Top 15 Ways To Secure A WordPress Site via @sejournal, @inmotionhosting

Thankfully, there are plenty of steps you can take to protect your WordPress website.
Easy WordPress Security Basics
When setting up your WordPress site security, there are some basic things you can do to beef up your protection.
Below, we will take a look at some of the first things you should do to help protect your website.
1. Implement SSL Certificates
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates are a standard technology that establishes an encrypted connection between a web server (host) and a web browser (client). This connection ensures all data passed between the two remains private and intrinsic.
SSL certificates are an industry-standard used by millions of websites to protect their online transactions with their customers, and obtaining one should be one of the first steps you take to secure your website.
2. Require & Use Strong Passwords
Along with obtaining an SSL certificate, one of the very first things you can do to protect your site is use strong passwords for all your logins.
It might be tempting to create or reuse a familiar or easy-to-remember password, but doing so puts both you and your website at risk. Improving your password strength and security decreases your chances of being hacked. The stronger your password, the less likely you are to be a victim of a cyberattack.
When creating a password, there are some general password best practices you should follow.
If you aren’t sure if you are using a strong enough password, you check the strength of one by using a free tool like this helpful Password Strength Checker.
3. Install A Security Plugin
WordPress plugins are a great way to quickly add useful features to your website, and there are several great security plugins available.
Installing a security plugin can add some extra layers of protection to your website without requiring much effort.
To get you started, check out this list of recommended WordPress security plugins.
4. Keep WordPress Core Files Updated
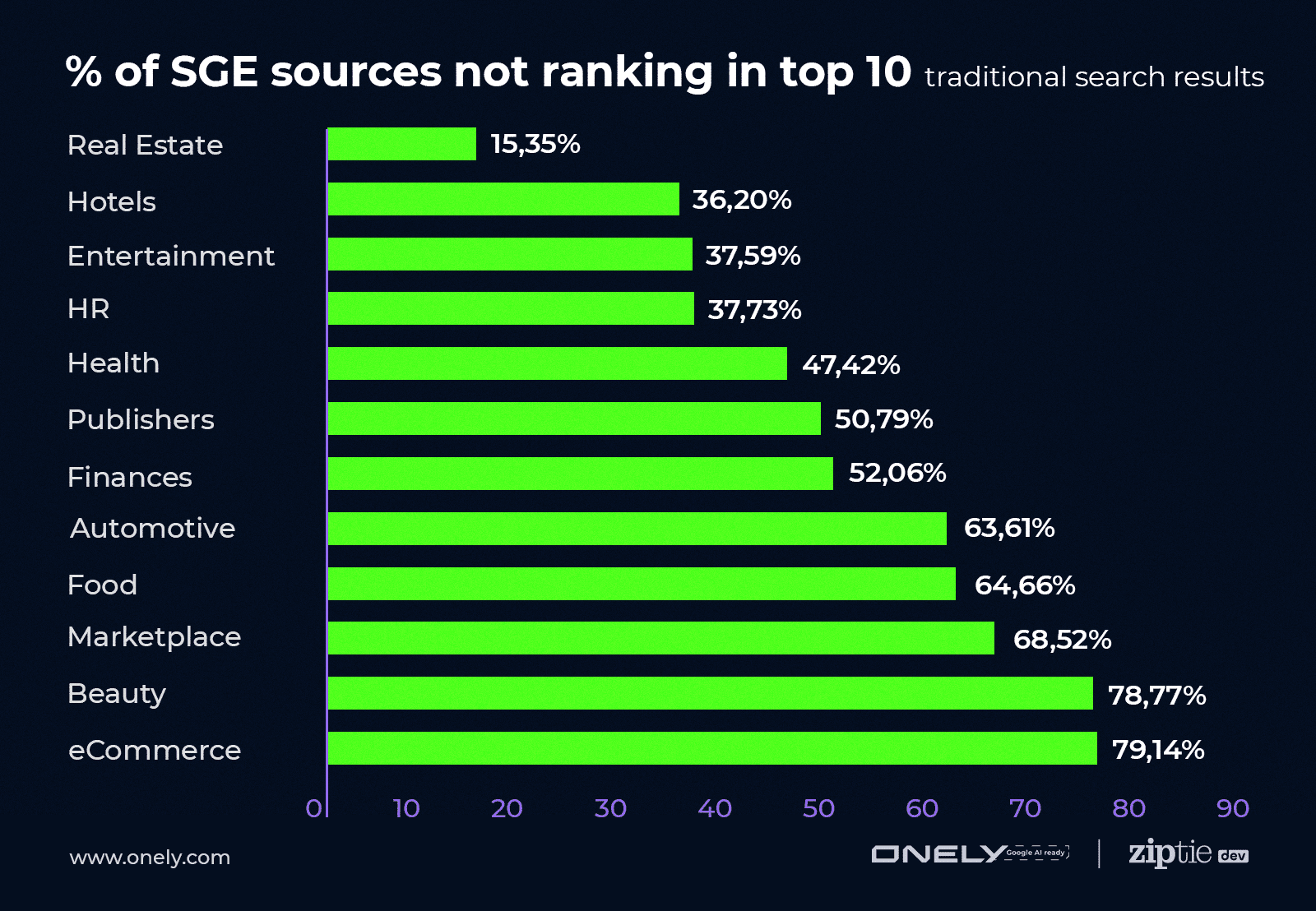
As of 2024, there are an estimated 1.09 billion total websites on the web with more than 810 million of those sites using WordPress.
Because of its popularity, WordPress websites are oftentimes a target for hackers, malware attacks, and data thieves.
Keeping your WordPress installation up to date at all times is critical to maintain the security and stability of your site.
Every time a WordPress security vulnerability is reported, the core team starts working to release an update that fixes the issue.
