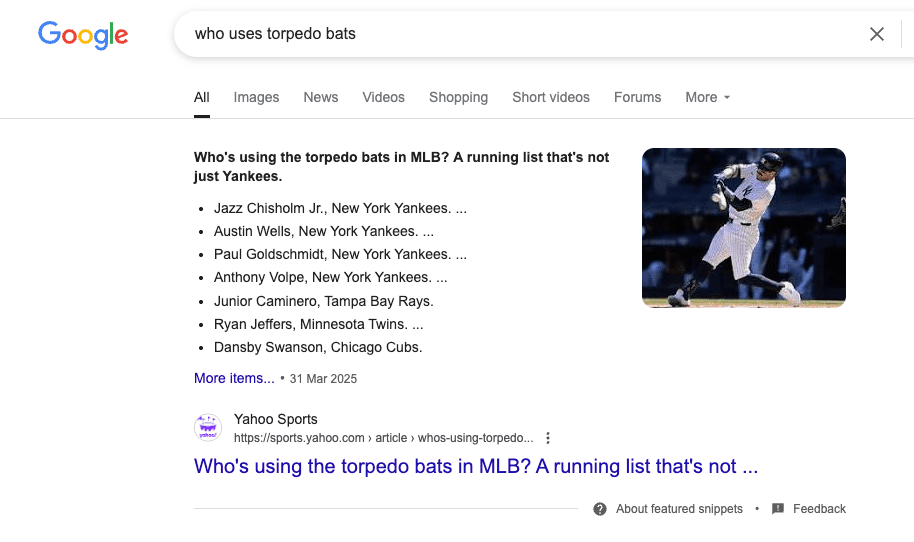
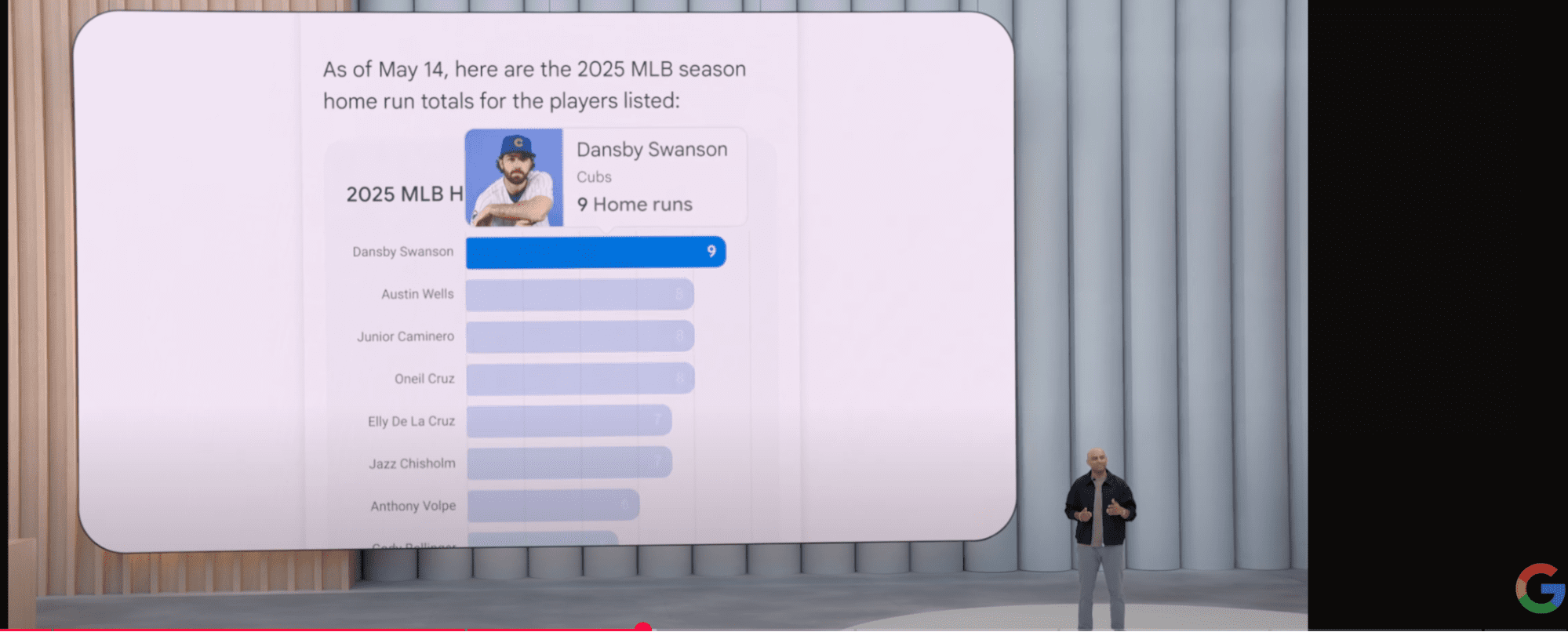
With the introduction of AI Overviews and ongoing Google updates, it’s been a challenging few years for news publishers, and the announcement that Google Discover will now appear on desktop was welcome.
