How to craft great page titles for SEO?
Writing strong page titles is one of the simplest and most impactful SEO optimizations you can make. The title tag is often the first thing users see in search results, and it helps search engines understand the content of your page.
In this article, you’ll learn what SEO page titles are, why they matter, and how to write titles that improve visibility and attract clicks.
Key takeaways
- Crafting a strong page title is vital for SEO; it attracts clicks and helps search engines understand your content
- An SEO page title appears in search results and browser tabs, serving as the first impression for users
- To optimize your page title, include relevant keywords and ensure it aligns with the content to improve your ranking
- Yoast SEO provides tools to help check title width and keyword usage, and includes an AI-powered title generator
- You can change the page title after publication, and doing so may significantly improve click-through rates
What is an SEO page title?
Let’s start with the basics. If you look at the source of a page (right-click on the page, then choose View Page Source), you find a title in the head section. It looks like this:
This is an example SEO title - Example.com
This is the HTML title tag, also called the SEO title. When you look something up in a search engine, you get a list of results that appear as snippets. The part that looks like a headline is the SEO title. The SEO title typically includes the post title but may also incorporate other elements, such as the site name. Or even emojis!
In most cases, the SEO title is the first thing people see, even before they get on your site. In tabbed browsers, you will usually also see the SEO title in the page tab, as shown in the image below.

What’s the purpose of an SEO title?
Your SEO title aims to entice people to click on it, visit your website, read your post, or purchase your product. If your title is not good enough, people will ignore it and move on to other results. Essentially, there are two goals that you want to achieve with an SEO title:
- It must help you rank for a keyword
- It must make the user want to click through to your page
Google uses many signals when deciding your relevance for a specific keyword. While click-through rate is not a direct ranking factor, user interaction with search results can be a signal that a result matches search intent.
If your page ranks well but attracts few clicks, that may indicate your title doesn’t resonate with searchers. Improving your SEO title can increase clicks and help you perform better over time.
Additionally, as mentioned earlier, Google uses the SEO title specified for your website as a ranking input. So, it’s not just about those clicks; you also need to ensure that your title reflects the topic being discussed on your page and the keyword that you’re focusing on. The SEO title you use has a direct influence on your ranking.
Now that you know the importance of SEO titles, let’s look at how to evaluate and improve them. Tools like Yoast SEO (Free) can help by checking key elements such as title width and keyword usage. Yoast SEO Premium uses generative AI to create titles.
A smarter analysis in Yoast SEO Premium
Yoast SEO Premium has a smart content analysis that helps you take your content to the next level!
Yoast SEO Premium includes an AI-powered title generator that can help you create SEO-friendly page titles based on your content and focus keyphrase. This can be useful for inspiration or for quickly generating alternatives when you’re unsure how to phrase a title.
As with any AI-generated content, it’s best to review and refine the suggested titles to ensure they align with your page’s intent, brand voice, and audience expectations.
In addition, if you use Yoast SEO Premium, you get various other AI features, like Yoast AI Optimize, that help you do the hard work.



What does the empty title check in Yoast SEO do?
The empty title check in Yoast SEO Premium is self-explanatory: it checks whether you’ve filled in any text in your post’s ‘Title’ section. If you haven’t, you’ll see a red traffic light reminding you to add a title. Once this is filled in, the post title can be automatically added to the SEO title field using the ‘Title’ variable.



Note that your post title is output as an H1 heading. A clear H1 helps users quickly understand what a page is about, improves accessibility for screen readers, and aids search engines in interpreting the page structure. You should only use one H1 heading per page to avoid confusing search engines. Don’t worry; we’ve got a check for multiple H1 headings in Yoast SEO!
What does the SEO title width check in Yoast SEO do?
You will find this check in the SEO tab of the Yoast SEO sidebar or meta box. If you haven’t written an SEO title yet, this will remind you to do so. Additionally, Yoast SEO verifies the width of your SEO title. When it is too long, you will get a warning.
We used to warn you if your SEO title was too short, but we’ve changed that since our Yoast 17.1 release. A title with an optimal width gets you a green traffic light in the analysis. Remember that we exclude the separator symbol and site title from the title width check. We don’t consider these when calculating the SEO title progress bar.



