Why OpenAI’s Open Source Models Are A Big Deal via @sejournal, @martinibuster
OpenAI has released two new open-weight language models under the permissive Apache 2.0 license. These models are designed to deliver strong real-world performance while running on consumer hardware, including a model that can run on a high-end laptop with only 16 GB of GPU.
Real-World Performance at Lower Hardware Cost
The two models are:
- gpt-oss-120b (117 billion parameters)
- gpt-oss-20b (21 billion parameters)
The larger gpt-oss-120b model matches OpenAI’s o4-mini on reasoning benchmarks while requiring only a single 80GB GPU. The smaller gpt-oss-20b model performs similarly to o3-mini and runs efficiently on devices with just 16GB of GPU. This enables developers to run the models on consumer machines, making it easier to deploy without expensive infrastructure.
Advanced Reasoning, Tool Use, and Chain-of-Thought
OpenAI explains that the models outperform other open source models of similar sizes on reasoning tasks and tool use.
According to OpenAI:
“These models are compatible with our Responses API(opens in a new window) and are designed to be used within agentic workflows with exceptional instruction following, tool use like web search or Python code execution, and reasoning capabilities—including the ability to adjust the reasoning effort for tasks that don’t require complex reasoning and/or target very low latency final outputs. They are entirely customizable, provide full chain-of-thought (CoT), and support Structured Outputs(opens in a new window).”
Designed for Developer Flexibility and Integration
OpenAI has released developer guides to support integration with platforms like Hugging Face, GitHub, vLLM, Ollama, and llama.cpp. The models are compatible with OpenAI’s Responses API and support advanced instruction-following and reasoning behaviors. Developers can fine-tune the models and implement safety guardrails for custom applications.
Safety In Open-Weight AI Models
OpenAI approached their open-weight models with the goal of ensuring safety throughout both training and release. Testing confirmed that even under purposely malicious fine-tuning, gpt-oss-120b did not reach a dangerous level of capability in areas of biological, chemical, or cyber risk.
Chain of Thought Unfiltered
OpenAI is intentionally leaving Chain of Thought (CoTs) unfiltered during training to preserve their usefulness for monitoring, based on the concern that optimization could cause models to hide their real reasoning. This, however, could result in hallucinations.
According to their model card (PDF version):
“In our recent research, we found that monitoring a reasoning model’s chain of thought can be helpful for detecting misbehavior. We further found that models could learn to hide their thinking while still misbehaving if their CoTs were directly pressured against having ‘bad thoughts.’
More recently, we joined a position paper with a number of other labs arguing that frontier developers should ‘consider the impact of development decisions on CoT monitorability.’
In accord with these concerns, we decided not to put any direct optimization pressure on the CoT for either of our two open-weight models. We hope that this gives developers the opportunity to implement CoT monitoring systems in their projects and enables the research community to further study CoT monitorability.”
Impact On Hallucinations
The OpenAI documentation states that the decision to not restrict the Chain Of Thought results in higher hallucination scores.
The PDF version of the model card explains why this happens:
Because these chains of thought are not restricted, they can contain hallucinated content, including language that does not reflect OpenAI’s standard safety policies. Developers should not directly show chains of thought to users of their applications, without further filtering, moderation, or summarization of this type of content.”
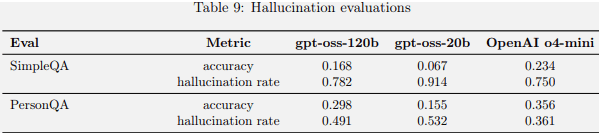
Benchmarking showed that the two open-source models performed less well on hallucination benchmarks in comparison to OpenAI o4-mini. The model card PDF documentation explained that this was to be expected because the new models are smaller and implies that the models will hallucinate less in agentic settings or when looking up information on the web (like RAG) or extracting it from a database.
OpenAI OSS Hallucination Benchmarking Scores
Takeaways
- Open-Weight Release
OpenAI released two open-weight models under the permissive Apache 2.0 license. - Performance VS. Hardware Cost
Models deliver strong reasoning performance while running on real-world affordable hardware, making them widely accessible. - Model Specs And Capabilities
gpt-oss-120b matches o4-mini on reasoning and runs on 80GB GPU; gpt-oss-20b performs similarly to o3-mini on reasoning benchmarks and runs efficiently on 16GB GPU. - Agentic Workflow
Both models support structured outputs, tool use (like Python and web search), and can scale their reasoning effort based on task complexity. - Customization and Integration
The models are built to fit into agentic workflows and can be fully tailored to specific use cases. Their support for structured outputs makes them adaptable to complex software systems. - Tool Use and Function Calling
The models can perform function calls and tool use with few-shot prompting, making them effective for automation tasks that require reasoning and adaptability. - Collaboration with Real-World Users
OpenAI collaborated with partners such as AI Sweden, Orange, and Snowflake to explore practical uses of the models, including secure on-site deployment and custom fine-tuning on specialized datasets. - Inference Optimization
The models use Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) to reduce compute load and grouped multi-query attention for inference and memory efficiency, making them easier to run at lower cost. - Safety
OpenAI’s open source models maintain safety even under malicious fine-tuning; Chain of Thoughts (CoTs) are left unfiltered for transparency and monitorability. - CoT transparency Tradeoff
No optimization pressure applied to CoTs to prevent masking harmful reasoning; may result in hallucinations. - Hallucinations Benchmarks and Real-World Performance
The models underperform o4-mini on hallucination benchmarks, which OpenAI attributes to their smaller size. However, in real-world applications where the models can look up information from the web or query external datasets, hallucinations are expected to be less frequent.
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Good dreams – Studio