However, the latest announcement of AI Mode could mean that users move away from the traditional search tab, and so the salvation of Discover might not be enough.
To get more insight into the state of SEO for new publishers, I spoke with John Shehata, a leading expert in Discover, digital audience development, and news SEO.
Shehata is the founder of NewzDash and brings over 25 years of experience, including executive roles at Condé Nast (Vogue, New Yorker, GQ, etc.).
In our conversation, we explore the implications of Google Discover launching on desktop, which could potentially bring back some lost traffic, and the emergence of AI Mode in search interfaces.
We also talk about AI becoming the gatekeeper of SERPs and John offers his advice for how brands and publishers can navigate this.
You can watch the full video here and find the full transcript below:
IMHO: Google Discover, AI, And What It Means For Publishers [Transcript]
Shelley Walsh: John, please tell me, in your opinion, how much traffic for news publishers do you think has been impacted by AIO?
John: In general, there are so many studies showing that sites are losing anywhere from 25 to 32% of all their traffic because of the new AI Overviews.
There is no specific study done yet for news publishers, so we are working on that right now.
In the past, we did an analysis about a year ago where we found that about 4% of all the news queries generate an AI Overview. That was like a year ago.
We are integrating a new feature in NewzDash where we actually track AI Overview for every news query as it trends immediately, and we will see. But the highest penetration we saw of AI Overview was in health and business.
Health was like 26% of all the news queries generated AI Overview. I think business, I can’t remember specifically, but it was like 8% or something. For big trending news, it was very, very small.
So, in a couple of months, we will have very solid data, but based on the study that I did a year ago, it’s not as integrated for news queries, except for specific verticals.
But overall, right now, the studies show there’s about a loss of anywhere from 25 to 32% of their traffic.
Can Google Discover Make Up The Loss?
Shelley: I know from my own experience as well that publishers are being really hammered quite hard, obviously not just by AIO but also the many wonderful Google updates that we’ve been blessed with over the last 18 months as well. I just pulled some stats while I was doing some research for our chat.
You said that Google Discover is already the No. 1 traffic source for most news publishers, sometimes accounting for up to 60% of their total Google traffic.
And based on current traffic splits of 90% mobile and 10% desktop, this update could generate an estimated 10-15% of additional Discover traffic for publishers.
Do you think that Discover can actually replace all this traffic that has been lost by AIO? And do you think Discover is enough of a strategy for publishers to go all in on and for them to survive in this climate?
John: Yeah, this is a great question. I have this conspiracy theory that Google is sending more traffic through Discover to publishers as they are taking away traffic from search.
It’s like, “You know what? Don’t get so sad about this. Just focus here: Discover, Discover, Discover.” Okay? And I could be completely wrong.
“The challenge is [that] Google Discover is very unreliable, but at the same time, it’s addictive. Publishers have seen 50-60% of their traffic coming through Discover.”
I think publishers are slowly forgetting about search and focusing more on Discover, which, in my opinion, is a very dangerous approach.
“I think Google Discover is more like a channel, not a strategy. So, the focus always should be on the content, regardless of what channel you’re pushing your content into – social, Discover, search, and so on.”
I believe that Discover is an extension of search. So, even if search is driving less traffic and Discover is driving more and more traffic, if you lose your status in search, eventually you will lose your traffic in Discover – and I have seen that.
We work with some clients where they went like very social-heavy or Discover-heavy kind of approach, you know – clicky headlines, short articles, publish the next one and the next one.
Within six months, they lost all their search traffic. They lost their Discover traffic, and [they] no longer appear in News.
So, Google went to a certain point where it started evaluating, “Okay, this publisher is not a news publisher anymore.”
So, it’s a word of caution.
You should not get addicted to Google Discover. It’s not a long-term strategy. Squeeze every visit you can get from Google Discover as much as you can, but remember, all the traffic can go away overnight for no specific reason.
