Agentic Commerce Optimization: A Technical Guide To Prepare For Google’s UCP via @sejournal, @alexmoss
In January, I wrote about the birth of agentic commerce through both Agentic Commerce Protocol (ACP) and Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP), and how this could impact us all as consumers, business owners, and SEOs. As we still sit on waitlists for both, this doesn’t mean that we can’t prepare for it.
UCP fixes a real-life problem for many, minimizing the fragmented commerce journey. Instead of building separate integrations for every agent platform as we have been mostly doing in the past, you can now [theoretically] integrate once and will integrate seamlessly with other tools and platforms.
But note here that, as opposed to ACP which focuses more so on the checkout → fulfillment → payment journey, UCP goes beyond this with six capabilities covering the entire commerce lifecycle.
This, of course, will impact an SEO’s ambit. As we shift from optimizing for clicks to optimizing for selection, we also need to ensure that it’s you/your client that is selected through data integrity, product signals, and AI-readable commerce capabilities. Structured data has always served an important role for the internet as a whole and will continue to be the driving force on how you can serve agents, crawlers, and humans in the best way possible.
I allude to a possible new acronym “ACO” – Agentic Commerce Optimization – and the following could be considered the closest we can get to guidelines on how we undertake it.
UCP Isn’t Coming, It’s Here
UCP was only announced in January, but there’s already confirmation that its capabilities are rolling out. On Feb. 11, 2026, Vidhya Srinivasan (VP/GM of Advertising & Commerce at Google) announced that Wayfair and Etsy now use UCP so that you can purchase directly within AI Mode, and was observed the next day by Brodie Clark.
UCP’s Six Layered Capabilities
On the day UCP was released, Google explained its methodology.
From this, I defined six core capabilities:
- Product Discovery – how agents find and surface your inventory during research.
- Cart Management – multi-item baskets, dynamic pricing, complex basket rules.
- Identity Linking – OAuth 2.0 authorization for personalized experiences and loyalty.
- Checkout – session creation, tax calculation, payment handling.
- Order Management – webhook-based lifecycle and logistical updates.
- Vertical Capabilities – extensible modules for specialized use cases like travel booking windows or subscription schedules.
UCP’s schema authoring guide shows how capabilities are defined through versioned JSON schemas, which act as the foundation of the protocol. When it comes to considering this as an SEO, properties such as offers, aggregateRating, and shippingDetails aren’t just for surfacing rich snippets, etc., for product discovery, they’re now what agents query during the entire process.
Schema Is, And Will Continue To Be, Essential
UCP’s technical specification uses its own JSON schema-based vocabulary. Whilst it doesn’t build on schema.org directly, it remains critical in the broader ecosystem. As Pascal Fleury Fleury said at Google Search Central Live in December, “schema is the glue that binds all these ontologies together”. UCP handles the transaction; schema.org helps agents decide who to transact with.
Ensure you’re on top of and populate product schema as much as you can. It may seem like SEO 101. Regardless, audit all of this now to ensure you’re not missing anything when UCP really rolls out.
This includes checks on:
- Product schema (with complete coverage): All core fields: name, description, SKU, GTIN, brand, related images, and offers.
- Offers must include: Price, priceCurrency, availability, URL, seller. Add aggregateRating and review to ensure you have positive third-party perspective.
- Ensure all product variants output correctly.
- Include shippingDetails with delivery estimates.
- Organization and Brand: Assists with “Merchant of Record” verification. If you’re not an Organization, then fallback to Person.
- Designated FAQPage: Ensure you have an FAQpage as these can be incorporated alongside product-level FAQs and used as part of its decision-making.
Prepare Your Merchant Center Feed
UCP will utilize your existing Merchant Center feed as the discovery layer. This means that beyond the normal on-site schema you provide, Merchant Center itself requires more details that you can populate within its platform.
- Return policies (required to be a Merchant of Record): Complete all return costs, return windows, and policy links. These will be used not just within the checkout and transactional areas, but again a consideration for selection at all. Advanced accounts need policies at each sub-account level.
- Customer support information: Not only would initial information be offered to the customer, but there may be ways in which entry-level customer support queries can be completely managed, thus increasing customer satisfaction while minimizing customer support agent capacity.