If you aren’t updating your WordPress website, then you are likely using a version of WordPress that has known vulnerabilities.
There is especially no excuse for using an outdated version of WordPress since the introduction of automatic updates.
Don’t leave yourself open to attack by using an old version of WordPress. Turn on auto updates and forget about it.
If you would like an even easier way to handle updates, consider a Managed WordPress solution that has auto updates built in.
5. Pay Attention To Themes & Plugins
Keeping WordPress updated ensures your core files are in check, but there are other areas where WordPress is vulnerable that core updates might not protect such as your themes and plugins.
For starters, only ever install plugins and themes from trusted developers. If a plugin or theme wasn’t developed by a credible source, you are probably safer not using it.
On top of that, make sure to update WordPress plugins and themes. Just like an outdated version of WordPress, using outdated plugins and themes makes your website more vulnerable to attack.
6. Run Frequent Website Backups
One way to protect your WordPress website is to always have a current backup of your site and important files.
The last thing you want is for something to happen to your site and you do not have a backup.
Backup your site, and do so often. That way if something does happen to your website, you can quickly restore a previous version of it and quickly get back up and running.
Intermediate WordPress Security Measures That Add More Protection
If you’ve completed all the basics but you still want to do more to protect your website, there are some more advanced steps you can take to bolster your security.
Let’s take a look at what you should do next.
7. Never Use The “Admin” Username
Never use the “admin” username. Doing so makes you susceptible to brute force attacks and social engineering scams.
Because “admin” is such a common username, it is easily-guessed and makes things much easier for scammers to trick people into giving away their login credentials.
Much like having a strong password, using a unique username for your logins is a good idea because it makes it much harder for hackers to crack your login info.
If you are currently using the “admin” username, change your WordPress admin username.
8. Hide Your WP Admin Login Page
On top of using a unique username another thing you can do to protect your login credentials is hide your WordPress admin login page with a plugin like WPS Hide Login.