We have so many complaints from Brazil and other countries, where people in April, like big, very big sites, lost all their traffic, and nothing changed in their technical, nothing changed in their editorial.
So, it’s not a strategy; it’s just a tactic for a short-term period of time. Utilize it as much as you can. I would think the correct strategy is to diversify.
Right now, Google is like 80% of publishers’ traffic, including search, Discover, and so on.
And it’s hard to find other sources because social [media] has kept diminishing over the years. Like Facebook, [it] only retains traffic on Facebook. They try as best as they can. LinkedIn, Twitter, and so on.
So, I think newsletters are very, very important, even if they’re not sexy or they won’t drive 80% [of] other partnerships, you know, and so on.
I think publishers need to seriously consider how they diversify their content, their traffic, and their revenue streams.
The Rise Of AI Mode
Shelley: Just shifting gears, I just wanted to have a chat with you about AI Mode. I picked up something you said recently on LinkedIn.
You said that AI Mode could soon become the default view, and when that happens, expect more impressions and much fewer clicks.
So on that basis, how do you expect the SERPs to evolve over the next year, obviously bearing in mind that publishers do still need to focus on SERPs?
John: If you think about the evolution of SERPs, we used to have the thin blue links, and then Google recognized that that’s not enough, so they created the universal search for us, where you can have all the different elements.
And that was not enough, so it started introducing featured snippets and direct answers. It’s all about the user at the end of the day.
And with the explosion of LLM models and ChatGPT, Perplexity, and all this stuff, and the huge adoption of users over the last 12 months, Google started introducing more and more AI.
It started with SGE and evolved to AI Overview, and recently, it launched AI Mode.
And if you listen to Sundar from Google, you hear the message is very clear: This is the future of search. AI is the future of search. It’s going to be integrated into every product and search. This is going to be very dominant and so on.
I believe right now they are testing the waters, to see how people interact with AI Overviews. How many of them will switch to AI Mode? Are they satisfied with the single summary of an answer?
And if they want to dig more, they can go to the citations or the reference sites, and so on.
I don’t know when AI Mode will become dominant, but if you think, if you go to Perplexity’s interface and how you search, it’s like it’s a mix between AI and results.
If you go to ChatGPT and so on, I think eventually, maybe sooner or later, this is going to be the new interface for how we deal with search engines and generative engines as well.
From all that we see, so I don’t know when, but I think eventually, we’re going to see it soon, especially knowing that Gen Z doesn’t do much search. It’s more conversational.
So, I think we’re going to see it soon. I don’t know when, but I think they are testing right now how users are interacting with AI Mode and AI Overviews to determine what are the next steps.
Visibility, Not Traffic, Is The New Metric
Shelley: I also picked up something else you said as well, which was [that] AI becomes the gatekeeper of SERPs.
So, considering that LLMs are not going to go away, AI Mode is not going to go away, how are you tackling this with the brands that you advise?
John: Yesterday, I had a long meeting with one of our clients, and we were talking about all these different things.
And I advised them [that] the first step is they need to start tracking, and then analyze, and then react. Because I think reacting without having enough data – what is the impact of AI on their platform, on their sites, and traffic – and traffic cannot be the only metric.
For generations now, it’s like, “How much traffic I’m getting?” This has to change.
Because in the new world, we will get less traffic. So, for publishers that solely depend on traffic, this is going to be a problem.
You can measure your transactions or conversions regardless of whether you get traffic or not.
ChatGPT is doing an integration with Shopify, you know.
Google AI Overview has direct links where you can shop through Google or through different sites. So, it doesn’t have to go through a site and then shop, and so on.
I think you have to track and analyze where you’re losing your traffic.
For publishers, are these verticals that you need to focus on or not? You need to track your visibility.
So now, more and more people are searching for news. I shared something on LinkedIn yesterday: If a user said, “Met Gala 2025,” Google will show the top stories and all the news and stuff like this.
But if you slightly change your query to say “What happened at Met Gala? What happened between Trump and Zelensky? What happened in that specific moment or event?”
Google now identifies that you don’t want to read a lot of stories to understand what happened. You want a summary.
It’s like, “Okay, yesterday this is what happened. That was the theme. These are the big moments,” and so on, and it gives you references to dive deeper.
More and more users will be like, “Just tell me the summary of what happened.” And that’s why we’re going to see less and less impressions back to the sites.
And I think also schema is going to be more and more important [in] how ChatGPT finds your content. I think more and more publishers will have direct relationships or direct deals with different LLMs.