How to write an SEO title with an optimal width
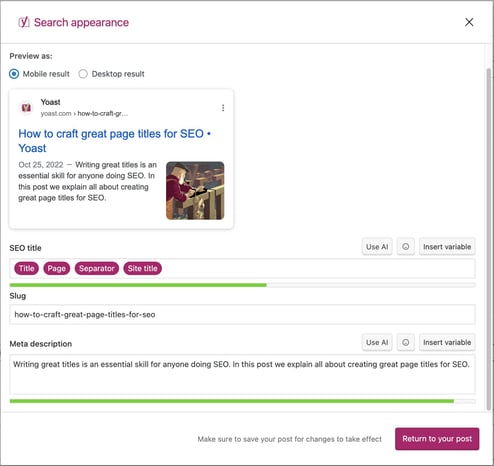
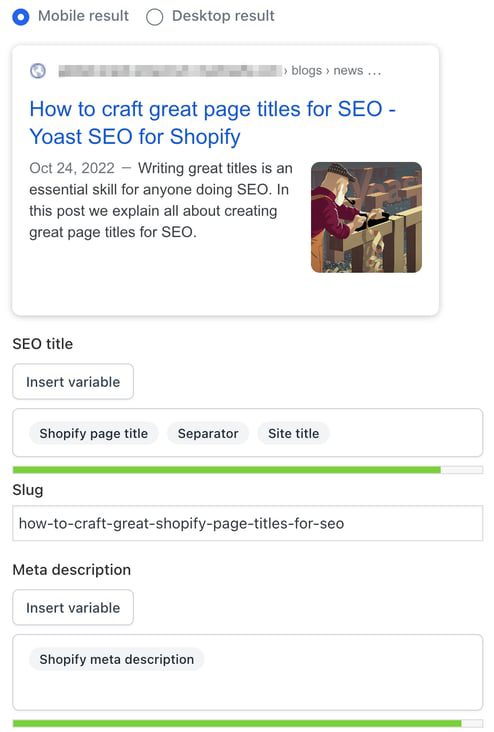
If your SEO title doesn’t have the correct width, parts of it may be cut off in Google’s search results. The result may vary, depending on the device you’re using. That’s why you can also check how your SEO title will look in the mobile and desktop search results in the Search appearance section of Yoast SEO. The tool defaults to the mobile version, but you can also switch to view it in the desktop version.
Here’s a desktop result:



And here’s the mobile result for the same URL:



As a general guideline, aim for a title that fully displays on mobile search results, clearly communicates the main topic, and avoids unnecessary filler words. If your title fits visually and still reads naturally, you’re on the right track.
Width vs. Length
Have you noticed that we talk about width rather than length? Why is that? Rather than using a character count, Google has a fixed width for the titles counted in pixels. While your title tags can be long, and Google doesn’t have a set limit on the number of characters you can use, there is a limit on what’s visible in the search results. If your SEO title is too wide, Google will visually truncate it. That might be different from what you want. Additionally, avoid wasting valuable space by keeping the title concise and clear. Additionally, the SEO title often informs other title-like elements, such as the og:title, which also has display constraints.
Luckily, our Search appearance section can help you out! You can fill in your SEO title; our plugin will provide you with immediate feedback. The green line underneath the SEO title turns red when your title is too long. Keep an eye on that and use the feedback to create great headlines.




What does the keyphrase in the SEO title check in Yoast SEO do?
This check appears in the SEO tab of the Yoast SEO sidebar in WordPress and Shopify, as well as in the meta box in WordPress. It checks if you’re using your keyphrase in the SEO title of your post or page. This check is intentionally strict because the SEO title plays an important role in signaling a page’s topic to both search engines and users. Since Google uses the title to figure out your page’s topic, not having the focus keyphrase in the SEO title may harm your rankings. Additionally, potential visitors are more likely to click on a search result that matches their query. For optimal results, try to include your keyphrase at the beginning of the SEO title.