By default, a majority of WordPress login pages can be accessed by adding “/wp-admin” or “/wp-login.php” to the end of a URL. Once a hacker or scammer has identified your login page, they can then attempt to guess your username and password in order to access your Admin Dashboard.
Hiding your WordPress login page is a good way to make you a less easy target.
9. Disable XML-RPC
WordPress uses an implementation of the XML-RPC protocol to extend functionality to software clients.
Most users don’t need WordPress XML-RPC functionality, and it’s one of the most common vulnerabilities that opens users up for exploits.
That’s why it’s a good idea to disable it. Thanks to the Wordfence Security plugin, it is really easy to do just that.
10. Harden wp-config.php File
The process of adding extra security features to your WordPress site is sometimes known as “hardening” because you are essentially giving your site some extra armor against hackers.
You can “harden” your website by protecting your wp-config.php file via your .htaccess file. Your WordPress wp-config.php file contains very sensitive information about your WordPress installation including your WordPress security keys and the WordPress database connection details, which is exactly why you don’t want it to be easy to access.
11. Run A Security Scanning Tool
Sometimes your WordPress website might have a vulnerability that you had no idea existed. That’s why it’s wise to use some tools that can find vulnerabilities and even fix them for you.
The WPScan plugin scans for known vulnerabilities in WordPress core files, plugins and themes. The plugin also notifies you by email when new security vulnerabilities are found.
Strengthen Your Server-Side Security
So you have taken all the above measures to protect your website but you still want to know if there is more you can do to make it as secure as possible.
The remaining actions you can take to beef up your security will need to be done on the server side of your website.
12. Look For A Hosting Company That Does This
One of the best things you can do to protect your site from the very get-go is to choose the right hosting company to host your WordPress website.
When looking for a hosting company, you want to find one that is fast, reliable, and secure, and will support you with great customer service.
That means they should have good, powerful resources, maintain an uptime of at least 99.5%, and use server-level security tactics.
If a host can’t check those basic boxes, they are not worth your time or money.
13. Use The Latest PHP Version
Like old versions of WordPress, outdated versions of PHP are no longer safe to use.
If you aren’t on the latest version of PHP, upgrade your PHP version to protect yourself from attack.
14. Host On A Fully-Isolated Server
Fully-isolated virtual private servers have a lot of advantages and one of those advantages is increased security.
The physical isolation offered from a cloud-based VPS is inherently secure, protecting your website against cross-infection from other customers. Combined with robust firewalls and DDoS protection, your data remains secure against potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Looking for the perfect cloud environment for your WordPress website? Look no further.
With InMotion Hosting’s Platform i, you receive unparalleled security features including managed server updates, real-time security patching, web application firewalls, and DDoS prevention, along with purpose-built high-availability servers optimized for fast and reliable WordPress sites.
15. Use A Web Application Firewall
One of the final things you can do to add extra security measures to your WordPress website is use a web application firewall (WAF).
A WAF is usually a cloud-based security system that offers another layer of protection around your site. Think of it as a gateway for your site. It blocks all hacking attempts and filters out other malicious types of traffic like distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks or spammers.
WAFs usually require monthly subscription fees, but adding one is worth the cost if you place a premium on your WordPress website security.
Make Sure Your Website & Business Is Safe & Secure
If your website is not secure, you could be leaving yourself open to a cyber attack.
Thankfully, securing a WordPress site doesn’t require too much technical knowledge as long as you have the right tools and hosting plan to fit your needs.
Instead of waiting to respond to threats once they happen, you should proactively secure your website to prevent security issues.
That way if someone does target your website, you are prepared to mitigate the risk and go about your business as usual instead of scrambling to locate a recent backup.
Get Managed WordPress Hosting featuring robust security measures on high-performance servers, complete with free SSL, dedicated IP address, automatic server updates, DDoS protection, and included WAF.
Learn more about how Managed WordPress Hosting can help protect your website and valuable data from exposure to hackers and scammers.