- Agentic checkout eligibility: Add the native_commerce attribute to your feed, as products are only eligible here if this is set up.
- Product identifiers: Each product must have an ID, and correlate to the product ID when using the checkout API.
- Product consumer warnings: Any product warning should assert the consumer_notice attribute.
Google recommends that this be done through a supplemental data source in Merchant Center rather than modifying your primary feed, which would prevent incorrect formatting or other invalidation.
Lastly, double-check if the products you’re selling aren’t included within its product restrictions list, as there are several that, if you do offer those things, you should consider how to manage alongside the abilities of UCP.
Optimizing Conversational Commerce Attributes
Within the UCP blog post announcement, Srinivasan introduced a way for more clarity with conversational commerce attributes:
“…we’re announcing dozens of new data attributes in Merchant Center designed for easy discovery in the conversational commerce era, on surfaces like AI Mode, Gemini and Business Agent. These new attributes complement retailers’ existing data feeds and go beyond traditional keywords to include things like answers to common product questions, compatible accessories or substitutes.”
These provide further clarity (and therefore minimize hallucinations) during the discovery process in order to be selected or ruled out.
Not only would this incorporate product and brand-related FAQs, but take this a step further to also consider:
- Compatibility: Potential up-sell opportunities.
- Substitution: An opportunity for dealing with out-of-stock items.
- Related products: Great for cross-sell opportunities.
Furthermore, this can be used to become even more specific, moving beyond basic attributes to agent-parseable details. Now, if a product is “purple” on a basic level, “dark purple” or even something unobvious, such as “Wolf” (real example below), may be more appropriate for finer detail while still falling under “purple.” The same can be considered for sizes, materials (or a mixture of materials), etc.
Multi-Modal Fan-Out Selection
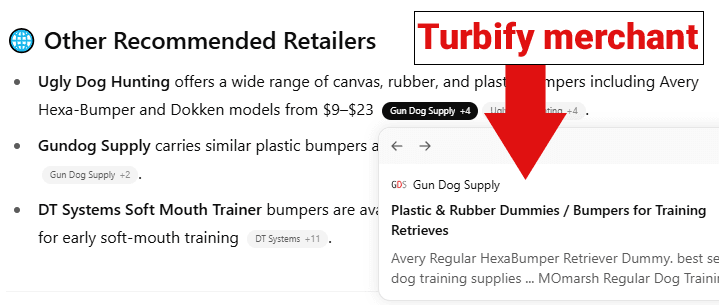
When executed well, optimizing for conversational commerce attributes will increase the possibility of selection within fan-out query results. When considering some of these attributes, it is worth looking at tools, such as WordLift’s Visual Fan-Out simulator, which illustrates how a single image decomposes into multiple search intents, revealing which attributes agents may prioritize when performing query fan-out. But how would this look?
