at the time of search.
With rapid ongoing expansion, by 2024, more than 10 search engines are expected to support it, and hundreds of millions of websites will support it.
21. Martha van Berkel, Schema App:
2024 is a year where the value of Schema Markup will go beyond just rich results. Its semantic value will determine how your marketing content is understood by search engines and other AI or Large Language Model (LLM) driven services that seek to provide answers to your customers.
This change will require SEOs to shift from optimizing pages to translating their brand story into the language of machines – Schema.org. They will do this by building a content knowledge graph using Schema Markup.
Your content knowledge graph will help AI and search engines understand the relationships between entities on your site and provide your organization with a control point to ensure your content and brand are understood as you intended.
[Discover:] Expert insights & actionable tips for SEO in 2024
As humans, we aren’t just reading the words when we read content. We’re relating concepts to our experiences and existing knowledge.
For example, the mention of chocolate makes us think of our favorite chocolate bar or reminds us of our childhood experiences. A story about ranking change reminds us of the emotions and learnings we experienced when we won or lost the SEO game.
How the machines’ neural brains work is not so different from ours. AI LLMs are reading content and making meaningful connections across words, topics, and entities to determine what content will evoke emotion, satisfaction, or a click for its human customers.
In 2024, SEOs can use schema markup to build meaningful connections in the data to connect and delight current and future customers.
There is no doubt that SEO is changing more rapidly than at any other time in the 25 year history of the industry.
The challenge for SEO professionals that have been in SEO for more than five years is that they are having to adapt and learn new skills of leveraging AI tools. The edge they have is understanding how search has evolved helps them to look more holistically and bring a deeper knowledge to problem solving.
For those just entering the industry, now is an exciting time and they will be more native at creating prompts and embracing new technology. However, understanding the fundamentals is still essential to be able to know how and when you can use tools.
Experience is still critical, because a tool can never be a replacement for knowledge.
More resources:
Featured Image: Fit Ztudio/Shutterstock