I think ChatGPT and other LLMs need to pay publishers for the content that they consume, either for the training data or for grounded data like search data that they retrieve.
I think there needs to be some kind of an exchange or revenue stream that should be an additional revenue stream for publishers.
Prioritize Analysis Over Commodity News
Shelley: That’s the massive issue, isn’t it? That news publishers are working very hard to produce high-quality breaking news content, and the LLMs are just trading off that.
If they’re just going to be creating their summaries, it does take us back, I suppose, to the very early days of Google when everybody complained that Google was doing exactly the same.
Do you think news publishers need to change their strategy and the content they actually produce? Is that even possible?
John: I think they need to focus on content that adds value and adds more information to the user. And this doesn’t apply to every publisher because some publishers are just reporting on what happened in the news. “This celebrity did that over there.”
This kind of news is probably available on hundreds and thousands of sites. So, if you stop writing this content, Google and other LLMs will find that content in 100 different ways, and it’s not a quality kind of content.
But the other content where there’s deep analysis of a situation or an event, or, you know, like, “Hey, this is how the market is behaving yesterday. This is what you need to do.”
This kind of content I think will be valuable more than anything else versus just simply reporting. I’m not saying reporting will go away, but I think this is going to be available from so many originals and copycats that just take the same article and keep rewriting it.
And if Google and other LLMs are telling us we want quality content, that content is not cheap. Producing that content and reporting on that content and the media, and so on, is not cheap.
So, I believe there must be a way for these platforms to pay publishers based on the content they consume or get from the publisher, and even the content that they use in their training model.
The original model was Google: “Hey, we will show one or two lines from your article, and then we will give you back the traffic. You can monetize it over there.” This agreement is broken now. It doesn’t work like before.
And there are people yelling, “Oh, you should not expect anything from Google.” But that was the deal. That was the unwritten deal, that we, for the last two generations, the last two decades, were behaving on.
So, yeah, that’s I think, this is where we have to go.
The Ethical Debate Around LLMs And Publisher Content
Shelley: It’s going to be a difficult situation to navigate. I agree with you totally about the expert content.
It’s something we’ve been doing at SEJ, investing quite heavily in creating expert columns for really good quality, unique thought-leadership content rather than just news cycle content.
But, this whole idea of LLMs – they are just rehashing; they are trading fully off other people’s hard work. It’s going to be quite a contentious issue over the next year, and it’s going to be interesting to see how it plays out. But that’s a much wider discussion for another time.
You touched on something before, which was interesting, and it was about tracking LLMs. And you know, this is something that I’ve been doing with the work that I do, trying to track more and more references, citations in AI, and then referrals from AI.
John: I think one of the things I’m doing is I meet with a lot of publishers. In any given week, I will meet with maybe 10 to 15 publishers.
And by meeting with publishers and listening to what’s happening in the newsroom – what their pain points are, [what] efficiency that they want to work on, and so on, that motivates us – that actually builds our roadmap.
For NewzDash, we have been tracking AI Overview for a while, and we’re launching this feature in a couple of months from now.
So, you can imagine that this is every term that you’re tracking, including your own headlines and what they need to rank for, and then we can tell you, “For this term, AI Overview is available there,” and we estimate the visibility, how it’s going to drop over there.
But we can also tell you for a group of terms or a category, “Hey, you write a lot about iPhones, and this category is saturated with AI Overview. So, 50% of the time for every new iPhone trend – iPhone 16 launch date – yes, you wrote about it, but guess what? AI Overview is all over there, and it’s pushing down your visibility.”
Then, we’re going to expand into other LLMs. So, we’re planning to track mentions and prompts and citations and references in ChatGPT, which is the biggest LLM driver out of all, and then Perplexity and any other big ones.
I think it’s very important to understand what’s going on, and then, based on the data, you develop your own strategy based on your own niche or your content.
Shelley: I think the biggest challenge [for] publisher SEOs right now is being fully informed and finding attribution for connecting to the referrals that are coming from AI traffic, etc. It’s certainly an area I’m looking at.
John, it’s been fantastic to speak to you today, and thank you so much for offering your opinion. And I hope to catch you soon in person at one of your meetups.
John: Thank you so much. It was a pleasure. Thanks for having me.
Thank you to John Shehata for being a guest on the IMHO show.
Note: This was filmed before Google I/O and the announcement of the rollout of AI Mode in the U.S.
More Resources:
Featured Image: Shelley Walsh/Search Engine Journal