As an example, I used one product image and browsed downward three horizons. Using On’s Cloudsurfer Max as an example (used with permission):
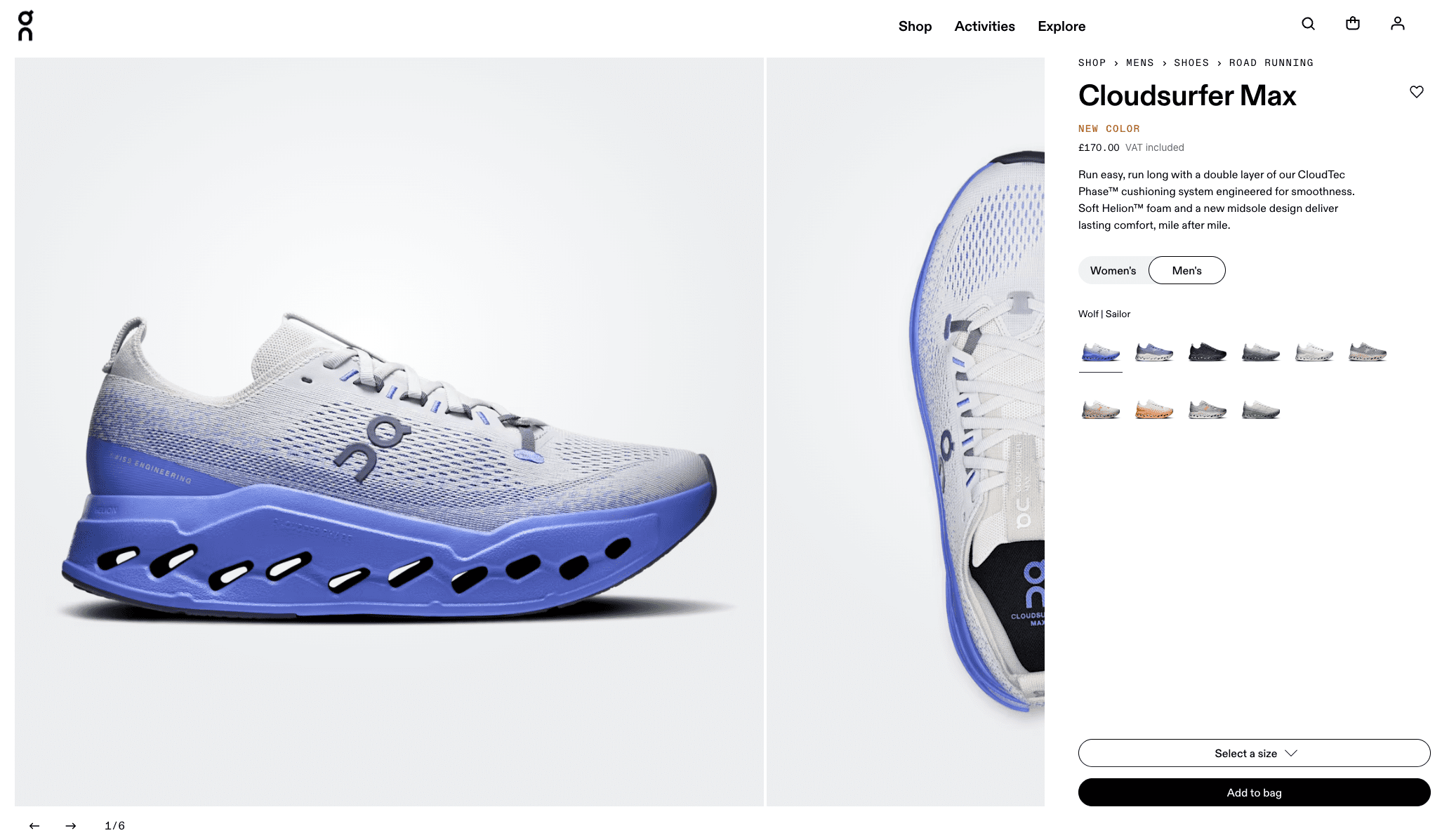
Using just one product image, this is what is presented on the surface:
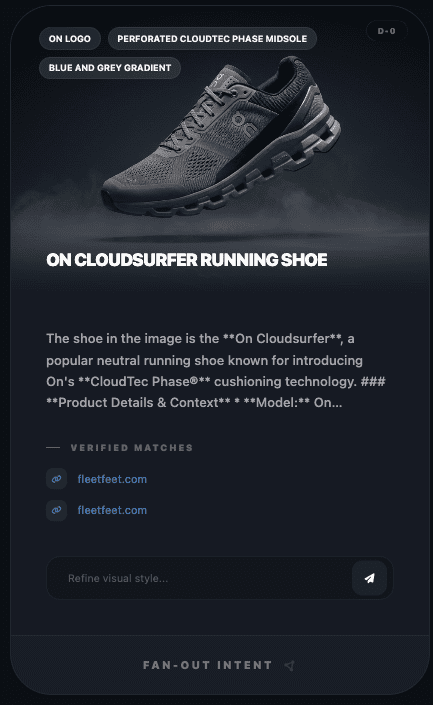


It immediately noticed that the product was On, and specifically from the Cloudsurfer range. Great start! Now let’s see what it sees over the horizon:
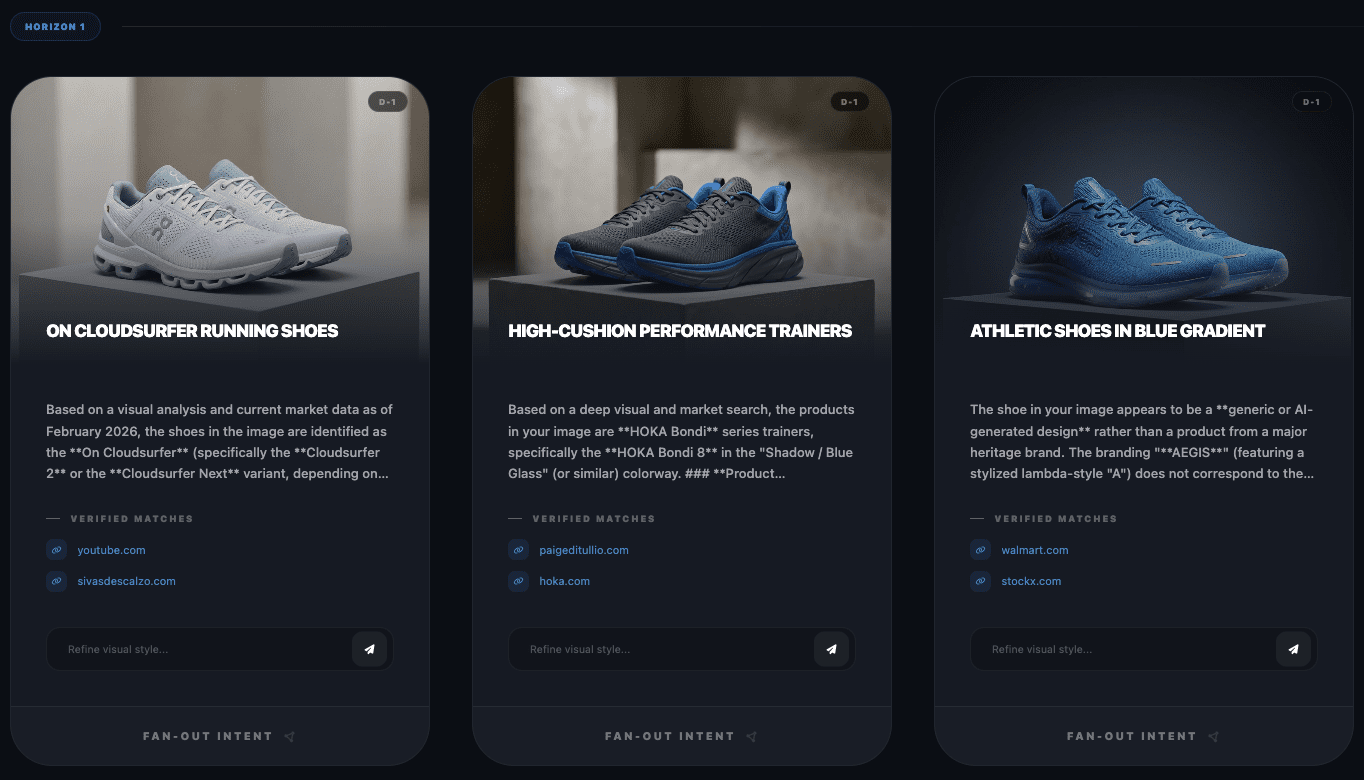


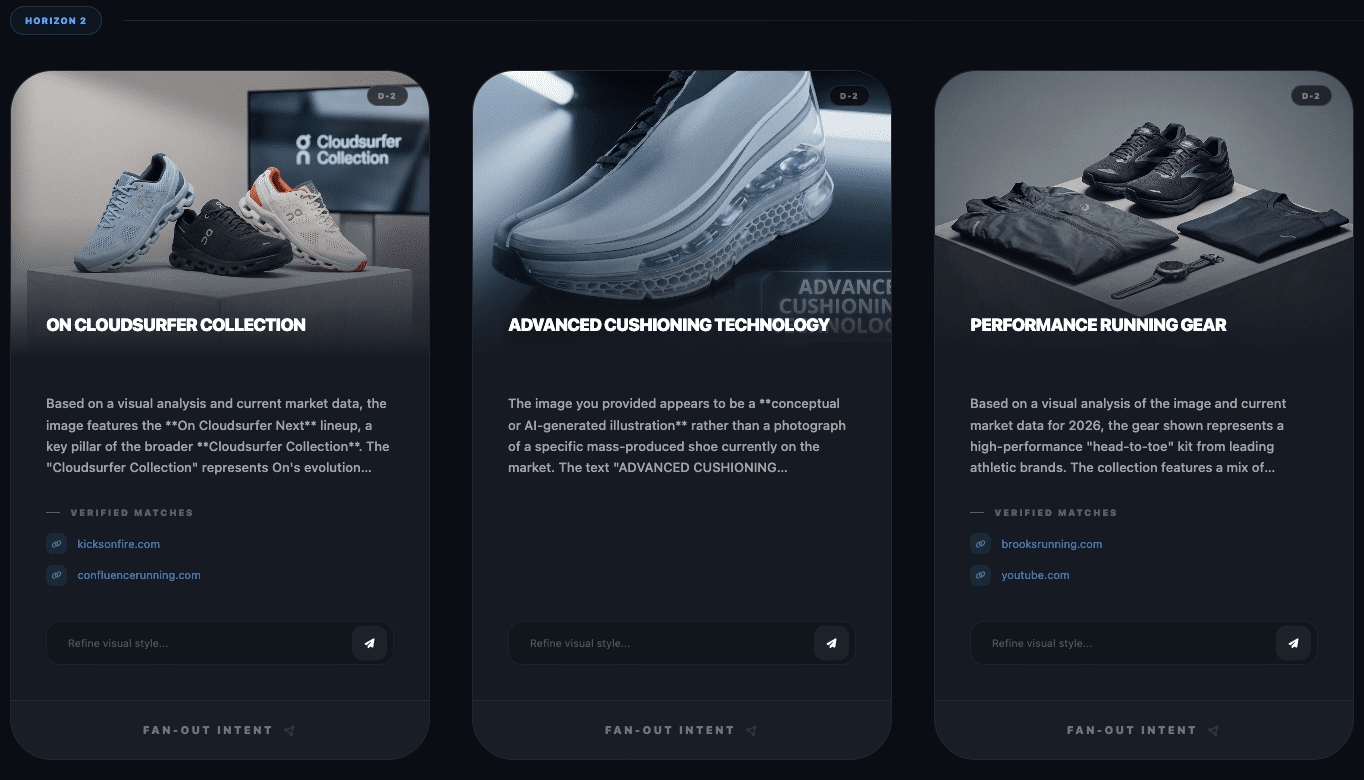


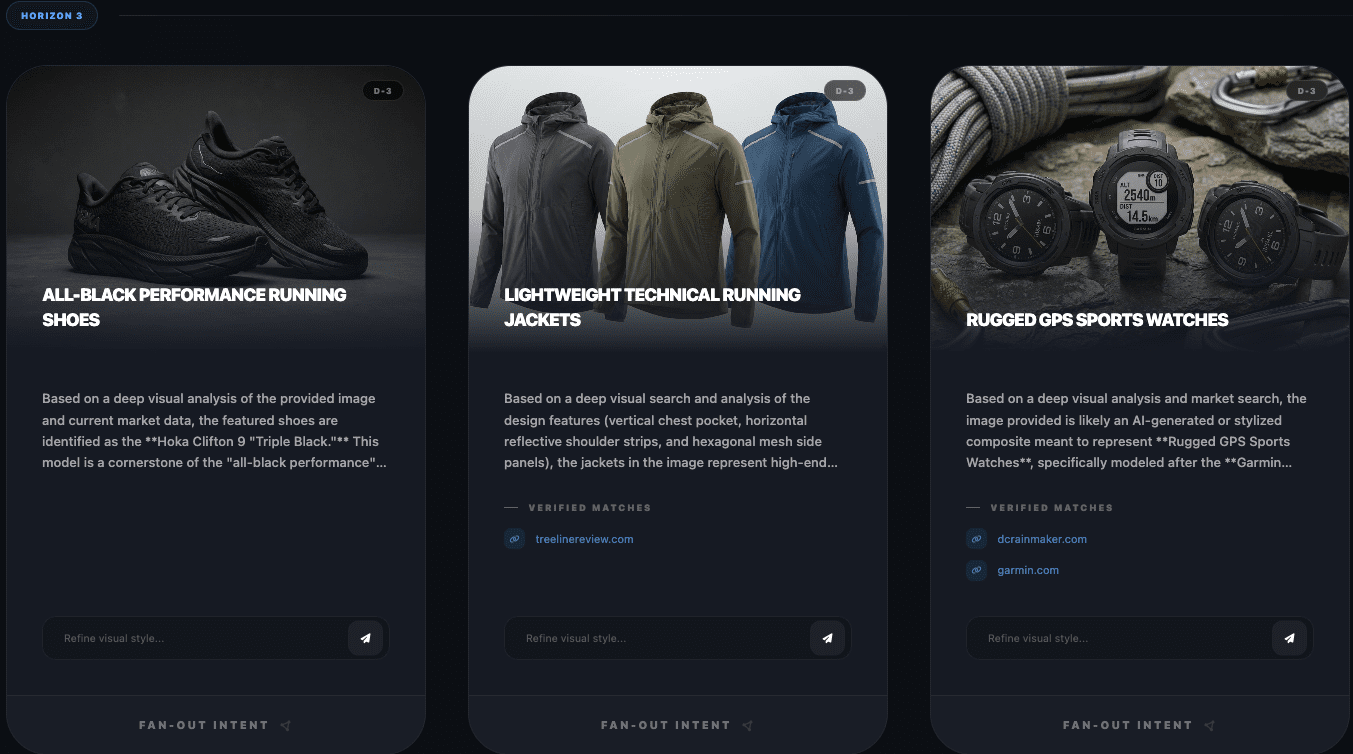


Here, you can draw inspiration or direction on how best to place yourself for potential and likely fan-out queries. With this example, I found it interesting that Horizon 2 mentions performance running gear as a large category, then when performing fan-out on that showed the related products around gear in general. This shows how wide LLMs consider selection and how you can present attributes to attract selection.
UCP’s Roadmap Is Expanding Into Multi-Verticals
UCP is already planning to go beyond one single purchase but expands beyond retail into travel, services, and other verticals. Its roadmap details several priorities over the coming year, including:
- Multi‑item carts and complex baskets: Moving beyond single‑item checkout to native multi‑item carts, bundling, promotions, tax/shipping logic, and more realistic fulfillment handling.
- Loyalty and account linking: Standardized loyalty program management and account linking so agents can apply points, member pricing, and benefits across merchants.
- Post‑purchase support: Support for order tracking, returns, and customer‑service handoff so agents can manage customer support post-sale.
- Personalization signals: Richer signals for cross‑sell/upsell, wishlists, history, and context‑based recommendations.
- New verticals: Expansion beyond retail into travel, services, digital goods, and food/restaurant use cases via extensions to the protocol.
Each of the points above is worth further reading and consideration if this is something your brand may offer. Furthermore, its plans to expand beyond retail into travel, services, digital goods, and hospitality mean that, if you’re working within any of these verticals, you need to be even more prepared to ensure eligibility.
Social Proof And Third-Party Perspective
Regardless of how well you may optimize on-site to prepare for UCP, all this data integrity still needs to be validated by trusted third-party sources.
Third-party platforms, such as Trustpilot and G2, appear to be frequently cited and trusted among most of the LLMs, so I’d still advise that you continue to collect those positive brand and product reviews in order to satisfy consensus, resulting in more opportunities to be selected during product discovery.
TL;DR – Prepare Now
If you own or manage any form of ecommerce site, now is the time to ensure you’re preparing for UCP’s rollout as soon as possible. It’s only a matter of time, and with AI Mode spreading into default experiences, getting ahead of the rollout is essential.
- Join the UCP waitlist.
- Prepare Merchant Center: return policies, native_commerce attribute.
- Ensure your developers research and understand the UCP documentation.
- Populate conversational attributes: question-answers, compatibility, substitutes.
- Audit and improve any schema where applicable.
This is moving faster than most previous commerce shifts, and brands that wait for full rollout signals will already be behind. This isn’t a short-term LLM gimmick but is part of the largest change in the ecommerce space.
More Resources:
Featured Image: Roman Samborskyi/Shutterstock