How to use your keyphrase in the SEO title
Sometimes, when optimizing for a highly competitive keyword, everyone will have the keyword at the beginning of the SEO title. In that case, you can try making it stand out by putting one or two words before your focus keyword, thereby slightly “indenting” your result. In Yoast SEO, if you start your SEO title with “the”, “a”, “who”, or another function word followed by your keyphrase, you’ll still get a green traffic light.
At other times, such as when you have a very long keyphrase, adding the complete keyphrase at the beginning doesn’t make sense. If your SEO title looks weird with the keyphrase at the beginning, try to add as much of the keyphrase as early in the SEO title as possible. But always keep an eye on the natural flow and readability.
How to reduce the chance of Google rewriting your SEO title
Google may rewrite titles when they are overly long, stuffed with keywords, misleading, or inconsistent with the page’s main heading.
To reduce the likelihood of rewrites:
- Make sure your SEO title closely matches your page’s H1
- Avoid excessive separators, repetition, or boilerplate text
- Ensure the title accurately reflects the page content
While rewrites can still happen, clear and concise titles are more likely to be shown as written.
Want to learn how to write text that’s pleasant to read and optimized for search engines? Our SEO copywriting course can help you with that. You can access this course and our other SEO courses with Yoast SEO Premium. This also gives you access to extra features in the Yoast SEO plugin.
Are you struggling with more aspects of SEO copywriting? Don’t worry! We can teach you to master all facets, so you’ll know how to write awesome copy that ranks. Take a look at our SEO copywriting training and try the free trial lessons!
Crafting SEO-friendly page title: FAQs
Are the SEO title and the H1 heading the same?
To be clear, you should not confuse the SEO title with the post title; both serve different purposes and do not have to be the same.
The post title, also known as the H1 heading, is the main heading users see on the page. Its primary role is to help readers understand what the page is about and to add structure to your content. You should always write your H1 with users in mind.
The SEO title is the title that appears in search results and in the browser tab. This title helps search engines understand the topic of your page and influences whether users click on your result.
While the SEO title and H1 can be similar, they do not need to be identical. In WordPress, tools like Yoast SEO allow you to set a separate SEO title, giving you more control over how your page appears in search results without changing the on-page heading.
Should you add your brand to the SEO title?
For quite some time, it was a common practice among some SEOs to omit the site name from the SEO title. The idea was that the “density” of the title mattered, and the site name wouldn’t help with that. Don’t do this. If possible, your SEO title should include your brand, preferably in a recognizable way. If people search for a topic and see your brand several times, even if they don’t click on it the first time, they might click when they see you again on their next page of results.
However, with the site name and favicon updates, be sure to fill in the site settings, upload a favicon, and make general changes to the design of the snippets. This will increase your brand’s visibility in search results. Today, you’ll notice that Google hardly shows your brand name in the snippet’s title. However, Google often has a mind of its own when generating titles to change them for any given reason. The design and function of the SERPs can change at any moment, so we still recommend adding your brand to your titles.
Can you change the SEO title after a page is published?
Yes. You can change the SEO title even after a page has been published, and doing so can improve performance.
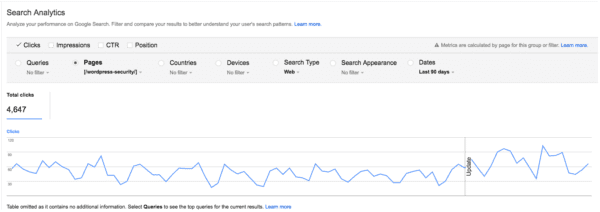
At Yoast, we once noticed that although we ranked well for “WordPress security,” the page was not getting as much traffic as expected. We updated the SEO title and meta description to make them more engaging and relevant. As a result, traffic to that page increased by over 30 percent.


The original SEO title was:
WordPress Security • Yoast
We changed it to:
WordPress Security in a few easy steps! • Yoast
This change did not significantly affect rankings, but it did improve click-through rates. The keywords stayed largely the same, but the title became more compelling for searchers.
This shows that optimizing SEO titles after publication can be an effective way to increase traffic, especially if your page already ranks well but receives fewer clicks than expected.
Does Google always use the SEO title you set?
No. Google does not always display the exact SEO title you set in search results.
That said, the HTML title tag is still the most common source Google uses for generating title links. Google Search uses the following sources to automatically determine title links:
- The
- The main visible heading on the page, such as the
- Other headings on the page
- Prominent text styled to stand out
- Anchor text from internal or external links
- Structured data related to the website
Google typically selects one title per page and does not change it for different queries.
What does this mean for you? The SEO title you set remains important for ranking and relevance. Even if Google sometimes displays a different version, your title still helps search engines understand the content of your page.
To stay on top of changes, monitor your key pages in Google Search Console, check how titles appear in search results, and watch for shifts in click-through rates.
Can you use the same title for SEO and social media?
You can, but it is often better not to.
What might be a good SEO title isn’t necessarily a good title for social media. In social media, keyword optimization is less important than creating a title that entices people to click. You often don’t need to include the brand name in the title. This is especially true for Facebook and X if you include some branding in your post image. Our social media appearance previews in Yoast SEO Premium and Yoast SEO for Shopify can help you.
If you use Yoast SEO, you can set different titles for Google, Facebook, and X. Enter your SEO title in the snippet editor, then customize the social media titles in the social tab. If you do not set a specific X title, X will use the Facebook title by default.
This flexibility allows you to optimize your titles for both search engines and social platforms without compromise.